Draft SelectPlane/pl: Difference between revisions
(Created page with "{{Caption|Kształty tworzone na różnych płaszczyznach roboczych.}}") |
(Created page with "# Wykonaj jedną z następujących czynności: #* Wybierz pojedynczy obiekt. Obsługiwane są następujące obiekty: #** Pośrednia płaszczyzna robocza: {{PropertyView|View Data}} ''(pozycja kamery)'' i {{PropertyView|Visibility Map}} ''(zapisana widoczność obiektów)'' pośredniej płaszczyzny roboczej są również przywracane. #** Architektura: Osie ({{Version/pl|0.22}}) #** Arch_AxisSystem/pl|Architektura: Układ o...") |
||
| Line 34: | Line 34: | ||
==Użycie ze wstępnym wyborem== |
==Użycie ze wstępnym wyborem== |
||
# Wykonaj jedną z następujących czynności: |
|||
# Do one of the following: |
|||
#* Wybierz pojedynczy obiekt. Obsługiwane są następujące obiekty: |
|||
#* Select a single object. The following objects are supported: |
|||
#** [[Draft_WorkingPlaneProxy| |
#** [[Draft_WorkingPlaneProxy/pl|Pośrednia płaszczyzna robocza]]: {{PropertyView|View Data}} ''(pozycja kamery)'' i {{PropertyView|Visibility Map}} ''(zapisana widoczność obiektów)'' pośredniej płaszczyzny roboczej są również przywracane. |
||
#** [[Arch_Axis| |
#** [[Arch_Axis/pl|Architektura: Osie]] ({{Version/pl|0.22}}) |
||
#** [[Arch_AxisSystem| |
#** [[Arch_AxisSystem/pl|Architektura: Układ osi]] ({{Version/pl|0.22}}) |
||
#** [[Arch_BuildingPart| |
#** [[Arch_BuildingPart/pl|Architektura: Część budowli - piętro]] |
||
#** [[Arch_SectionPlane| |
#** [[Arch_SectionPlane/pl|Architektura: Płaszczyzna przekroju]] |
||
#** [[Std_Part|Std |
#** [[Std_Part/pl|Std: Część]]: aby uniknąć zaznaczania elementów podrzędnych, zaleca się zaznaczanie ich w [[Tree_view/pl|widoku drzewa]]. |
||
#** |
#** Obiekty nie będące bryłami, które składają się z pojedynczej płaskiej powierzchni lub pojedynczej zakrzywionej krawędzi, lub ({{Version/pl|0.22}}), które mają trzy lub więcej wierzchołków. |
||
#** |
#** Obiekty bryłowe lub obiekty bez kształtu, które mają właściwość {{PropertyData|Umiejscowienie}}. ({{Version/pl|0.22}}) |
||
#* Wybierz jeden lub więcej elementów podrzędnych. Można wybrać: |
|||
#* Select one or more subelements. You can select: |
|||
#** |
#** Płaską powierzchnię. |
||
#** |
#** Zakrzywioną krawędź. |
||
#** |
#** Trzy wierzchołki. |
||
#** |
#** Krawędź i wierzchołek lub dwie krawędzie. Połączone wierzchołki muszą definiować płaszczyznę. ({{Version/pl|0.22}}) |
||
# Polecenie można wywołać na kilka sposobów: |
|||
# There are several ways to invoke the command: |
|||
#* |
#* Naciśnij przycisk [[Image:Draft_tray_button_plane.png]] w [[Draft_Tray/pl|Tacka narzędziowa]]. |
||
#* |
#* Wybierz z menu opcję {{MenuCommand|Narzędzia → [[Image:Draft_SelectPlane.svg|16px]] Wybierz płaszczyznę}}. |
||
#* |
#* Użyj skrótu klawiaturowego: {{KEY|W}}, a następnie {{KEY|P}}. |
||
# |
# Płaszczyzna robocza i przycisk w [[Draft_Tray/pl|Tacka narzędziowa]] zostaną zaktualizowane. |
||
<span id="Usage_with_post-selection"></span> |
<span id="Usage_with_post-selection"></span> |
||
Revision as of 11:33, 20 December 2023
|
|
| Lokalizacja w menu |
|---|
| Kreślenie → Przybory → Wybierz płaszczyznę |
| Środowisko pracy |
| Rysunek Roboczy, Architektura |
| Domyślny skrót |
| W P |
| Wprowadzono w wersji |
| - |
| Zobacz także |
| Ustaw pośrednią płaszczyznę roboczą, Pokaż / ukryj siatkę |
Opis
Polecenie Wybór płaszczyzny roboczej definiuje bieżącą płaszczyznę roboczą. Jest to płaszczyzna zdefiniowana w widoku 3D, na której tworzone są nowe obiekty Rysunku Roboczego. Płaszczyzna robocza może być oparta na jednym z kilku nastaw lub na zaznaczeniu. Zaznaczenie może zostać utworzone przed (wyborem wstępnym) lub po (uruchomieniu polecenia).
introduced in version 0.22: Dla każdego widoku 3D zapisywana jest osobna płaszczyzna robocza.
Przycisk ![]() w Tacka narzędziowa zmienia swój wygląd w zależności od bieżącej płaszczyzny roboczej. dostępne w wersji 0.22: Jeśli płaszczyzna robocza nie jest ustawiona na Automatyczną, gwiazdka (*) jest dodawana do etykiety przycisku, jeśli punkt odniesienia położenia płaszczyzny roboczej nie pasuje do globalnego punktu odniesienia.
w Tacka narzędziowa zmienia swój wygląd w zależności od bieżącej płaszczyzny roboczej. dostępne w wersji 0.22: Jeśli płaszczyzna robocza nie jest ustawiona na Automatyczną, gwiazdka (*) jest dodawana do etykiety przycisku, jeśli punkt odniesienia położenia płaszczyzny roboczej nie pasuje do globalnego punktu odniesienia.
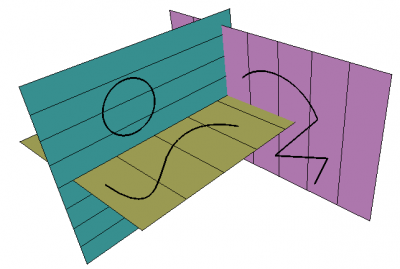
Kształty tworzone na różnych płaszczyznach roboczych.
Użycie ze wstępnym wyborem
- Wykonaj jedną z następujących czynności:
- Wybierz pojedynczy obiekt. Obsługiwane są następujące obiekty:
- Pośrednia płaszczyzna robocza: WIDOKView Data (pozycja kamery) i WIDOKVisibility Map (zapisana widoczność obiektów) pośredniej płaszczyzny roboczej są również przywracane.
- Architektura: Osie (dostępne w wersji 0.22)
- Architektura: Układ osi (dostępne w wersji 0.22)
- Architektura: Część budowli - piętro
- Architektura: Płaszczyzna przekroju
- Std: Część: aby uniknąć zaznaczania elementów podrzędnych, zaleca się zaznaczanie ich w widoku drzewa.
- Obiekty nie będące bryłami, które składają się z pojedynczej płaskiej powierzchni lub pojedynczej zakrzywionej krawędzi, lub (dostępne w wersji 0.22), które mają trzy lub więcej wierzchołków.
- Obiekty bryłowe lub obiekty bez kształtu, które mają właściwość DANEUmiejscowienie. (dostępne w wersji 0.22)
- Wybierz jeden lub więcej elementów podrzędnych. Można wybrać:
- Płaską powierzchnię.
- Zakrzywioną krawędź.
- Trzy wierzchołki.
- Krawędź i wierzchołek lub dwie krawędzie. Połączone wierzchołki muszą definiować płaszczyznę. (dostępne w wersji 0.22)
- Wybierz pojedynczy obiekt. Obsługiwane są następujące obiekty:
- Polecenie można wywołać na kilka sposobów:
- Naciśnij przycisk
 w Tacka narzędziowa.
w Tacka narzędziowa. - Wybierz z menu opcję Narzędzia →
Wybierz płaszczyznę.
- Użyj skrótu klawiaturowego: W, a następnie P.
- Naciśnij przycisk
- Płaszczyzna robocza i przycisk w Tacka narzędziowa zostaną zaktualizowane.
Użycie z wyborem w kolejnym kroku
- There are several ways to invoke the command:
- Press the
 button in the Draft Tray.
button in the Draft Tray. - Select the Utilities →
Select plane option from the menu.
- Use the keyboard shortcut: W then P.
- Press the
- The Working plane setup task panel opens. See Options for more information.
- Do one of the following:
- Select a single object. See the previous paragraph.
- Select one or more subelements. See the previous paragraph.
- Click anywhere in the 3D view to confirm the selection and finish the command.
- The working plane and the button in the Draft Tray are updated.
Użycie z ustawieniami wstępnymi
- There are several ways to invoke the command:
- Press the
 button in the Draft Tray.
button in the Draft Tray. - Select the Utilities →
Select plane option from the menu.
- Use the keyboard shortcut: W then P.
- Press the
- The Working plane setup task panel opens. See Options for more information.
- Press any of the buttons to finish the command.
- The working plane and the button in the Draft Tray are updated.
Options
- Press the
Top (XY) button to align the working plane with the XY plane of the global coordinate system.
- Press the
Front (XZ) button to align the working plane with the XZ plane of the global coordinate system.
- Press the
Side (YZ) button to align the working plane with the YZ plane of the global coordinate system.
- Press the
Align to view button to align the working plane with the current 3D view. If the Center plane on view checkbox is not checked the working plane origin will match the origin of the global coordinate system, else it will match the center of the current 3D view.
- Press the
Automatic button to set the working plane to Auto. A working plane set to Auto will automatically align with the current 3D view whenever a Draft or Arch command requiring point input is started. This is equivalent to pressing the
Align to view button before using the command. Additionally the working plane will align to planar faces that have been selected before starting the command, or when points on planar faces are picked during the command.
- The Offset defines the perpendicular distance between the calculated plane and the actual working plane.
- Check the Center plane on view checkbox to put the origin of the working plane in the center of to the current 3D view. This option can be useful in combination with the
Align to view button.
- Select a vertex in the 3D view and press the
Move working plane button to move the working plane so that its origin matches the position of the selected vertex.
- The Grid spacing defines the distance between grid lines.
- The Main line every value determines where main grid lines are drawn. Main grid lines are slightly thicker than normal grid lines. For example if the grid spacing is
0.5 mand there is a main line every10 lines, such a line will occur every5 m. - The Grid extension value determines the number of grid lines in the X and Y direction of the grid.
- The Snapping radius is the maximum distance at which Draft Snap Grid detects the intersections of grid lines.
- Press the
Center view button to align the 3D view with the current working plane.
- Press the
Previous button to reset the working plane to its previous position.
- Press the Next
button to reset the working plane to its next position. introduced in version 0.22
- Press Esc or the Close button to abort the command.
Notes
- It can be useful to align the 3D view with the selected Draft working plane. For example after switching the working plane to Front you may want to switch to the Front view as well.
- The grid can be toggled with the Draft ToggleGrid command.
- By double-clicking Draft WorkingPlaneProxies in the Tree view you can quickly switch between working planes.
Preferences
See also: Preferences Editor and Draft Preferences.
- The grid settings in the task panel as well as several other grid settings are available as preferences: Edit → Preferences... → Draft → Grid and snapping.
- The Snapping radius can also be changed on-the-fly (see Draft Snap) or by changing: Tools → Edit parameters... → BaseApp → Preferences → Mod → Draft → snapRange.
Scripting
See also: Autogenerated API documentation and FreeCAD Scripting Basics.
The WorkingPlane module offers two classes to create working plane objects: the PlaneBase class and the PlaneGui class. The second class inherits from the first. Objects of the PlaneGui class interact with the GUI (the Draft Tray button), the 3D view and the grid. PlaneBase objects do not.
Use the get_working_plane() method of the WorkingPlane module to get an instance of the PlaneGui class linked to the current 3D view. The method either returns the existing working plane linked to the view or creates a new working plane if required.
import FreeCAD as App
import WorkingPlane
wp = WorkingPlane.get_working_plane()
origin = App.Vector(0, 0, 0)
normal = App.Vector(1, 1, 1).normalize()
offset = 17
wp.align_to_point_and_axis(origin, normal, offset)
point = App.Vector(10, 15, 2)
projection = wp.project_point(point)
print(projection)
The PlaneBase class can be used to create working planes independent of the GUI:
import WorkingPlane
wp = WorkingPlane.PlaneBase()
- Kreślenie: Linia, Polilinia, Zaokrąglenie, Łuk, Łuk przez 3 punkty, Okrąg, Elipsa, Wielokąt foremny, Krzywa złożona, Krzywa Bezier'a, Punkt, Łącznik ścian, Kształt z tekstu, Kreskowanie, Prostokąt
- Adnotacje: Adnotacja wieloliniowa, Wymiarowanie, Etykieta, Edytor stylów adnotacji, Widżet skali anotacji
- Modyfikacja: Przesuń, Obróć, Skala, Odbicie lustrzane, Odsunięcie, Przytnij, Rozciągnij, Klonuj, Szyk, Szyk biegunowy, Szyk kołowy, Szyk po ścieżce, Szyk powiązań po ścieżce, Szyk z punktów, Szyk powiązań w punktach, Edycja, Podświetl element podrzędny, Połącz, Rozdziel, Ulepsz kształt, Rozbij obiekt na elementy, Polilinia na krzywą złożoną, Rysunek Roboczy do szkicu, Nachylenie, Obróć wymiar, Widok 2D kształtu
- Tacka narzędziowa: Wybór płaszczyzny, Ustaw styl, Przełącz tryb konstrukcyjny, Grupowanie automatyczne
- Przyciąganie: Przełącz przyciąganie, Przyciągnij do punktu końcowego, Przyciągnij do punktu środkowego, Przyciągnij do środka, Przyciągnij do kąta, Przyciąganie do punktu przecięcia, Przyciągnij prostopadle, Rozszerz, Przyciągnij równolegle, Przyciągnij specjalnie, Przyciąganie do najbliższego, Przyciągnij ortogonalnie, Przyciągnij do siatki, Przyciągnij do płaszczyzny roboczej, Przyciągnij do wymiaru, Pokaż / ukryj siatkę
- Różności: Zastosuj bieżący styl, Warstwa, Zarządzaj warstwami, Dodaj grupę o nazwie, Dodaj do grupy, Wybierz grupę, Dodaj do grupy konstrukcyjnej, Przełącz tryb wyświetlania, Pośrednia płaszczyzna robocza, Ulecz, Przełącz tryb kontynuacji, Pokaż przybornik przyciągania
- Dodatkowe:: Wiązania, Wypełnienie wzorem, Preferencje, Ustawienia Importu i Eksportu, DXF/DWG, SVG, OCA, DAT
- Menu podręczne:
- Kontener warstwy: Połącz duplikaty warstw, Dodaj warstwę
- Warstwa: Aktywuj warstwę, Zaznacz zawartość warstwy
- Pośrednia płaszczyzna robocza: Zapisz ujęcie widoku, Zapisz stan obiektów
- Jak zacząć
- Instalacja: Pobieranie programu, Windows, Linux, Mac, Dodatkowych komponentów, Docker, AppImage, Ubuntu Snap
- Podstawy: Informacje na temat FreeCAD, Interfejs użytkownika, Profil nawigacji myszką, Metody wyboru, Nazwa obiektu, Edytor ustawień, Środowiska pracy, Struktura dokumentu, Właściwości, Pomóż w rozwoju FreeCAD, Dotacje
- Pomoc: Poradniki, Wideo poradniki
- Środowiska pracy: Strona Startowa, Architektura, Assembly, CAM, Rysunek Roboczy, MES, Inspekcja, Siatka, OpenSCAD, Część, Projekt Części, Punkty, Inżynieria Wsteczna, Robot, Szkicownik, Arkusz Kalkulacyjny, Powierzchnia 3D, Rysunek Techniczny, Test Framework