Rysunek Roboczy: Wymiar
|
|
| Lokalizacja w menu |
|---|
| Adnotacja → Wymiar |
| Środowisko pracy |
| Rysunek roboczy, Architektura |
| Domyślny skrót |
| D I |
| Wprowadzono w wersji |
| 0.8 |
| Zobacz także |
| Obróć wymiar |
Opis
Polecenie Draft Dimension tworzy Wymiar liniowy, Wymiar promieniowy lub Wymiar kątowy. Polecenie może być również użyte do konwersji obiektów Std: Pomiar.
Wymiary liniowe oparte na krawędziach i wymiary promieniowe są parametryczne. Oznacza to, że będą one aktualizowane, jeśli zmierzona krawędź zostanie zmodyfikowana. Zmierzone krawędzie mogą należeć do obiektów środowiska Rysunek Roboczy, ale także do brył. Wymiary kątowe nie są parametryczne.
Wymiary środowiska pracy Rysunek Techniczny mogą być wyświetlane na stronie Rysunku Technicznego za pomocą poleceń Wstaw widok rysunku lub Wstaw obiekt środowiska Architektura. środowisko Rysunek Techniczny oferuje swoje własne narzędzia wymiarowania. Tworzą one jednak wymiary, które są wyświetlane tylko na stronie rysunku, a nie w oknie widoku 3D.
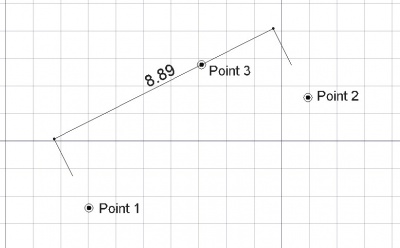
Wymiar określony przez trzy punkty
Tworzenie
Zapoznaj się również z informacjami na stronie: Tacka narzędziowa, Przyciąganie oraz Wiązania.
Zastosowanie wymiaru liniowego
- Opcjonalnie wybierz prostą krawędź w oknie widoku 3D.
- Polecenie można wywołać na kilka sposobów:
- Naciśnij przycisk
Wymiar.
- Wybierz z menu opcję Opisy →
Wymiar.
- Użyj skrótu klawiaturowego: D, a następnie I.
- Naciśnij przycisk
- Otworzy się panel zadań Wymiar. Więcej informacji znajduje się w sekcji Opcje.
- Jeśli krawędź nie została jeszcze wybrana, wykonaj jedną z poniższych czynności:
- Naciśnij E lub przycisk
Wybierz krawędź i wybierz prostą krawędź w 3D view.
- Przytrzymaj klawisz Alt, wybierz prostą krawędź w oknie widoku 3Di zwolnij klawisz Alt.
- Zdefiniuj zmierzoną odległość, wybierając punkty:
- Naciśnij E lub przycisk
- Aby ustawić linię wymiarową, wykonaj jedną z poniższych czynności:
- Dla wymiaru wyrównanego:
- Wybierz punkt w oknie widoku 3D lub wpisz współrzędne i naciśnij przycisk
Wprowadź punkt.
- Wybierz punkt w oknie widoku 3D lub wpisz współrzędne i naciśnij przycisk
- Dla wymiaru poziomego:
- Przesuń wskaźnik powyżej lub poniżej krawędzi lub punktów.
- Przytrzymaj klawisz Shift, przesuń wskaźnik i wybierz punkt w oknie widoku 3D.
- Dla wymiaru pionowego:
- Przesuń wskaźnik w lewo lub w prawo od krawędzi lub punktów.
- Przytrzymaj klawisz Shift, przesuń wskaźnik i wybierz punkt w oknie widoku 3D.
- Dla wymiaru wyrównanego:
Zastosowanie wymiaru promieniowego
- Opcjonalnie wybierz okrągłą krawędź w oknie widoku 3D.
- Istnieje kilka sposobów wywołania polecenia:
- Naciśnij przycisk
Wymiar.
- Wybierz z menu opcję Opisy →
Wymiar.
- Użyj skrótu klawiaturowego: D, a następnie I.
- Naciśnij przycisk
- Otworzy się panel zadań Wymiar. Więcej informacji znajduje się w sekcji Opcje.
- Jeśli krawędź nie została jeszcze wybrana, wykonaj jedną z poniższych czynności:
- Aby ustawić linię wymiarową, wykonaj jedną z poniższych czynności:
Zastosowanie wymiaru kątowego
- There are several ways to invoke the command:
- Press the
Draft Dimension button.
- Select the Annotation →
Dimension option from the menu.
- Use the keyboard shortcut: D then I.
- Press the
- The Dimension task panel opens. See Options for more information.
- Do one of the following:
- To position the dimension arc pick a point in the 3D view.
- The displayed angle depends on the edges and the picked point.
Opcje
Skróty klawiaturowe jedno znakowe dostępne w panelu zadań można zmienić. Zobacz stronę Preferencji. Skróty wymienione tutaj są skrótami domyślnymi.
- To manually enter coordinates enter the X, Y and Z component, and press Enter after each. Or you can press the
Enter point button when you have the desired values. It is advisable to move the pointer out of the 3D view before entering coordinates.
- Press R or click the Relative checkbox to toggle relative mode. If relative mode is on, coordinates are relative to the last point, if available, else they are relative to the coordinate system origin.
- Press G or click the Global checkbox to toggle global mode. If global mode is on, coordinates are relative to the global coordinate system, else they are relative to the working plane coordinate system. introduced in version 0.20
- Press T or click the Continue checkbox to toggle continue mode. This mode only works for linear dimensions. If continue mode is on, the command will restart after finishing, allowing you to continue creating dimensions. All subsequent dimensions will start from the final point of the previous dimension, and will use the same baseline as the first dimension. Note that edge selection is not possible for subsequent dimensions.
- Press S to switch Draft snapping on or off.
- Press Esc or the Close button to finish the command.
Konwersja
Użycie
- Wybierz jeden lub więcej obiektów Wymiarowanie odległości.
- Polecenie można wywołać na kilka sposobów:
- Każdy wybrany obiekt zostanie zastąpiony nieparametrycznym liniowym wymiarem Draft Dimension.
Uwagi
Liniowe i promieniowe wymiary środowiska Rysunek Roboczy można edytować za pomocą polecenia Edytuj.
- Wymiary szkicu utworzone lub zapisane w wersji FreeCAD 0.21 nie są kompatybilne wstecz.
Właściwości
See also: Property editor.
A Draft Dimension object is derived from an App FeaturePython object and inherits all its properties. The following properties are additional unless otherwise stated:
Data linear and radial dimension
Dimension
- DANEDimline (
VectorDistance): specifies the point through which the dimension line passes. - DANELinked Geometry (
LinkSubList): specifies the object and its subelement(s) the dimension is linked to. - DANENormal (
Vector): specifies the normal of the plane of the text. - DANE (hidden)Support (
Link): specifies the measured object.
Linear/radial dimension
- DANEDirection (
Vector): specifies the direction of the measurement. - DANEDistance (
Length): (read-only) specifies the value of the measurement. - DANEEnd (
VectorDistance): specifies the end point of the measurement. - DANEStart (
VectorDistance): specifies the start point of the measurement.
Radial dimension
- DANEDiameter (
Bool): specifies if a radial dimension is displayed as a diameter dimension. Not used for linear dimensions.
Data angular dimension
Angular dimension
- DANEAngle (
Angle): (read-only) specifies the value of the measurement. - DANECenter (
VectorDistance): specifies the center of the measurement. - DANEFirst Angle (
Angle): specifies the start angle of the measurement. - DANELast Angle (
Angle): specifies the end angle of the measurement.
Dimension
- DANEDimline (
VectorDistance): specifies the point through which the dimension arc passes. - DANE (hidden)Linked Geometry (
LinkSubList): not used. - DANE (hidden)Normal (
Vector): specifies the normal of the plane of the dimension. - DANE (hidden)Support (
Link): not used.
Widok
Annotation
- WIDOKAnnotation Style (
Enumeration): specifies the annotation style applied to the dimension. See Draft AnnotationStyleEditor. - WIDOKScale Multiplier (
Float): specifies the general scaling factor applied to the dimension.
Display Options
- WIDOKDisplay Mode (
Enumeration): specifies how the text is displayed. If it isWorldthe text will be displayed on a plane defined by the DANENormal of the measurement. If it isScreenthe text will always face the screen. This is an inherited property. The mentioned options are the renamed options (introduced in version 0.21).
Graphics
- WIDOKArrow Size (
Length): specifies the size of the symbols displayed at the ends of the dimension line or arc. - WIDOKArrow Type (
Enumeration): specifies the type of symbol displayed at the ends of the dimension line or arc, which can beDot,Circle,Arrow,TickorTick-2. - WIDOKDim Overshoot (
Distance): specifies the additional length added to the dimension line. Not used for angular dimensions. - WIDOKExt Lines (
Distance): specifies the length of the extension lines that go from the dimension line to the measured points. Use0for full extension lines. A negative value defines the gap between the ends of the extension lines and the measured points. A positive value defines the maximum length of the extension lines. Only used for linear dimensions. - WIDOKExt Overshoot (
Distance): specifies the additional length of the extension lines beyond the dimension line. Not used for angular dimensions. - WIDOKFlip Arrows (
Bool): specifies whether to flip the orientation of the symbols at the ends of the dimension line or arc. Only works if the symbols are arrows. - WIDOKLine Color (
Color): specifies the color of the dimension line or arc, and the arrows. - WIDOKLine Width (
Float): specifies the width of the lines or arc belonging to the dimension. - WIDOKShow Line (
Bool): specifies whether to display the dimension line. Does not affect the display of extension lines and overshoots. Not used for angular dimensions.
Text
- WIDOKFlip Text (
Bool): specifies whether to flip the orientation of the text. - WIDOKFont Name (
Font): specifies the font used to draw the text. It can be a font name, such asArial, a default style such assans,seriformono, a family such asArial,Helvetica,sans, or a name with a style such asArial:Bold. If the given font is not found on the system, a default font is used instead. - WIDOKFont Size (
Length): specifies the size of the letters. The text can be invisible in the 3D view if this value is very small. - WIDOKOverride (
String): specifies a custom text to display instead of the actual measurement. Use the string$diminside the text to include the measurement. - WIDOKText Color (
Color): specifies the color of the text. introduced in version 0.21 - WIDOKText Position (
VectorDistance): specifies the position of the text in absolute coordinates.[0, 0, 0]will display the text in its default position near the dimension line or arc. - WIDOKText Spacing (
Length): specifies the space between the text and the dimension line or arc.
Units
- WIDOKDecimals (
Integer): specifies the number of decimal places to display for the measurement. - WIDOKShow Unit (
Bool): specifies whether to display the unit next to the numerical value of the measurement. Not used for angular dimensions. - WIDOKUnit Override (
String): specifies the unit in which to express the measurement, for example,km,m,cm,mm,mi,ft,inorarchfor arch units. Leave this blank to use the default unit. Not used for angular dimensions.
Tworzenie skryptów
See also: Autogenerated API documentation and FreeCAD Scripting Basics.
To create a Draft Dimension use the make_dimension method (introduced in version 0.19) of the Draft module. This method replaces the deprecated makeDimension method.
dimension = make_dimension(p1, p2, p3=None, p4=None)
There are various ways to invoke this method, depending on the arguments passed to it:
dimension = make_dimension(p1, p2, p3=None)
dimension = make_dimension(object, i1, i2, p4=None)
dimension = make_dimension(object, i1, mode, p4=None)
- Creates a linear
dimensionby measuring the distance between pointsp1andp2. - Creates a linear
dimensionlinked toobject, measuring the distance between its vertices indexedi1andi2. - Creates a circular
dimensionlinked toobject, withi1being the index of the curved edge to measure, andmodebeing either"radius"or"diameter"to specify the type of dimension.p3in the first call, andp4in the other two, specify an optional point through which the dimension line should go.- All points are defined by their
FreeCAD.Vector.
To create an angular dimension use the following method:
dimension = make_angular_dimension(center, angles, p3, normal=None)
dimension = make_angular_dimension(center, [angle1, angle2], p3, normal=None)
- Creates an angular
dimensionfrom the givencenterpoint, theangleslist with two elements, and the pointp3through which the arc should go.- If
angle1 > angle2, the displayed angle is the differenceangle1 - angle2; otherwise, the explementary angle is displayed,360 - (angle2 - angle1). - The angles should be given in degrees.
- If
The view properties of dimension can be changed by overwriting its attributes; for example, overwrite ViewObject.FontSize with the new size in millimeters.
Przykład:
import FreeCAD as App
import Draft
doc = App.newDocument()
p1 = App.Vector(0, 0, 0)
p2 = App.Vector(1000, 1000, 0)
p3 = App.Vector(-2500, 0, 0)
dimension1 = Draft.make_dimension(p1, p2, p3)
dimension1.ViewObject.FontSize = 200
polygon = Draft.make_polygon(3, radius=1000)
doc.recompute()
p4 = App.Vector(-2000, 1500, 0)
dimension2 = Draft.make_dimension(polygon, 1, 2, p4)
dimension2.ViewObject.FontSize = 200
center = App.Vector(2000, 0, 0)
p5 = App.Vector(3000, 1000, 0)
angle1 = 45
angle2 = 10
dimension3 = Draft.make_angular_dimension(center, [angle1, angle2], p5)
dimension3.ViewObject.FontSize = 200
dimension4 = Draft.make_angular_dimension(center, [angle2, angle1], p5*1.2)
dimension4.ViewObject.FontSize = 200
doc.recompute()
- Kreślenie: Linia, Polilinia, Zaokrąglenie, Łuk, Łuk przez 3 punkty, Okrąg, Elipsa, Wielokąt foremny, Krzywa złożona, Krzywa Bezier'a, Punkt, Łącznik ścian, Kształt z tekstu, Kreskowanie, Prostokąt
- Adnotacje: Adnotacja wieloliniowa, Wymiarowanie, Etykieta, Edytor stylów adnotacji, Widżet skali anotacji
- Modyfikacja: Przesuń, Obróć, Skala, Odbicie lustrzane, Odsunięcie, Przytnij, Rozciągnij, Klonuj, Szyk, Szyk biegunowy, Szyk kołowy, Szyk po ścieżce, Szyk powiązań po ścieżce, Szyk z punktów, Szyk powiązań w punktach, Edycja, Podświetl element podrzędny, Połącz, Rozdziel, Ulepsz kształt, Rozbij obiekt na elementy, Polilinia na krzywą złożoną, Rysunek Roboczy do szkicu, Nachylenie, Obróć wymiar, Widok 2D kształtu
- Tacka narzędziowa: Wybór płaszczyzny, Ustaw styl, Przełącz tryb konstrukcyjny, Grupowanie automatyczne
- Przyciąganie: Przełącz przyciąganie, Przyciągnij do punktu końcowego, Przyciągnij do punktu środkowego, Przyciągnij do środka, Przyciągnij do kąta, Przyciąganie do punktu przecięcia, Przyciągnij prostopadle, Rozszerz, Przyciągnij równolegle, Przyciągnij specjalnie, Przyciąganie do najbliższego, Przyciągnij ortogonalnie, Przyciągnij do siatki, Przyciągnij do płaszczyzny roboczej, Przyciągnij do wymiaru, Pokaż / ukryj siatkę
- Różności: Zastosuj bieżący styl, Warstwa, Zarządzaj warstwami, Dodaj grupę o nazwie, Dodaj do grupy, Wybierz grupę, Dodaj do grupy konstrukcyjnej, Przełącz tryb wyświetlania, Pośrednia płaszczyzna robocza, Ulecz, Przełącz tryb kontynuacji, Pokaż przybornik przyciągania
- Dodatkowe:: Wiązania, Wypełnienie wzorem, Preferencje, Ustawienia Importu i Eksportu, DXF/DWG, SVG, OCA, DAT
- Menu podręczne:
- Kontener warstwy: Połącz duplikaty warstw, Dodaj warstwę
- Warstwa: Aktywuj warstwę, Zaznacz zawartość warstwy
- Pośrednia płaszczyzna robocza: Zapisz ujęcie widoku, Zapisz stan obiektów
- Jak zacząć
- Instalacja: Pobieranie programu, Windows, Linux, Mac, Dodatkowych komponentów, Docker, AppImage, Ubuntu Snap
- Podstawy: Informacje na temat FreeCAD, Interfejs użytkownika, Profil nawigacji myszką, Metody wyboru, Nazwa obiektu, Edytor ustawień, Środowiska pracy, Struktura dokumentu, Właściwości, Pomóż w rozwoju FreeCAD, Dotacje
- Pomoc: Poradniki, Wideo poradniki
- Środowiska pracy: Strona Startowa, Architektura, Assembly, CAM, Rysunek Roboczy, MES, Inspekcja, Siatka, OpenSCAD, Część, Projekt Części, Punkty, Inżynieria Wsteczna, Robot, Szkicownik, Arkusz Kalkulacyjny, Powierzchnia 3D, Rysunek Techniczny, Test Framework