Sketcher Workbench/cs: Difference between revisions
(Updating to match new version of source page) |
(Updating to match new version of source page) |
||
| Line 7: | Line 7: | ||
|IconR=Workbench_Spreadsheet.svg |
|IconR=Workbench_Spreadsheet.svg |
||
}} |
}} |
||
{{VeryImportantMessage|This page has been marked for translation. But it is still a work in progress!!!}} |
|||
[[Image:Workbench_Sketcher.svg|thumb|128px|Sketcher workbench icon]] |
[[Image:Workbench_Sketcher.svg|thumb|128px|Sketcher workbench icon]] |
||
| Line 19: | Line 21: | ||
Obecně jsou 2D konstrukce zamýšleny jako startovní bod pro většinu CAD modelů - jednoduchý 2D náčrt může být 'vysunut' do 3D tvaru, dále mohou být 2D náčrty použity k vytváření kapes v povrchu objektu a náčrty mohou být využity pro definování 'desek' (vysunutí) na povrchu 3D objektů. Spolu s [[Part_Workbench/cs|logickými operacemi]], náčrt vytváří jádro generativního návrhu dílu tělesa. |
Obecně jsou 2D konstrukce zamýšleny jako startovní bod pro většinu CAD modelů - jednoduchý 2D náčrt může být 'vysunut' do 3D tvaru, dále mohou být 2D náčrty použity k vytváření kapes v povrchu objektu a náčrty mohou být využity pro definování 'desek' (vysunutí) na povrchu 3D objektů. Spolu s [[Part_Workbench/cs|logickými operacemi]], náčrt vytváří jádro generativního návrhu dílu tělesa. |
||
</div> |
</div> |
||
Together with boolean operations defined in the [[Image:Workbench_Part.svg|16px]] [[Part Workbench|Part Workbench]], the Sketcher Workbench, or "The Sketcher" for short, forms the basis of the [[constructive solid geometry|constructive solid geometry]] (CSG) method of building solids. Together with [[Image:Workbench_PartDesign.svg|16px]] [[PartDesign_Workbench|PartDesign Workbench]] operations, it also forms the basis of the [[feature editing|feature editing]] methodology of creating solids. But many other workbenches use sketches as well. |
|||
<div class="mw-translate-fuzzy"> |
<div class="mw-translate-fuzzy"> |
||
| Line 24: | Line 28: | ||
</div> |
</div> |
||
[[File:FC_ConstrainedSketch.png|450px]] |
|||
<div class="mw-translate-fuzzy"> |
<div class="mw-translate-fuzzy"> |
||
=== Pro co není Skicář vhodný === |
|||
''Základní plně vazbený náčrt.'' |
|||
Skicář není určen pro vytváření 2D výkresů. Protože náčrty jsou používány pro generování těles, jsou automaticky skrývány. Rozměry jsou viditelné pouze v editačním módu Náčrtu. |
|||
</div> |
</div> |
||
[[File:FC_ConstrainedSketch.png|450px]] |
|||
== Basics of constraint sketching == |
|||
<div class="mw-translate-fuzzy"> |
<div class="mw-translate-fuzzy"> |
||
''Základní plně vazbený náčrt.'' |
|||
=== Základy vazeb v náčrtu === |
|||
Pro vysvětlení funkce Skicáře může být užitečné porovnání s "tradičním" způsobem kreslení. |
|||
</div> |
|||
==== Traditional Drafting ==== |
|||
<div class="mw-translate-fuzzy"> |
|||
==== Tradiční kreslení ==== |
|||
Tradiční způsob kreslení v CADu vychází ze starého [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Drawing_board kreslicího prkna]. [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Multiview_orthographic_projection Ortogonální (2D) pohledy] jsou kresleny ručně a určeny pro vytváření technických výkresů (také známé jako blueprints). Objekty jsou kresleny přesně pro zamýšlený rozměr nebo velikost. Chcete-li nakreslit vodorovnou přímku dlouhou 100mm a začínající v (0,0), aktivujete nástroj Přímka buď kliknutím na obrazovku nebo zadáte souřadnice prvního bodu (0,0), potom uděláte druhý klik nebo zadáte souřadnice druhého bodu (100,0). Nebo nakreslíte přímku bez ohledu na její pozici a posunete ji později. Když dokončíte kreslení konstrukce, přidáte k ní kóty. |
|||
</div> |
|||
==== Constraint Sketching ==== |
|||
<div class="mw-translate-fuzzy"> |
|||
==== Skicování s vazbami ==== |
|||
'''Skicář''' se vzdaluje od této logiky. Objekty nemusejí být kresleny přesně tak jak zamýšlíte, protože budou definovány později pomocí vazeb. Objekty mohou být kresleny volně a pokud nejsou vazbeny mohou být upravovány. Provedením jsou "plovoucí" a mohou být posunovány, natahovány, otáčeny, lze jim měnit měřítko, atd. To dodává velkou flexibilitu v procesu návrhu. |
|||
</div> |
</div> |
||
== Constraints == |
|||
==== What are constraints? ==== |
|||
<div class="mw-translate-fuzzy"> |
<div class="mw-translate-fuzzy"> |
||
| Line 61: | Line 49: | ||
<div class="mw-translate-fuzzy"> |
<div class="mw-translate-fuzzy"> |
||
Více objektů může být vazbeno mezi sebou vzájemně. Dvě přímky mohou být spojeny prostřednictvím jejich bodů pomocí vazby souhlasných bodů. Může být nastaven úhel mezi nimi nebo mohou být nastaveny kolmo k sobě. Přímka se může dotýkat oblouku nebo kružnice, atd. |
Více objektů může být vazbeno mezi sebou vzájemně. Dvě přímky mohou být spojeny prostřednictvím jejich bodů pomocí vazby souhlasných bodů. Může být nastaven úhel mezi nimi nebo mohou být nastaveny kolmo k sobě. Přímka se může dotýkat oblouku nebo kružnice, atd. |
||
</div> |
</div> |
||
<div class="mw-translate-fuzzy"> |
<div class="mw-translate-fuzzy"> |
||
| Line 67: | Line 55: | ||
</div> |
</div> |
||
=== Driving vs. reference constraints === |
|||
==== What the Sketcher is not good for ==== |
|||
=== Edit constraints === |
|||
<div class="mw-translate-fuzzy"> |
|||
=== Pro co není Skicář vhodný === |
|||
Skicář není určen pro vytváření 2D výkresů. Protože náčrty jsou používány pro generování těles, jsou automaticky skrývány. Rozměry jsou viditelné pouze v editačním módu Náčrtu. |
|||
</div> |
|||
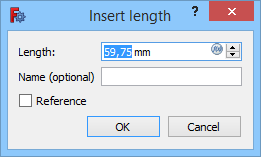
When a [[Sketcher_ToggleDrivingConstraint|driving constraint]] is created, and if the {{MenuCommand|Ask for value after creating a dimensional constraint}} [[Sketcher_Preferences#Display|preference]] is selected (default), a dialog opens to edit its value. |
|||
<div class="mw-translate-fuzzy"> |
|||
Jestliže potřebujete vytvářet pouze 2D pohledy pro tisk a nepotřebujete vytvářet 3D modely, podívejte se na [[Draft_Workbench/cs|Pracovní plochu kreslení]] (a nezapomínejte na to, že pracovní plocha Kreslení je také užitečná pro vytváření 2D konstrukcí nedostupných v současné době ve Skicáři, jako je třeba B-křivka). |
|||
</div> |
|||
[[Image:Sketcher_Edit_Constraint.png|Sketcher_Edit_Constraint.png]] |
|||
The tool [[Draft_Draft2Sketch|Draft2Sketch]] converts a Draft object to a Sketch object, and vice versa. Many tools that require a 2D element as input work with either type of object as an internal conversion is done automatically. |
|||
You can enter a numerical value or an [[Expressions|expression]], and it is possible to name the constraint to facilitate its use in other expressions. You can also check the {{MenuCommand|Reference}} checkbox to switch the constrain to reference mode. |
|||
== Sketching Workflow == |
|||
To edit the value of an existing dimensional constraint do one of the following: |
|||
<div class="mw-translate-fuzzy"> |
|||
* Double-click the constraint value in the [[3D_view|3D view]]. |
|||
=== Postup práce ve Skicáři === |
|||
* Double-click the constraint in the [[Sketcher_Dialog|Sketcher Dialog]]. |
|||
Bude přidáno |
|||
* Right-click the constraint in the Sketcher Dialog and select the {{MenuCommand|Change value}} option from the context menu. |
|||
</div> |
|||
=== Reposition constraints === |
|||
Constraints can be repositioned in the 3D view by dragging. Hold down the left mouse button over the constraint value and move the mouse. |
|||
== Profile sketches == |
|||
To create a sketch that can be used as a profile for generating solids certain rules must be followed: |
|||
* The sketch must contain only closed contours. Gaps between endpoints, however small, are not allowed. |
|||
* Contours can be nested, to create voids, but should not self-intersect or intersect other contours. |
|||
* Contours cannot share edges with other contours. Duplicate edges should be avoided. |
|||
* T-connections, that is more than two edges sharing a common point, or a point touching an edge, are not allowed. |
|||
These rules do not apply to construction geometry (default color blue), which is not shown outside edit mode, or if the sketch is used for a different purpose. Depending on the workbench and the tool that will use the profile sketch, additional restrictions may apply. |
|||
== Drawing aids == |
|||
The Sketcher Workbench has several drawing aids and other features that can help when creating geometry and applying constraints. |
|||
=== Continue modes === |
|||
There are two continue modes: '''Geometry creation "Continue Mode"''' and '''Constraint creation "Continue Mode"'''. If these are checked (default) in the [[Sketcher_Preferences#Display|preferences]], related tools will restart after finishing. To exit an continuous tool press {{KEY|Esc}} or the right mouse button. This must be repeated if a continuous geometry tool has already received input. You can also exit a continuous tool by starting another geometry or constraint creation tool. Note that pressing {{KEY|Esc}} if no tool is active will exit sketch edit mode. Uncheck the '''Esc can leave sketch edit mode''' [[Sketcher_Preferences#General|preference]] if you often inadvertently press {{KEY|Esc}} too many times. |
|||
=== Auto constraints === |
|||
In sketches that have '''Auto constraints''' checked (default) several constraints are applied automatically when hovering the cursor properly (their symbols are displayed next to the cursor before applying). This is a per-sketch setting that can be changed in the [[Sketcher_Dialog#Constraints|Sketcher Dialog]] or by changing the {{PropertyView|Autoconstraints}} [[Property_editor|property]] of the sketch. The following constraints are applied automatically: |
|||
* [[Sketcher_ConstrainCoincident|Coincident]] |
|||
* [[Sketcher_ConstrainPointOnObject|Point on object]] |
|||
* [[Sketcher_ConstrainHorizontal|Horizontal]] |
|||
* [[Sketcher_ConstrainVertical|Vertical]] |
|||
* [[Sketcher_ConstrainTangent|Tangent]] |
|||
* {{Version|0.22}}: [[Sketcher_ConstrainSymmetric|Symmetric]] (line midpoint) |
|||
=== Snapping === |
|||
{{Version|0.21}} |
|||
It is possible to [[Sketcher_Snap|snap]] to grid lines and grid intersection, to edges of geometry and midpoints of lines and arcs, and to certain angles. Please note that snapping does not produce constraints in and of itself. For example, only if Auto constraints is switched on will snapping to an edge produce a [[Sketcher_ConstrainPointOnObject|Point on object constraint]]. But just picking a point on the edge would then have the same result. |
|||
=== On-View-Parameters === |
|||
{{Version|0.22}} |
|||
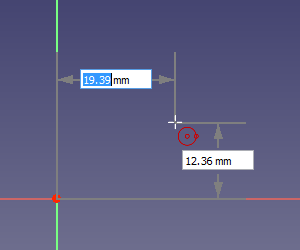
Depending on the selected option in the [[Sketcher_Preferences#General|preferences]] only the dimensional On-View-Parameters or both the dimensional and the positional On-View-Parameters can be enabled. Positional parameters allow the input of exact coordinates, for example the center of a circle, or the start point of a line. Dimensional parameters allow the input of exact dimensions, for example the radius of a circle, or the length and angle of a line. On-View-Parameters are not available for all tools. |
|||
[[Image:Sketcher_On_view_parameters_positional.png]] |
|||
{{Caption|Determining the center point of a circle with the positional parameters enabled}} |
|||
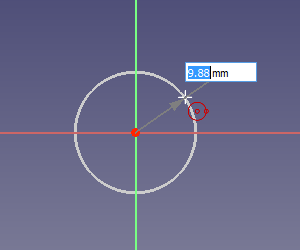
[[Image:Sketcher_On_view_parameters_dimensional.png]] |
|||
{{Caption|Determining the radius of a circle with the dimensional parameters enabled}} |
|||
If values are entered and confirmed by pressing {{KEY|Enter}} or {{KEY|Tab}}, related constraints are added automatically. If two parameters are displayed at the same time, for example the X and Y coordinate of a point, it is possible to enter one value and pick a point to define the other. Depending on the object additional constraints may be required to fully constrain it. Constraints resulting from On-View-Parameters take precedence over those that may result from [[Sketcher_Dialog#Constraints|Auto constraints]]. |
|||
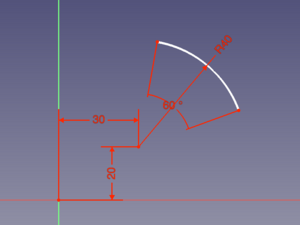
[[Image:Sketcher_ArcExample3.png|300px]] |
|||
{{Caption|Arc created by entering all On-View-Parameters with resulting automatically created constraints}} |
|||
=== Coordinate display === |
|||
If the '''Show coordinates beside cursor while editing''' [[Sketcher_Preferences#Display|preference]] is checked (default), the parameters of the current geometry tool (coordinates, radius, or length and angle) are displayed next to the cursor. This is deactivated while On-View-Parameters are shown. |
|||
== Selection == |
|||
No need for Ctrl, but... |
|||
Select in Sketcher Dialog... |
|||
=== Box selection === |
|||
=== Connected geometry selection === |
|||
== Copy, cut and paste == |
|||
If a Sketch has segments that cross one another, places where a Point is not directly on a segment, or places where there are gaps between endpoints of adjacent segments, Pad or Revolve won't create a solid. Sometimes a Sketch which contains lines which cross one another will work for a simple operation such as Pad, but later operations such as Linear Pattern will fail. It is best to avoid crossing lines. The exception to this rule is that it doesn't apply to Construction (blue) Geometry. |
|||
{{Version|0.22}} |
|||
Inside the enclosed area we can have smaller non-overlapping areas. These will become voids when the 3D solid is created. |
|||
The standard keyboard shortcuts can be used to copy, {{KEY|Ctrl}}+{{KEY|C}}, cut, {{KEY|Ctrl}}+{{KEY|X}}, and paste, {{KEY|Ctrl}}+{{KEY|V}}, the currently selected Sketcher geometry including related constraints. But these tools are also available from the {{MenuCommand|Sketch → Sketcher tools}} menu. They can be used within the same sketch but also between different sketches or separate instances of FreeCAD. Since the data is copied to the clipboard in the form of Python code, it can be used in other ways too (e.g. shared on the forum). |
|||
Once a Sketch is fully constrained, the Sketch features will turn green; Construction Geometry will remain blue. It is usually "finished" at this point and suitable for use in creating a 3D solid. However, once the Sketch dialog is closed it may be worthwhile going to [[Image:Workbench_Part.svg|24px]] [[Part_Workbench|Part Workbench]] and running {{Button|[[File:Part_CheckGeometry.svg|16px]] [[Part_CheckGeometry|Check geometry]]}} to ensure there are no features in the Sketch which may cause later problems. |
|||
== Tools == |
== Tools == |
||
| Line 106: | Line 157: | ||
==== Sketcher toolbar ==== |
==== Sketcher toolbar ==== |
||
* [[Image:Sketcher_NewSketch.svg|32px]] [[Sketcher_NewSketch|Create sketch]]: |
* [[Image:Sketcher_NewSketch.svg|32px]] [[Sketcher_NewSketch|Create sketch]]: Creates a new sketch and opens the [[Sketcher_Dialog|Sketcher Dialog]] to edit it. |
||
* [[Image:Sketcher_EditSketch.svg|32px]] [[Sketcher_EditSketch|Edit sketch]]: |
* [[Image:Sketcher_EditSketch.svg|32px]] [[Sketcher_EditSketch|Edit sketch]]: Opens the Sketcher Dialog to edit an existing sketch. |
||
* [[Image:Sketcher_MapSketch.svg|32px]] [[Sketcher_MapSketch| |
* [[Image:Sketcher_MapSketch.svg|32px]] [[Sketcher_MapSketch|Attach sketch]]: Attaches a sketch to selected geometry. |
||
* [[File:Sketcher_ReorientSketch.svg|32px]] [[Sketcher_ReorientSketch|Reorient sketch]]: |
* [[File:Sketcher_ReorientSketch.svg|32px]] [[Sketcher_ReorientSketch|Reorient sketch]]: Places a sketch on one of the main planes with an optional offset. It can also be used to detach a sketch. |
||
* [[File:Sketcher_ValidateSketch.svg|32px]] [[Sketcher_ValidateSketch|Validate sketch]]: |
* [[File:Sketcher_ValidateSketch.svg|32px]] [[Sketcher_ValidateSketch|Validate sketch]]: Can analyze and repair a sketch that is no longer editable or has invalid constraints, or add missing coincident constraints. |
||
* [[Image:Sketcher_MergeSketches.svg|32px]] [[Sketcher_MergeSketches|Merge sketches]]: |
* [[Image:Sketcher_MergeSketches.svg|32px]] [[Sketcher_MergeSketches|Merge sketches]]: Merges two or more sketches. |
||
* [[Image:Sketcher_MirrorSketch.svg|32px]] [[Sketcher_MirrorSketch|Mirror sketch]]: |
* [[Image:Sketcher_MirrorSketch.svg|32px]] [[Sketcher_MirrorSketch|Mirror sketch]]: Mirrors sketches along their X axis, Y axis, or origin. |
||
==== Sketcher Edit Mode toolbar ==== |
==== Sketcher Edit Mode toolbar ==== |
||
* [[Image:Sketcher_LeaveSketch.svg|32px]] [[Sketcher_LeaveSketch|Leave sketch]]: |
* [[Image:Sketcher_LeaveSketch.svg|32px]] [[Sketcher_LeaveSketch|Leave sketch]]: Finishes sketch edit mode and closes the [[Sketcher_Dialog|Sketcher Dialog]]. |
||
* [[Image:Sketcher_ViewSketch.svg|32px]] [[Sketcher_ViewSketch|View sketch]]: Sets the |
* [[Image:Sketcher_ViewSketch.svg|32px]] [[Sketcher_ViewSketch|View sketch]]: Sets the [[3D_view|3D view]] perpendicular to the sketch plane. |
||
* [[Image:Sketcher_ViewSection.svg|32px]] [[Sketcher_ViewSection|View section]]: |
* [[Image:Sketcher_ViewSection.svg|32px]] [[Sketcher_ViewSection|View section]]: Toggles a temporary section plane that hides any objects and parts of objects in front of the sketch plane. |
||
==== Sketcher edit tools toolbar ==== |
==== Sketcher edit tools toolbar ==== |
||
| Line 138: | Line 189: | ||
==== Other ==== |
==== Other ==== |
||
* [[File:Sketcher_StopOperation.svg|32px]] [[Sketcher_StopOperation|Stop operation]]: |
* [[File:Sketcher_StopOperation.svg|32px]] [[Sketcher_StopOperation|Stop operation]]: Stops any currently running geometry or constraint creation tool. |
||
===Sketcher geometries=== |
===Sketcher geometries=== |
||
| Line 212: | Line 263: | ||
:* [[Image:Sketcher_CreateSlot.svg|32px]] [[Sketcher_CreateSlot|Slot]]: Draws an oval by selecting the center of one semicircle and an endpoint of the other semicircle. |
:* [[Image:Sketcher_CreateSlot.svg|32px]] [[Sketcher_CreateSlot|Slot]]: Draws an oval by selecting the center of one semicircle and an endpoint of the other semicircle. |
||
:* [[Image:Sketcher_CreateArcSlot.svg|32px]] [[Sketcher_CreateArcSlot|Arc slot]]: |
:* [[Image:Sketcher_CreateArcSlot.svg|32px]] [[Sketcher_CreateArcSlot|Arc slot]]: Draws an arc slot consisting of two semicircles connected by two parallel concentric arcs. {{Version|0.22}} |
||
* <span id="Sketcher_CompCreateFillets">[[Image:Sketcher_CreateFillet.svg|x32px]][[Image:Toolbar_flyout_arrow_blue_background.svg|x32px]] Create fillet:</span><!--Do not edit span id: the Sketcher_CompCreateFillets pages redirect here--> |
* <span id="Sketcher_CompCreateFillets">[[Image:Sketcher_CreateFillet.svg|x32px]][[Image:Toolbar_flyout_arrow_blue_background.svg|x32px]] Create fillet/chamfer:</span><!--Do not edit span id: the Sketcher_CompCreateFillets pages redirect here--> |
||
:* [[Image:Sketcher_CreateFillet.svg|32px]] [[Sketcher_CreateFillet|Fillet]]: Creates a fillet between two non-parallel |
:* [[Image:Sketcher_CreateFillet.svg|32px]] [[Sketcher_CreateFillet|Fillet]]: Creates a fillet between two non-parallel edges. |
||
:* [[Image: |
:* [[Image:Sketcher_CreateChamfer.svg|32px]] [[Sketcher_CreateChamfer|Chamfer]]: Creates a chamfer between two non-parallel edges. |
||
* <span id="Sketcher_CompCurveEdition">[[Image:Sketcher_Trimming.svg|x32px]][[Image:Toolbar_flyout_arrow_blue_background.svg|x32px]] Edit edge:</span><!--Do not edit span id: the Sketcher_CompCurveEdition pages redirect here--> |
* <span id="Sketcher_CompCurveEdition">[[Image:Sketcher_Trimming.svg|x32px]][[Image:Toolbar_flyout_arrow_blue_background.svg|x32px]] Edit edge:</span><!--Do not edit span id: the Sketcher_CompCurveEdition pages redirect here--> |
||
| Line 238: | Line 289: | ||
Constraints are used to define lengths, set rules between sketch elements, and to lock the sketch along the vertical and horizontal axes. Some constraints require use of [[Sketcher_helper_constraint|Helper constraints]]. |
Constraints are used to define lengths, set rules between sketch elements, and to lock the sketch along the vertical and horizontal axes. Some constraints require use of [[Sketcher_helper_constraint|Helper constraints]]. |
||
* [[File:Sketcher_ConstrainCoincidentUnified.svg|32px]] [[Sketcher_ConstrainCoincidentUnified|Coincident (unified)]]: |
* [[File:Sketcher_ConstrainCoincidentUnified.svg|32px]] [[Sketcher_ConstrainCoincidentUnified|Coincident (unified)]]: Can replace the [[Sketcher_ConstrainCoincident|Coincident]] and [[Sketcher_ConstrainPointOnObject|Point on object]] constraints. {{Version|0.22}} |
||
* [[File:Sketcher_ConstrainCoincident.svg|32px]] [[Sketcher_ConstrainCoincident|Coincident]]: Affixes a point onto (coincident with) one or more other points. It acts as a concentric constraint if two or more circles, arcs, ellipses or arcs of ellipses are selected. |
* [[File:Sketcher_ConstrainCoincident.svg|32px]] [[Sketcher_ConstrainCoincident|Coincident]]: Affixes a point onto (coincident with) one or more other points. It acts as a concentric constraint if two or more circles, arcs, ellipses or arcs of ellipses are selected. |
||
| Line 246: | Line 297: | ||
* <span id="Sketcher_CompHorVer">[[Image:Sketcher_ConstrainHorVer.svg|x32px]][[Image:Toolbar_flyout_arrow_blue_background.svg|x32px]]Horizontal/Vertical constraints:</span><!--Do not edit span id: the Sketcher_CompHorVer pages redirect here--> |
* <span id="Sketcher_CompHorVer">[[Image:Sketcher_ConstrainHorVer.svg|x32px]][[Image:Toolbar_flyout_arrow_blue_background.svg|x32px]]Horizontal/Vertical constraints:</span><!--Do not edit span id: the Sketcher_CompHorVer pages redirect here--> |
||
:* [[File:Sketcher_ConstrainHorVer.svg|32px]] [[Sketcher_ConstrainHorVer|Horizontal/Vertical]]: |
:* [[File:Sketcher_ConstrainHorVer.svg|32px]] [[Sketcher_ConstrainHorVer|Horizontal/Vertical]]: Automatically applies [[Sketcher_ConstrainHorizontal|Horizontal]] or [[Sketcher_ConstrainVertical|Vertical]] constraint depending on the orientation of a line. {{Version|0.22}} |
||
:* [[File:Sketcher_ConstrainHorizontal.svg|32px]] [[Sketcher_ConstrainHorizontal|Horizontal]]: Constrains the selected lines or polyline elements to a true horizontal orientation. More than one object can be selected before applying this constraint. |
:* [[File:Sketcher_ConstrainHorizontal.svg|32px]] [[Sketcher_ConstrainHorizontal|Horizontal]]: Constrains the selected lines or polyline elements to a true horizontal orientation. More than one object can be selected before applying this constraint. |
||
| Line 266: | Line 317: | ||
* <span id="Sketcher_CompDimensionTools">[[Image:Sketcher_Dimension.svg|x32px]][[Image:Toolbar_flyout_arrow_blue_background.svg|x32px]] Dimensional constraints:</span><!--Do not edit span id: the Sketcher_CompDimensionTools pages redirect here--> |
* <span id="Sketcher_CompDimensionTools">[[Image:Sketcher_Dimension.svg|x32px]][[Image:Toolbar_flyout_arrow_blue_background.svg|x32px]] Dimensional constraints:</span><!--Do not edit span id: the Sketcher_CompDimensionTools pages redirect here--> |
||
:* [[File:Sketcher_Dimension.svg|32px]] [[Sketcher_Dimension|Dimension]]: |
:* [[File:Sketcher_Dimension.svg|32px]] [[Sketcher_Dimension|Dimension]]: Provides context-sensitive dimensional constraint tool. {{Version|0.22}} |
||
:* [[File:Sketcher_ConstrainLock.svg|32px]] [[Sketcher_ConstrainLock|Lock]]: Constrains the selected item by setting vertical and horizontal distances relative to the origin, thereby locking the location of that item. These constraint distances can be edited later. |
|||
:* [[File:Sketcher_ConstrainDistanceX.svg|32px]] [[Sketcher_ConstrainDistanceX|Horizontal distance]]: Fixes the horizontal distance between two points or line endpoints. If only one item is selected, the distance is set to the origin. |
:* [[File:Sketcher_ConstrainDistanceX.svg|32px]] [[Sketcher_ConstrainDistanceX|Horizontal distance]]: Fixes the horizontal distance between two points or line endpoints. If only one item is selected, the distance is set to the origin. |
||
| Line 276: | Line 325: | ||
:* [[File:Sketcher_ConstrainDistance.svg|32px]] [[Sketcher_ConstrainDistance|Distance]]: Defines the length of a line, the perpendicular distance between a point and a line, the distance between two points, or, {{Version|0.21}}, the distance between the edges of two circles. |
:* [[File:Sketcher_ConstrainDistance.svg|32px]] [[Sketcher_ConstrainDistance|Distance]]: Defines the length of a line, the perpendicular distance between a point and a line, the distance between two points, or, {{Version|0.21}}, the distance between the edges of two circles. |
||
:* <span id="Sketcher_CompConstrainRadDia">[[File: |
:* <span id="Sketcher_CompConstrainRadDia">[[File:Sketcher_ConstrainRadiam.svg|32px]] [[Sketcher_ConstrainRadiam|Auto radius/diameter]]: Defines the radius of an arc, the diameter of a circle or the weight of a B-spline pole. {{Version|0.20}}</span><!--Do not edit span id: the Sketcher_CompConstrainRadDia pages redirect here--> |
||
:* [[File:Sketcher_ConstrainRadius.svg|32px]] [[Sketcher_ConstrainRadius|Radius]]: Defines the radius of an arc or circle or the weight of a B-spline pole. |
|||
:* [[File:Sketcher_ConstrainDiameter.svg|32px]] [[Sketcher_ConstrainDiameter|Diameter]]: Defines the diameter of an arc or circle. |
:* [[File:Sketcher_ConstrainDiameter.svg|32px]] [[Sketcher_ConstrainDiameter|Diameter]]: Defines the diameter of an arc or circle. |
||
:* [[File:Sketcher_ConstrainRadiam.svg|32px]] [[Sketcher_ConstrainRadiam|Auto radius/diameter]]: Defines the radius of an arc, the diameter of a circle or the weight of a B-spline pole. {{Version|0.20}} |
|||
:* [[File:Sketcher_ConstrainAngle.svg|32px]] [[Sketcher_ConstrainAngle|Angle]]: Defines the internal angle between two selected lines. |
:* [[File:Sketcher_ConstrainAngle.svg|32px]] [[Sketcher_ConstrainAngle|Angle]]: Defines the internal angle between two selected lines. |
||
:* [[File:Sketcher_ConstrainLock.svg|32px]] [[Sketcher_ConstrainLock|Lock]]: Constrains the selected item by setting vertical and horizontal distances relative to the origin, thereby locking the location of that item. These constraint distances can be edited later. |
|||
==== Special constraints ==== |
==== Special constraints ==== |
||
| Line 298: | Line 349: | ||
===Sketcher tools=== |
===Sketcher tools=== |
||
* [[File:Sketcher_SelectElementsWithDoFs.svg|32px]] [[Sketcher_SelectElementsWithDoFs|Select unconstrained DoF]]: Highlights in green the geometry with degrees of freedom ( |
* [[File:Sketcher_SelectElementsWithDoFs.svg|32px]] [[Sketcher_SelectElementsWithDoFs|Select unconstrained DoF]]: Highlights in green the geometry with degrees of freedom (DoFs), i.e. not fully constrained. |
||
* [[File:Sketcher_SelectConstraints.svg|32px]] [[Sketcher_SelectConstraints|Select associated constraints]]: Selects the constraints of a |
* [[File:Sketcher_SelectConstraints.svg|32px]] [[Sketcher_SelectConstraints|Select associated constraints]]: Selects the constraints of a Sketcher element. |
||
* [[File:Sketcher_SelectElementsAssociatedWithConstraints.svg|32px]] [[Sketcher_SelectElementsAssociatedWithConstraints|Select associated geometry]]: Select |
* [[File:Sketcher_SelectElementsAssociatedWithConstraints.svg|32px]] [[Sketcher_SelectElementsAssociatedWithConstraints|Select associated geometry]]: Select Sketcher elements associated with constraints. |
||
* [[File:Sketcher_SelectRedundantConstraints.svg|32px]] [[Sketcher_SelectRedundantConstraints|Select redundant constraints]]: Selects redundant constraints of a sketch. |
* [[File:Sketcher_SelectRedundantConstraints.svg|32px]] [[Sketcher_SelectRedundantConstraints|Select redundant constraints]]: Selects redundant constraints of a sketch. |
||
| Line 318: | Line 369: | ||
* [[File:Sketcher_Offset.svg|32px]] [[Sketcher_Offset|Offset geometry]]: Adds an equidistant outline around selected edges. {{Version|0.22}} |
* [[File:Sketcher_Offset.svg|32px]] [[Sketcher_Offset|Offset geometry]]: Adds an equidistant outline around selected edges. {{Version|0.22}} |
||
* [[File:Sketcher_Rotate.svg|32px]] [[Sketcher_Rotate|Polar transform]]: |
* [[File:Sketcher_Rotate.svg|32px]] [[Sketcher_Rotate|Polar transform]]: Rotates and optionally copies (to create polar patterns) selected geometries. {{Version|0.22}} |
||
* [[File:Sketcher_Symmetry.svg|32px]] [[Sketcher_Symmetry|Symmetry]]: Copies a sketcher element symmetrical to a chosen line. |
|||
* [[File:Sketcher_Clone.svg|32px]] [[Sketcher_Clone|Clone]]: Clones a sketcher element. |
|||
* [[File: |
* [[File:Sketcher_Scale.svg|32px]] [[Sketcher_Scale|Scale transform]]: Scales and optionally copies selected geometries. {{Version|0.22}} |
||
* [[File: |
* [[File:Sketcher_Symmetry.svg|32px]] [[Sketcher_Symmetry|Symmetry]]: Copies a Sketcher element symmetrically to a chosen line. |
||
* [[File: |
* [[File:Sketcher_Translate.svg|32px]] [[Sketcher_Translate|Array transform]]: Translates and optionally copies (to create linear patterns) selected geometries. {{Version|0.22}} |
||
* [[File:Sketcher_RemoveAxesAlignment.svg|32px]] [[Sketcher_RemoveAxesAlignment|Remove axes alignment]]: Remove axes alignment while trying to preserve the constraint relationship of the selection. {{Version|0.20}} |
* [[File:Sketcher_RemoveAxesAlignment.svg|32px]] [[Sketcher_RemoveAxesAlignment|Remove axes alignment]]: Remove axes alignment while trying to preserve the constraint relationship of the selection. {{Version|0.20}} |
||
| Line 335: | Line 382: | ||
* [[File:Sketcher_DeleteAllConstraints.svg|32px]] [[Sketcher_DeleteAllConstraints|Delete all constraints]]: Deletes all constraints from the sketch. |
* [[File:Sketcher_DeleteAllConstraints.svg|32px]] [[Sketcher_DeleteAllConstraints|Delete all constraints]]: Deletes all constraints from the sketch. |
||
* <span id="Sketcher_CopyClipboard">[[File:Edit-copy.svg|32px]] Copy in Sketcher: See [[#Copy,_cut_and_paste|Copy, cut and paste]].</span><!--Do not edit span id: the Sketcher_CopyClipboard pages redirect here--> |
|||
* <span id="Sketcher_Cut">[[File:Edit-cut.svg|32px]] Cut in Sketcher: See [[#Copy,_cut_and_paste|Copy, cut and paste]].</span><!--Do not edit span id: the Sketcher_Cut pages redirect here--> |
|||
* <span id="Sketcher_Paste">[[File:Edit-paste.svg|32px]] Paste in Sketcher: See [[#Copy,_cut_and_paste|Copy, cut and paste]].</span><!--Do not edit span id: the Sketcher_Paste pages redirect here--> |
|||
===Sketcher B-spline tools=== |
===Sketcher B-spline tools=== |
||
* [[File: |
* [[File:Sketcher_BSplineConvertToNURBS.svg|32px]] [[Sketcher_BSplineConvertToNURBS|Convert geometry to B-spline]]: Converts compatible geometry, edges and curves, into a B-spline. |
||
* [[File:Sketcher_BSplineIncreaseDegree.svg|32px]] [[Sketcher_BSplineIncreaseDegree|Increase B-spline degree]]: Increases the degree (order) of a B-spline. |
* [[File:Sketcher_BSplineIncreaseDegree.svg|32px]] [[Sketcher_BSplineIncreaseDegree|Increase B-spline degree]]: Increases the degree (order) of a B-spline. |
||
| Line 366: | Line 419: | ||
* [[File:Sketcher_BSplinePoleWeight.svg|32px]] [[Sketcher_BSplinePoleWeight|Show/hide B-spline control point weight]]: Shows or hides the display of the weights for the control points of a B-spline. |
* [[File:Sketcher_BSplinePoleWeight.svg|32px]] [[Sketcher_BSplinePoleWeight|Show/hide B-spline control point weight]]: Shows or hides the display of the weights for the control points of a B-spline. |
||
* [[File:Sketcher_ArcOverlay.svg|32px]] [[Sketcher_ArcOverlay|Show/hide circular helper for arcs]]: |
* [[File:Sketcher_ArcOverlay.svg|32px]] [[Sketcher_ArcOverlay|Show/hide circular helper for arcs]]: Shows or hides the circular helpers (circle outlines) for arcs. {{Version|0.22}} |
||
===Obsolete tools=== |
===Obsolete tools=== |
||
* [[File:Sketcher_Clone.svg|32px]] [[Sketcher_Clone|Clone]]: Clones a Sketcher element. Not available in {{VersionPlus|0.22}}. |
|||
* [[File:Sketcher_CloseShape.svg|32px]] [[Sketcher_CloseShape|Close shape]]: Creates a closed shape by applying coincident constraints to endpoints. Not available in {{VersionPlus|0.21}}. |
* [[File:Sketcher_CloseShape.svg|32px]] [[Sketcher_CloseShape|Close shape]]: Creates a closed shape by applying coincident constraints to endpoints. Not available in {{VersionPlus|0.21}}. |
||
* [[File: |
* [[File:Sketcher_CreatePointFillet.svg|32px]] [[Sketcher_CreatePointFillet|Corner-preserving fillet]]: Creates a fillet between two non-parallel lines while preserving their corner point. Not available in {{VersionPlus|0.22}}. |
||
* [[File:Sketcher_ConnectLines.svg|32px]] [[Sketcher_ConnectLines|Connect edges]]: Connect Sketcher elements by applying coincident constraints to endpoints. Not available in {{VersionPlus|0.21}}. |
|||
* [[File:Sketcher_Copy.svg|32px]] [[Sketcher_Copy|Copy]]: Copies a Sketcher element. Not available in {{VersionPlus|0.22}}. |
|||
* [[File:Sketcher_Move.svg|32px]] [[Sketcher_Move|Move]]: Moves the selected geometry taking as reference the last selected point. Not available in {{VersionPlus|0.22}}. |
|||
* [[File:Sketcher_RectangularArray.svg|32px]] [[Sketcher_RectangularArray|Rectangular array]]: Creates an array of selected Sketcher elements. Not available in {{VersionPlus|0.22}}. |
|||
== Preferences == |
== Preferences == |
||
* [[Image:Workbench_Sketcher.svg|32px]] [[Sketcher_Preferences|Preferences]]: Preferences for the |
* [[Image:Workbench_Sketcher.svg|32px]] [[Sketcher_Preferences|Preferences]]: Preferences for the Sketcher Workbench. |
||
== Best |
== Best practices == |
||
<div class="mw-translate-fuzzy"> |
<div class="mw-translate-fuzzy"> |
||
| Line 397: | Line 460: | ||
== Tutorials == |
== Tutorials == |
||
* [https://forum.freecadweb.org/viewtopic.php?f=36&t=30104 Sketcher |
* [https://forum.freecadweb.org/viewtopic.php?f=36&t=30104 Sketcher Lecture] by chrisb. This is a more than 80 page PDF document that serves as a detailed manual for the Sketcher. It explains the basics of Sketcher usage, and goes into a lot of detail about the creation of geometrical shapes, and each of the constraints. |
||
* [[Basic_Sketcher_Tutorial|Basic Sketcher Tutorial]] for beginners |
* [[Basic_Sketcher_Tutorial|Basic Sketcher Tutorial]] for beginners |
||
* [[Sketcher_Micro_Tutorial_-_Constraint_Practices|Sketcher Micro Tutorial - Constraint Practices]] |
* [[Sketcher_Micro_Tutorial_-_Constraint_Practices|Sketcher Micro Tutorial - Constraint Practices]] |
||
Latest revision as of 09:26, 14 April 2024

Úvod
Pracovní plocha Skicář je používána pro vytváření 2D konstrukcí určených pro použití v Pracovní ploše Návrh dílu a dalších pracovních plochách. Obecně jsou 2D konstrukce zamýšleny jako startovní bod pro většinu CAD modelů - jednoduchý 2D náčrt může být 'vysunut' do 3D tvaru, dále mohou být 2D náčrty použity k vytváření kapes v povrchu objektu a náčrty mohou být využity pro definování 'desek' (vysunutí) na povrchu 3D objektů. Spolu s logickými operacemi, náčrt vytváří jádro generativního návrhu dílu tělesa.
Together with boolean operations defined in the Part Workbench, the Sketcher Workbench, or "The Sketcher" for short, forms the basis of the constructive solid geometry (CSG) method of building solids. Together with
PartDesign Workbench operations, it also forms the basis of the feature editing methodology of creating solids. But many other workbenches use sketches as well.
Samotná pracovní plocha Skicář obsahuje vazby - umožňující 2D tvarům mít vazby pro přesné definice konstrukcí. A kalkulátor vazeb který počítá rozšíření vazeb 2D konstrukcí a umožňuje interaktivní zkoumání stupňů volnosti náčrtů.
Pro co není Skicář vhodný
Skicář není určen pro vytváření 2D výkresů. Protože náčrty jsou používány pro generování těles, jsou automaticky skrývány. Rozměry jsou viditelné pouze v editačním módu Náčrtu.
Základní plně vazbený náčrt.
Constraints
Co jsou vazby?
Vazby jsou použity k omezení stupňů volnosti objektu. Například přímka bez vazeb má 4 stupně volnosti: může se posunovat vodorovně nebo svisle, může být natahována a otáčena.
Použití vodorovné nebo svislé vazby nebo vazbu úhlu (relativně k jiné přímce nebo k některé z os) omezí její možnosti otáčení, takže jí zbudou jen tři stupně volnosti. Zavazbení jednoho bodu v relaci k počátku odebere další 2 stupně volnosti. A aplikace vazby rozměru odebere poslední stupeň volnosti. Přímka je potom považována za plně vazbenou.
Více objektů může být vazbeno mezi sebou vzájemně. Dvě přímky mohou být spojeny prostřednictvím jejich bodů pomocí vazby souhlasných bodů. Může být nastaven úhel mezi nimi nebo mohou být nastaveny kolmo k sobě. Přímka se může dotýkat oblouku nebo kružnice, atd.
Jsou dva druhy vazeb: konstrukční a rozměrové. Detailně jsou rozebrány v sekci 'Nástroje' dále.
Driving vs. reference constraints
Edit constraints
When a driving constraint is created, and if the Ask for value after creating a dimensional constraint preference is selected (default), a dialog opens to edit its value.
You can enter a numerical value or an expression, and it is possible to name the constraint to facilitate its use in other expressions. You can also check the Reference checkbox to switch the constrain to reference mode.
To edit the value of an existing dimensional constraint do one of the following:
- Double-click the constraint value in the 3D view.
- Double-click the constraint in the Sketcher Dialog.
- Right-click the constraint in the Sketcher Dialog and select the Change value option from the context menu.
Reposition constraints
Constraints can be repositioned in the 3D view by dragging. Hold down the left mouse button over the constraint value and move the mouse.
Profile sketches
To create a sketch that can be used as a profile for generating solids certain rules must be followed:
- The sketch must contain only closed contours. Gaps between endpoints, however small, are not allowed.
- Contours can be nested, to create voids, but should not self-intersect or intersect other contours.
- Contours cannot share edges with other contours. Duplicate edges should be avoided.
- T-connections, that is more than two edges sharing a common point, or a point touching an edge, are not allowed.
These rules do not apply to construction geometry (default color blue), which is not shown outside edit mode, or if the sketch is used for a different purpose. Depending on the workbench and the tool that will use the profile sketch, additional restrictions may apply.
Drawing aids
The Sketcher Workbench has several drawing aids and other features that can help when creating geometry and applying constraints.
Continue modes
There are two continue modes: Geometry creation "Continue Mode" and Constraint creation "Continue Mode". If these are checked (default) in the preferences, related tools will restart after finishing. To exit an continuous tool press Esc or the right mouse button. This must be repeated if a continuous geometry tool has already received input. You can also exit a continuous tool by starting another geometry or constraint creation tool. Note that pressing Esc if no tool is active will exit sketch edit mode. Uncheck the Esc can leave sketch edit mode preference if you often inadvertently press Esc too many times.
Auto constraints
In sketches that have Auto constraints checked (default) several constraints are applied automatically when hovering the cursor properly (their symbols are displayed next to the cursor before applying). This is a per-sketch setting that can be changed in the Sketcher Dialog or by changing the PohledAutoconstraints property of the sketch. The following constraints are applied automatically:
- Coincident
- Point on object
- Horizontal
- Vertical
- Tangent
- introduced in version 0.22: Symmetric (line midpoint)
Snapping
It is possible to snap to grid lines and grid intersection, to edges of geometry and midpoints of lines and arcs, and to certain angles. Please note that snapping does not produce constraints in and of itself. For example, only if Auto constraints is switched on will snapping to an edge produce a Point on object constraint. But just picking a point on the edge would then have the same result.
On-View-Parameters
Depending on the selected option in the preferences only the dimensional On-View-Parameters or both the dimensional and the positional On-View-Parameters can be enabled. Positional parameters allow the input of exact coordinates, for example the center of a circle, or the start point of a line. Dimensional parameters allow the input of exact dimensions, for example the radius of a circle, or the length and angle of a line. On-View-Parameters are not available for all tools.
Determining the center point of a circle with the positional parameters enabled
Determining the radius of a circle with the dimensional parameters enabled
If values are entered and confirmed by pressing Enter or Tab, related constraints are added automatically. If two parameters are displayed at the same time, for example the X and Y coordinate of a point, it is possible to enter one value and pick a point to define the other. Depending on the object additional constraints may be required to fully constrain it. Constraints resulting from On-View-Parameters take precedence over those that may result from Auto constraints.
Arc created by entering all On-View-Parameters with resulting automatically created constraints
Coordinate display
If the Show coordinates beside cursor while editing preference is checked (default), the parameters of the current geometry tool (coordinates, radius, or length and angle) are displayed next to the cursor. This is deactivated while On-View-Parameters are shown.
Selection
No need for Ctrl, but... Select in Sketcher Dialog...
Box selection
Connected geometry selection
Copy, cut and paste
The standard keyboard shortcuts can be used to copy, Ctrl+C, cut, Ctrl+X, and paste, Ctrl+V, the currently selected Sketcher geometry including related constraints. But these tools are also available from the Sketch → Sketcher tools menu. They can be used within the same sketch but also between different sketches or separate instances of FreeCAD. Since the data is copied to the clipboard in the form of Python code, it can be used in other ways too (e.g. shared on the forum).
Tools
Nástroje
Nástroje pracovní plochy Skicář jsou umístěny v menu Skicář, které se zobrazí když natáhnete pracovní plochu Skicář.
introduced in version 0.21: If a sketch is in edit mode the Structure toolbar is hidden as none of its tools can then be used.
General
Sketcher toolbar
Create sketch: Creates a new sketch and opens the Sketcher Dialog to edit it.
Edit sketch: Opens the Sketcher Dialog to edit an existing sketch.
Attach sketch: Attaches a sketch to selected geometry.
Reorient sketch: Places a sketch on one of the main planes with an optional offset. It can also be used to detach a sketch.
Validate sketch: Can analyze and repair a sketch that is no longer editable or has invalid constraints, or add missing coincident constraints.
Merge sketches: Merges two or more sketches.
Mirror sketch: Mirrors sketches along their X axis, Y axis, or origin.
Sketcher Edit Mode toolbar
Leave sketch: Finishes sketch edit mode and closes the Sketcher Dialog.
View sketch: Sets the 3D view perpendicular to the sketch plane.
View section: Toggles a temporary section plane that hides any objects and parts of objects in front of the sketch plane.
Sketcher edit tools toolbar
Toggle grid: Toggles the grid in the sketch currently being edited. Settings can be changed in the related menu. introduced in version 0.21
Toggle snap: Toggles snapping in all sketches. Settings can be changed in the related menu. introduced in version 0.21
Configure rendering order: The rendering order of all sketches can be changed in the related menu. introduced in version 0.21
Other
Stop operation: Stops any currently running geometry or constraint creation tool.
Sketcher geometries
These are tools for creating objects.
Point: Draws a point.
Line: Draws a line segment between 2 points. Lines are infinite regarding certain constraints.
Arc: Draws an arc segment from center, radius, start angle and end angle.
Arc by 3 points: Draws an arc segment from two endpoints and another point on the circumference.
Circle: Draws a circle from center and radius.
Circle by 3 points: Draws a circle from three points on the circumference.
Ellipse by center: Draws an ellipse by center point, major radius point and minor radius point.
Ellipse by 3 points: Draws an ellipse by major diameter (2 points) and minor radius point.
Arc of ellipse: Draws an arc of ellipse by center point, major radius point, starting point and ending point.
Arc of hyperbola: Draws an arc of hyperbola.
Arc of parabola: Draws an arc of parabola.
B-spline by control points: Draws a B-spline curve by its control points.
Periodic B-spline by control points: Draws a periodic (closed) B-spline curve by its control points.
B-spline by knots: Draws a B-spline curve by its knots. introduced in version 0.21
Periodic B-spline by knots: Draws a periodic (closed) B-spline curve by its knots. introduced in version 0.21
Polyline (multiple-point line): Draws a line made of multiple line segments. Pressing the M key while drawing a Polyline toggles between the different polyline modes.
Rectangle: Draws a rectangle from 2 opposite points.
Centered rectangle: Draws a rectangle from a central point and an edge point. introduced in version 0.20
Rounded rectangle: Draws a rounded rectangle from 2 opposite points. introduced in version 0.20
Triangle: Draws a regular triangle inscribed in a construction geometry circle.
Square: Draws a regular square inscribed in a construction geometry circle.
Pentagon: Draws a regular pentagon inscribed in a construction geometry circle.
Hexagon: Draws a regular hexagon inscribed in a construction geometry circle.
Heptagon: Draws a regular heptagon inscribed in a construction geometry circle.
Octagon: Draws a regular octagon inscribed in a construction geometry circle.
Regular polygon : Draws a regular polygon by selecting the number of sides and picking two points: the center and one corner.
Slot: Draws an oval by selecting the center of one semicircle and an endpoint of the other semicircle.
Arc slot: Draws an arc slot consisting of two semicircles connected by two parallel concentric arcs. introduced in version 0.22
Fillet: Creates a fillet between two non-parallel edges.
Chamfer: Creates a chamfer between two non-parallel edges.
Trim: Trims a line, circle or arc with respect to the clicked point.
Split: Splits an edge into two while keeping most of the constraints. introduced in version 0.20
Extend: Extends a line or an arc to a boundary line, arc, ellipse, arc of ellipse or a point in space.
External geometry: Creates an edge linked to external geometry.
Carbon copy: Copies the geometry of another sketch.
Toggle construction geometry: Toggles sketch geometry from/to construction mode. Construction geometry is shown in blue and is discarded outside of Sketch editing mode.
Sketcher constraints
Constraints are used to define lengths, set rules between sketch elements, and to lock the sketch along the vertical and horizontal axes. Some constraints require use of Helper constraints.
Coincident (unified): Can replace the Coincident and Point on object constraints. introduced in version 0.22
Coincident: Affixes a point onto (coincident with) one or more other points. It acts as a concentric constraint if two or more circles, arcs, ellipses or arcs of ellipses are selected.
Point on object: Affixes a point onto another object such as a line, arc, or axis.
Horizontal/Vertical: Automatically applies Horizontal or Vertical constraint depending on the orientation of a line. introduced in version 0.22
Horizontal: Constrains the selected lines or polyline elements to a true horizontal orientation. More than one object can be selected before applying this constraint.
Vertical: Constrains the selected lines or polyline elements to a true vertical orientation. More than one object can be selected before applying this constraint.
Parallel: Constrains two or more lines parallel to one another.
Perpendicular: Constrains two lines perpendicular to one another, or constrains a line perpendicular to an arc endpoint.
Tangent: Creates a tangent constraint between two selected entities, or a co-linear constraint between two line segments. A line segment does not have to lie directly on an arc or circle to be constrained tangent to that arc or circle.
Equal: Constrains two selected entities equal to one another. If used on circles or arcs their radii will be set equal.
Symmetric: Constrains two points symmetrically about a line, or constrains the first two selected points symmetrically about a third selected point.
Block: it blocks an edge from moving, that is, it prevents its vertices from changing their current positions. It should be particularly useful to fix the position of B-Splines. See the Block Constraint forum topic.
Dimension: Provides context-sensitive dimensional constraint tool. introduced in version 0.22
Horizontal distance: Fixes the horizontal distance between two points or line endpoints. If only one item is selected, the distance is set to the origin.
Vertical distance: Fixes the vertical distance between 2 points or line endpoints. If only one item is selected, the distance is set to the origin.
Distance: Defines the length of a line, the perpendicular distance between a point and a line, the distance between two points, or, introduced in version 0.21, the distance between the edges of two circles.
Auto radius/diameter: Defines the radius of an arc, the diameter of a circle or the weight of a B-spline pole. introduced in version 0.20
Radius: Defines the radius of an arc or circle or the weight of a B-spline pole.
Diameter: Defines the diameter of an arc or circle.
Angle: Defines the internal angle between two selected lines.
Lock: Constrains the selected item by setting vertical and horizontal distances relative to the origin, thereby locking the location of that item. These constraint distances can be edited later.
Special constraints
Refraction (Snell's law): Constrains two lines to obey a refraction law to simulate the light going through an interface.
Constraint tools
The following tools can be used the change the effect of constraints:
Toggle driving/reference constraint: Toggles the toolbar or the selected constraints to/from reference mode.
Activate/deactivate constraint: Enable or disable an already placed constraint.
Sketcher tools
Select unconstrained DoF: Highlights in green the geometry with degrees of freedom (DoFs), i.e. not fully constrained.
Select associated constraints: Selects the constraints of a Sketcher element.
Select associated geometry: Select Sketcher elements associated with constraints.
Select redundant constraints: Selects redundant constraints of a sketch.
Select conflicting constraints: Selects conflicting constraints of a sketch.
Show/hide internal geometry: Recreates missing/deletes unneeded internal geometry of a selected ellipse, arc of ellipse/hyperbola/parabola or B-spline.
Select origin: Selects the origin of a sketch.
Select horizontal axis: Selects the horizontal axis of a sketch.
Select vertical axis: Selects the vertical axis of a sketch.
Offset geometry: Adds an equidistant outline around selected edges. introduced in version 0.22
Polar transform: Rotates and optionally copies (to create polar patterns) selected geometries. introduced in version 0.22
Scale transform: Scales and optionally copies selected geometries. introduced in version 0.22
Symmetry: Copies a Sketcher element symmetrically to a chosen line.
Array transform: Translates and optionally copies (to create linear patterns) selected geometries. introduced in version 0.22
Remove axes alignment: Remove axes alignment while trying to preserve the constraint relationship of the selection. introduced in version 0.20
Delete all geometry: Deletes all geometry from the sketch.
Delete all constraints: Deletes all constraints from the sketch.
Copy in Sketcher: See Copy, cut and paste.
Cut in Sketcher: See Copy, cut and paste.
Paste in Sketcher: See Copy, cut and paste.
Sketcher B-spline tools
Convert geometry to B-spline: Converts compatible geometry, edges and curves, into a B-spline.
Increase B-spline degree: Increases the degree (order) of a B-spline.
Decrease B-spline degree: Decreases the degree (order) of a B-spline.
Increase knot multiplicity: Increases the multiplicity of a B-spline knot.
Decrease knot multiplicity: Decreases the multiplicity of a B-spline knot.
Insert knot: Inserts a knot into an existing B-spline. introduced in version 0.20
Join curves: Joins two curves at selected end points. introduced in version 0.21
Sketcher visual
Switch virtual space: Allows you to hide all constraints of a sketch and make them visible again.
Show/hide B-spline degree: Shows or hides the display of the degree of a B-spline.
Show/hide B-spline control polygon: Shows or hides the display of the defining polygon of a B-spline.
Show/hide B-spline curvature comb: Shows or hides the display of the curvature comb of a B-spline.
Show/hide B-spline knot multiplicity: Shows or hides the display of the knot multiplicity of a B-spline.
Show/hide B-spline control point weight: Shows or hides the display of the weights for the control points of a B-spline.
Show/hide circular helper for arcs: Shows or hides the circular helpers (circle outlines) for arcs. introduced in version 0.22
Obsolete tools
Clone: Clones a Sketcher element. Not available in version 0.22 and above.
Close shape: Creates a closed shape by applying coincident constraints to endpoints. Not available in version 0.21 and above.
Corner-preserving fillet: Creates a fillet between two non-parallel lines while preserving their corner point. Not available in version 0.22 and above.
Connect edges: Connect Sketcher elements by applying coincident constraints to endpoints. Not available in version 0.21 and above.
Copy: Copies a Sketcher element. Not available in version 0.22 and above.
Move: Moves the selected geometry taking as reference the last selected point. Not available in version 0.22 and above.
Rectangular array: Creates an array of selected Sketcher elements. Not available in version 0.22 and above.
Preferences
Preferences: Preferences for the Sketcher Workbench.
Best practices
Dobrá praxe
Každý uživatel CADu si časem vytvoří svůj vlastní způsob práce, ale je několik obecných principů, které je dobré následovat.
- Je snadnější pracovat se sérií jednoduchých náčrtů než s jedním složitým. Například první náčrt může být vytvořen jako základ 3D tvarů (buď deska nebo obtáčení), zatímco druhý může obsahovat otvory nebo vyřezy (kapsy). Některé detaily mohou být vynechány s pozdější realizací na 3D tvaru. Pokud je na náčrtu mnoho zaoblení, můžete je vynechat a přidat je až na 3D tvaru.
- Vždy vytvářejte uzavřený profil jinak náčrt nebude generovat těleso, ale místo toho skupinu otevřených ploch. Pokud chcete aby některé objekty nebyly zahrnuty při vytváření tělesa, změňte je na konstrukční prvky pomocí nástroje Konstrukční mód.
- Použijte vlastnost autovazba pro omezení počtu vazeb, když je musíte přidávat ručně.
- Je obecné pravidlo, nejprve nastavit konstrukční vazby, potom délkové vazby a nakonec uzamknout náčrt. Ale pamatujte si: pravidla jsou k tomu aby se porušovala. Když máte problémy s manipulací s náčrtem, může se hodit nastavit vazby mezi několika objekty před kompletací profilu.
- Pokud je to možné vystřeďte náčrt na počátek (0,0) s vazbou uzamčení. Není-li náčrt symetrický, umístěte jeden z jeho bodů do počátku nebo vyberte pěkné kulaté číslo pro uzamčenou vzdálenost. Ve verzi v0.12 nejsou implementovány externí vazby (vazbí náčrt k existující 3D konstrukci jako jsou hrany nebo jiné náčrty).
To znamená, že pro umístění následujících konstrukčních náčrtů na první náčrt budete potřebovat nastavit vzdálenost relativně k prvnímu náčrtu ručně. Vazba uzamčení na (25,75) od počátku je mnohem jednodušší pro zapamatování než (23.47,73.02).
- Máte-li možnost vybrat si mezi vazbou Délky a vazbou Svislé nebo Vodorovné vzdálenosti, dejte přednost té druhé. Vazby Svislé nebo Vodorovné vzdálenosti jsou méně náročné na výpočty.
Tutorials
- Sketcher Lecture by chrisb. This is a more than 80 page PDF document that serves as a detailed manual for the Sketcher. It explains the basics of Sketcher usage, and goes into a lot of detail about the creation of geometrical shapes, and each of the constraints.
- Basic Sketcher Tutorial for beginners
- Sketcher Micro Tutorial - Constraint Practices
- Sketcher requirement for a sketch Minimum requirement for a sketch and Complete determination of a sketch
Scripting
The Sketcher scripting page contains examples on how to create constraints from Python scripts.
Examples
For some ideas of what can be achieved with Sketcher tools, have a look at: Sketcher examples.


- General: Create sketch, Edit sketch, Map sketch to face, Reorient sketch, Validate sketch, Merge sketches, Mirror sketch, Leave sketch, View sketch, View section, Toggle grid, Toggle snap, Configure rendering order, Stop operation
- Sketcher geometries: Point, Line, Arc, Arc by 3 points, Circle, Circle by 3 points, Ellipse, Ellipse by 3 points, Arc of ellipse, Arc of hyperbola, Arc of parabola, B-spline by control points, Periodic B-spline by control points, B-spline by knots, Periodic B-spline by knots, Polyline, Rectangle, Centered rectangle, Rounded rectangle, Triangle, Square, Pentagon, Hexagon, Heptagon, Octagon, Regular polygon, Slot, Fillet, Corner-preserving fillet, Trim, Extend, Split, External geometry, Carbon copy, Toggle construction geometry
- Sketcher constraints:
- Geometric constraints: Coincident, Point on object, Vertical, Horizontal, Parallel, Perpendicular, Tangent, Equal, Symmetric, Block
- Dimensional constraints: Lock, Horizontal distance, Vertical distance, Distance, Radius or weight, Diameter, Auto radius/diameter, Angle, Refraction (Snell's law)
- Constraint tools: Toggle driving/reference constraint, Activate/deactivate constraint
- Sketcher tools: Select unconstrained DoF, Select associated constraints, Select associated geometry, Select redundant constraints, Select conflicting constraints, Show/hide internal geometry, Select origin, Select horizontal axis, Select vertical axis, Symmetry, Clone, Copy, Move, Rectangular array, Remove axes alignment, Delete all geometry, Delete all constraints
- Sketcher B-spline tools: Show/hide B-spline degree, Show/hide B-spline control polygon, Show/hide B-spline curvature comb, Show/hide B-spline knot multiplicity, Show/hide B-spline control point weight, Convert geometry to B-spline, Increase B-spline degree, Decrease B-spline degree, Increase knot multiplicity, Decrease knot multiplicity, Insert knot, Join curves
- Sketcher virtual space: Switch virtual space
- Additional: Sketcher Dialog, Preferences, Sketcher scripting
- Getting started
- Installation: Download, Windows, Linux, Mac, Additional components, Docker, AppImage, Ubuntu Snap
- Basics: About FreeCAD, Interface, Mouse navigation, Selection methods, Object name, Preferences, Workbenches, Document structure, Properties, Help FreeCAD, Donate
- Help: Tutorials, Video tutorials
- Workbenches: Std Base, Arch, Assembly, CAM, Draft, FEM, Inspection, Mesh, OpenSCAD, Part, PartDesign, Points, Reverse Engineering, Robot, Sketcher, Spreadsheet, Start, Surface, TechDraw, Test Framework, Web
- Hubs: User hub, Power users hub, Developer hub