Assembly Workbench/pl: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
(Created page with "====Dodawanie złożenia głównego====") |
||
| (23 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 18: | Line 18: | ||
Środowisko pracy [[File:Workbench_Assembly.svg|24px]] [[Assembly_Workbench/pl|Złożenie]] to nowe wbudowane środowisko pracy FreeCAD. |
Środowisko pracy [[File:Workbench_Assembly.svg|24px]] [[Assembly_Workbench/pl|Złożenie]] to nowe wbudowane środowisko pracy FreeCAD. |
||
Czekamy na więcej ... |
|||
<span id="Tools"></span> |
<span id="Tools"></span> |
||
==Narzędzia== |
==Narzędzia== |
||
Funkcje eksperymentalne nie są domyślnie dostępne. Aby je włączyć, zapoznaj się z informacjami na stronie [[Fine-tuning/pl#środowisko_pracy_Złożenie|Dostrajanie parametrów]]. |
|||
<span id="Assembly"></span> |
|||
===Złożenie=== |
|||
* [[Image:Assembly_CreateAssembly.svg|32px]] [[Assembly_CreateAssembly/pl|Utwórz złożenie]] |
* [[Image:Assembly_CreateAssembly.svg|32px]] [[Assembly_CreateAssembly/pl|Utwórz złożenie]] |
||
| Line 29: | Line 32: | ||
* [[Image:Assembly_SolveAssembly.svg|32px]] [[Assembly_SolveAssembly/pl|Rozwiązywanie złożeń]] |
* [[Image:Assembly_SolveAssembly.svg|32px]] [[Assembly_SolveAssembly/pl|Rozwiązywanie złożeń]] |
||
* [[Image:Assembly_CreateView.svg|32px]] [[Assembly_CreateView/pl|Utwórz widok rozłożenia]]: [[Fine-tuning/pl#środowisko_pracy_Złożenie|{{Emphasis|Funkcja eksperymentalna}}]]. |
|||
* [[Image:Assembly_ExportASMT.svg|32px]] [[Assembly_ExportASMT/pl|Eksport pliku ASMT]] |
* [[Image:Assembly_ExportASMT.svg|32px]] [[Assembly_ExportASMT/pl|Eksport pliku ASMT]] |
||
<span id="Joints"></span> |
|||
===Połączenia=== |
|||
* [[Image:Assembly_ToggleGrounded.svg|32px]] [[Assembly_ToggleGrounded/pl|Przełącz zakotwienie]] |
* [[Image:Assembly_ToggleGrounded.svg|32px]] [[Assembly_ToggleGrounded/pl|Przełącz zakotwienie]] |
||
| Line 45: | Line 53: | ||
* [[Image:Assembly_CreateJointDistance.svg|32px]] [[Assembly_CreateJointDistance/pl|Utwórz połączenie dystansowe]] |
* [[Image:Assembly_CreateJointDistance.svg|32px]] [[Assembly_CreateJointDistance/pl|Utwórz połączenie dystansowe]] |
||
* [[Image:Assembly_CreateJointRackPinion.svg|32px]] [[Assembly_CreateJointRackPinion/pl|Utwórz połączenie zębatki i koła zębatego]]: [[Fine-tuning/pl#środowisko_pracy_Złożenie|{{Emphasis|Funkcja eksperymentalna}}]]. |
|||
* [[Image:Assembly_CreateJointScrew.svg|32px]] [[Assembly_CreateJointScrew/pl|Utwórz połączenie śrubowe]]: [[Fine-tuning/pl#środowisko_pracy_Złożenie|{{Emphasis|Funkcja eksperymentalna}}]]. |
|||
* <span id="Assembly_CreateJointGearBelt">[[Image:Assembly_CreateJointGears.svg|x32px]][[Image:Toolbar_flyout_arrow_blue_background.svg|x32px]] Utwórz połączenie koła zębatego / pasa:</span><!--Do not edit span id: the Assembly_CompCreateJointGearBelt pages redirect here--> |
|||
:* [[Image:Assembly_CreateJointGears.svg|32px]] [[Assembly_CreateJointGears/pl|Utwórz połączenie kół zębatych]]: [[Fine-tuning/pl#środowisko_pracy_Złożenie|{{Emphasis|Funkcja eksperymentalna}}]]. |
|||
:* [[Image:Assembly_CreateJointBelt.svg|32px]] [[Assembly_CreateJointBelt/pl|Utwórz połączenie pasowe]]: [[Fine-tuning/pl#środowisko_pracy_Złożenie|{{Emphasis|Funkcja eksperymentalna}}]]. |
|||
<span id="Example"></span> |
|||
==Przykład== |
|||
<div class="mw-collapsible mw-collapsed toccolours"> |
|||
[[Image:Assembly3_KinematicExample-01.png|80px]] Ten przykład jest tymczasowy i może zostać usunięty, gdy dostępne będą odpowiednie opisy / poradniki. |
|||
<div class="mw-collapsible-content"> |
|||
<span id="A_kinematic_assembly"></span> |
|||
===Złożenie kinematyczne=== |
|||
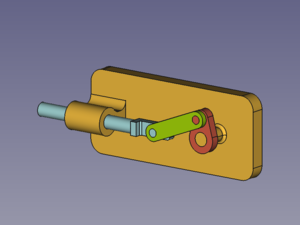
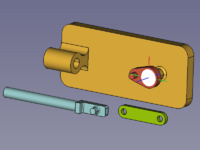
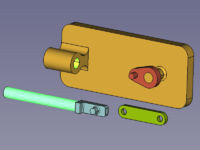
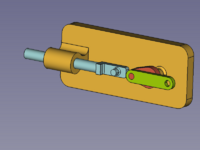
Zespół kinematyczny, który ma zostać utworzony, składa się z czterech części: podstawy, suwaka, korby i pręta łączącego. Są one połączone czterema przegubami. |
|||
[[Image:Assembly3_KinematicExample-01.png|300px]] |
|||
{{Caption|Złożone części: Podstawa ''(bursztynowy)'', Suwak ''(jasnoniebieski)'', Korba ''(czerwony)'', Korbowód ''(zielony)''}} |
|||
<span id="Prepare_parts"></span> |
|||
====Przygotowanie części==== |
|||
W tym przykładzie wszystkie części i zespół są tworzone w jednym dokumencie. |
|||
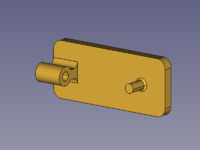
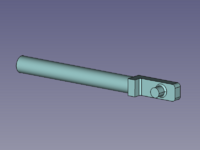
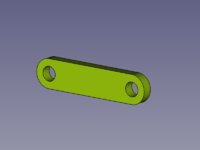
[[Image:Assembly3_KinematicExample-02.png|200px]] |
|||
[[Image:Assembly3_KinematicExample-03.png|200px]] |
|||
[[Image:Assembly3_KinematicExample-04.png|200px]] |
|||
[[Image:Assembly3_KinematicExample-05.png|200px]] |
|||
{{Caption|Od lewej do prawej: Podstawa, suwak, korba, korbowód.}} |
|||
Geometrie cylindryczne są równoległe lub prostopadłe, pozostałe kształty nie są istotne dla tego przykładu, chyba że powodują kolizje. Mając to na uwadze, wymodeluj własne kształty. |
|||
<span id="Add_a_root_assembly"></span> |
|||
====Dodawanie złożenia głównego==== |
|||
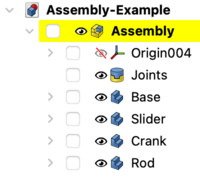
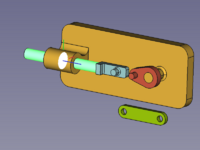
[[Image:Assembly_CreateAssembly.svg|16px]] [[Assembly_CreateAssembly/pl|Utwórz złożenie]] dodaje do dokumentu złożenie główne. ''(narzędzie to może również dodać podzespół do istniejącego wybranego złożenia)'' |
|||
[[Image:Assembly_KinematicExample-01.png|200px]] |
|||
<div lang="en" dir="ltr" class="mw-content-ltr"> |
|||
{{Caption|Tree view of Parts and Assembly in a document}} |
|||
</div> |
|||
<div lang="en" dir="ltr" class="mw-content-ltr"> |
|||
====Move the parts into the assembly container==== |
|||
</div> |
|||
<div lang="en" dir="ltr" class="mw-content-ltr"> |
|||
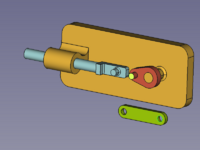
In the [[Tree_view|Tree view]] drag and drop the parts on the Assembly object. Now they can be handled by the Assembly's solver. |
|||
</div> |
|||
[[Image:Assembly_KinematicExample-02.png|200px]] |
|||
<div lang="en" dir="ltr" class="mw-content-ltr"> |
|||
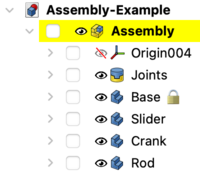
{{Caption|The Parts are in the Assembly container now}} |
|||
</div> |
|||
<div lang="en" dir="ltr" class="mw-content-ltr"> |
|||
====Ground a part==== |
|||
</div> |
|||
<div lang="en" dir="ltr" class="mw-content-ltr"> |
|||
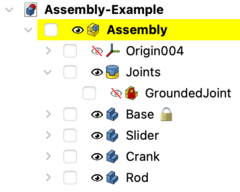
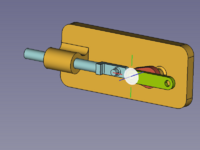
To keep the assembly at the desired position, the base part should be locked, or grounded as it is called here. Select the Base in the [[Tree_view|Tree view]] or in the [[3D_view|3D view]] and use the [[Image:Assembly_ToggleGrounded.svg|16px]] [[Assembly_ToggleGrounded|Toggle grounded]] command. This fixes the position of the Base in relation to the local coordinate system (LCS) of the Assembly container. This (also suffixes a lock icon to the label of the Base object and (before weekly build 0.22 - 37213)) adds a GroundedJoint object in the Joints container. |
|||
</div> |
|||
[[Image:Assembly_KinematicExample-03.png|200px]] |
|||
[[Image:Button_right.svg|16px|link=]] |
|||
[[Image:Assembly_KinematicExample-04.png|240px]] |
|||
<div lang="en" dir="ltr" class="mw-content-ltr"> |
|||
{{Caption|Expand the Joints container to find the GroundedJoint object}} |
|||
</div> |
|||
<div lang="en" dir="ltr" class="mw-content-ltr"> |
|||
(The GroundedJoint object cannot be unhidden and has no representation in the 3D view (before weekly build 0.22 - 37213)) |
|||
</div> |
|||
<div lang="en" dir="ltr" class="mw-content-ltr"> |
|||
====Apply joints==== |
|||
</div> |
|||
<div lang="en" dir="ltr" class="mw-content-ltr"> |
|||
A joint connects exactly two elements of different parts. They can optionally be selected before the desired joint tool is invoked (any number of selected elements other than two results in an empty selection).<br>The elements define the position and orientation of a LCS represented by a filled circle on the local XY plane and three lines along the local X (red), Y (green), and Z (blue) axes. |
|||
</div> |
|||
<div lang="en" dir="ltr" class="mw-content-ltr"> |
|||
* A Revolute joint between Base and Crank |
|||
</div> |
|||
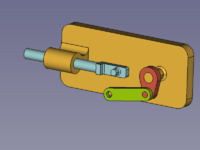
[[Image:Assembly_KinematicExample-05.png|200px]] |
|||
[[Image:Button_right.svg|16px|link=]] |
|||
[[Image:Assembly_KinematicExample-06.png|200px]] |
|||
<div lang="en" dir="ltr" class="mw-content-ltr"> |
|||
{{Caption|Selected elements + [[Image:Assembly_CreateJointRevolute.svg|16px]] [[Assembly_CreateJointRevolute|Create Revolute Joint]] → rearranged Crank}} |
|||
</div> |
|||
<div lang="en" dir="ltr" class="mw-content-ltr"> |
|||
* A Cylindrical joint between Base and Slider |
|||
</div> |
|||
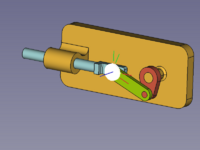
[[Image:Assembly_KinematicExample-07.png|200px]] |
|||
[[Image:Button_right.svg|16px|link=]] |
|||
[[Image:Assembly_KinematicExample-08.png|200px]] |
|||
<div lang="en" dir="ltr" class="mw-content-ltr"> |
|||
{{Caption|Selected elements +[[Image:Assembly_CreateJointCylindrical.svg|16px]] [[Assembly_CreateJointCylindrical|Create Cylindrical Joint]] → rearranged Slider}} |
|||
</div> |
|||
<div lang="en" dir="ltr" class="mw-content-ltr"> |
|||
* A Revolute joint between Crank and Rod |
|||
</div> |
|||
[[Image:Assembly_KinematicExample-09.png|200px]] |
|||
[[Image:Button_right.svg|16px|link=]] |
|||
[[Image:Assembly_KinematicExample-10.png|200px]] |
|||
<div lang="en" dir="ltr" class="mw-content-ltr"> |
|||
{{Caption|Selected elements + [[Image:Assembly_CreateJointRevolute.svg|16px]] [[Assembly_CreateJointRevolute|Create Revolute Joint]] → rearranged Rod}} |
|||
</div> |
|||
[[Image:Assembly_KinematicExample-11.png|200px]] |
|||
[[Image:Button_right.svg|16px|link=]] |
|||
[[Image:Assembly_KinematicExample-12.png|200px]] |
|||
<div lang="en" dir="ltr" class="mw-content-ltr"> |
|||
{{Caption|Now there are several joints in a line and we have to help the solver to find a sensible solution.<br>Click and drag the parts → into an easier to compute position.}} |
|||
</div> |
|||
<div lang="en" dir="ltr" class="mw-content-ltr"> |
|||
* A Cylindrical joint between Rod and Slider |
|||
</div> |
|||
[[Image:Assembly_KinematicExample-13.png|200px]] |
|||
[[Image:Button_right.svg|16px|link=]] |
|||
[[Image:Assembly_KinematicExample-14.png|200px]] |
|||
<div lang="en" dir="ltr" class="mw-content-ltr"> |
|||
{{Caption|Selected elements +[[Image:Assembly_CreateJointCylindrical.svg|16px]] [[Assembly_CreateJointCylindrical|Create Cylindrical Joint]] → finished Assembly}} |
|||
</div> |
|||
<div lang="en" dir="ltr" class="mw-content-ltr"> |
|||
In the finished assembly use the mouse pointer to drag the parts according to the used joints. |
|||
</div> |
|||
<div lang="en" dir="ltr" class="mw-content-ltr"> |
|||
====Drive the crank==== |
|||
</div> |
|||
<div lang="en" dir="ltr" class="mw-content-ltr"> |
|||
To control the layout of the assembly by the angle between the Base and the Crank we have to change the Revolute joint to a Fixed joint.<br> |
|||
To do so double-click on the Revolute object in the Tree view. In the dialog change Revolute to Fixed and change the Rotation value as desired (the movement should follow the mouse wheel action). |
|||
</div> |
|||
<div lang="en" dir="ltr" class="mw-content-ltr"> |
|||
Now only the Label of the joint was changed but not its Name! (Each change of the joint type will also change the Label) |
|||
</div> |
|||
<div lang="en" dir="ltr" class="mw-content-ltr"> |
|||
The Rotation property of the Fixed joint can be controlled via macro or from the python console (just copy and paste the following lines): |
|||
</div> |
|||
{{Code|code= |
|||
actuator = FreeCAD.ActiveDocument.getObject('Revolute') |
|||
for angle in range(0,361,10): |
|||
# A full rotation of the Crank in steps of 10° |
|||
actuator.Rotation = angle |
|||
App.activeDocument().recompute(None,True,True) |
|||
}} |
|||
Or alternatively: |
|||
{{Code|code= |
|||
actuator = FreeCAD.ActiveDocument.getObject('Revolute') |
|||
for angle in range(0,361,10): |
|||
# A full rotation of the Crank in steps of 10° |
|||
actuator.Rotation = angle |
|||
Gui.runCommand('Assembly_SolveAssembly',0) |
|||
}} |
|||
<div lang="en" dir="ltr" class="mw-content-ltr"> |
|||
(The Name of the joint is still Revolute while its Label has changed to Fixed, and the end of the range must be greater than 360 to also include this angle as a valid result.) |
|||
</div> |
|||
<div lang="en" dir="ltr" class="mw-content-ltr"> |
|||
</div> <!-- End of collapsible element for ... section. Do not remove! --> |
|||
</div> <!-- End of collapsible element for ... section. Do not remove! --> |
|||
</div> |
|||
Revision as of 16:22, 23 May 2024

Wprowadzenie
Środowisko pracy Złożenie to nowe wbudowane środowisko pracy FreeCAD.
Narzędzia
Funkcje eksperymentalne nie są domyślnie dostępne. Aby je włączyć, zapoznaj się z informacjami na stronie Dostrajanie parametrów.
Złożenie
Połączenia
Przykład
 Ten przykład jest tymczasowy i może zostać usunięty, gdy dostępne będą odpowiednie opisy / poradniki.
Ten przykład jest tymczasowy i może zostać usunięty, gdy dostępne będą odpowiednie opisy / poradniki.
Złożenie kinematyczne
Zespół kinematyczny, który ma zostać utworzony, składa się z czterech części: podstawy, suwaka, korby i pręta łączącego. Są one połączone czterema przegubami.
Złożone części: Podstawa (bursztynowy), Suwak (jasnoniebieski), Korba (czerwony), Korbowód (zielony)
Przygotowanie części
W tym przykładzie wszystkie części i zespół są tworzone w jednym dokumencie.
Od lewej do prawej: Podstawa, suwak, korba, korbowód.
Geometrie cylindryczne są równoległe lub prostopadłe, pozostałe kształty nie są istotne dla tego przykładu, chyba że powodują kolizje. Mając to na uwadze, wymodeluj własne kształty.
Dodawanie złożenia głównego
Utwórz złożenie dodaje do dokumentu złożenie główne. (narzędzie to może również dodać podzespół do istniejącego wybranego złożenia)
Tree view of Parts and Assembly in a document
Move the parts into the assembly container
In the Tree view drag and drop the parts on the Assembly object. Now they can be handled by the Assembly's solver.
The Parts are in the Assembly container now
Ground a part
To keep the assembly at the desired position, the base part should be locked, or grounded as it is called here. Select the Base in the Tree view or in the 3D view and use the Toggle grounded command. This fixes the position of the Base in relation to the local coordinate system (LCS) of the Assembly container. This (also suffixes a lock icon to the label of the Base object and (before weekly build 0.22 - 37213)) adds a GroundedJoint object in the Joints container.
Expand the Joints container to find the GroundedJoint object
(The GroundedJoint object cannot be unhidden and has no representation in the 3D view (before weekly build 0.22 - 37213))
Apply joints
A joint connects exactly two elements of different parts. They can optionally be selected before the desired joint tool is invoked (any number of selected elements other than two results in an empty selection).
The elements define the position and orientation of a LCS represented by a filled circle on the local XY plane and three lines along the local X (red), Y (green), and Z (blue) axes.
- A Revolute joint between Base and Crank
Selected elements + Create Revolute Joint → rearranged Crank
- A Cylindrical joint between Base and Slider
Selected elements + Create Cylindrical Joint → rearranged Slider
- A Revolute joint between Crank and Rod
Selected elements + Create Revolute Joint → rearranged Rod
Now there are several joints in a line and we have to help the solver to find a sensible solution.
Click and drag the parts → into an easier to compute position.
- A Cylindrical joint between Rod and Slider
Selected elements + Create Cylindrical Joint → finished Assembly
In the finished assembly use the mouse pointer to drag the parts according to the used joints.
Drive the crank
To control the layout of the assembly by the angle between the Base and the Crank we have to change the Revolute joint to a Fixed joint.
To do so double-click on the Revolute object in the Tree view. In the dialog change Revolute to Fixed and change the Rotation value as desired (the movement should follow the mouse wheel action).
Now only the Label of the joint was changed but not its Name! (Each change of the joint type will also change the Label)
The Rotation property of the Fixed joint can be controlled via macro or from the python console (just copy and paste the following lines):
actuator = FreeCAD.ActiveDocument.getObject('Revolute')
for angle in range(0,361,10):
# A full rotation of the Crank in steps of 10°
actuator.Rotation = angle
App.activeDocument().recompute(None,True,True)
Or alternatively:
actuator = FreeCAD.ActiveDocument.getObject('Revolute')
for angle in range(0,361,10):
# A full rotation of the Crank in steps of 10°
actuator.Rotation = angle
Gui.runCommand('Assembly_SolveAssembly',0)
(The Name of the joint is still Revolute while its Label has changed to Fixed, and the end of the range must be greater than 360 to also include this angle as a valid result.)
- Złożenie: Utwórz złożenie, Wstaw łącze, Rozwiąż złożenie, Utwórz widok rozłożenia, Eksportuj do pliku ASMT
- Połaczenia: Włącz / wyłącz zakotwienie, Utwórz połączenie stałe, Utwórz połączenie obrotowe, Utwórz połączenie cylindryczne, Utwórz połączenie przesuwne, Utwórz przegub kulowy, Utwórz połączenie dystansowe, Utwórz połączenie zębatki i koła zębatego, Utwórz połączenie śrubowe, Utwórz połączenie kół zębatych, Utwórz połączenie pasowe
- Jak zacząć
- Instalacja: Pobieranie programu, Windows, Linux, Mac, Dodatkowych komponentów, Docker, AppImage, Ubuntu Snap
- Podstawy: Informacje na temat FreeCAD, Interfejs użytkownika, Profil nawigacji myszką, Metody wyboru, Nazwa obiektu, Edytor ustawień, Środowiska pracy, Struktura dokumentu, Właściwości, Pomóż w rozwoju FreeCAD, Dotacje
- Pomoc: Poradniki, Wideo poradniki
- Środowiska pracy: Strona Startowa, Złożenie, BIM, CAM, Rysunek Roboczy, MES, Inspekcja, Siatka, OpenSCAD, Część, Projekt Części, Punkty, Inżynieria Wsteczna, Robot, Szkicownik, Arkusz Kalkulacyjny, Powierzchnia 3D, Rysunek Techniczny, Test Framework