Surface Filling/pl: Difference between revisions
(Created page with "* {{PropertyView|Punkty kontrolne|Bool}}: wartość domyślna to {{FALSE/pl}}, Jeśli ustawiono {{TRUE/pl}}, wyświetlona zostanie nakładka z punktami kontrolnymi krzywej.") |
(Created page with "===Widok===") |
||
| Line 107: | Line 107: | ||
* {{PropertyData|Maximum Segments|Integer}}: maximum number of segments, it defaults to {{Value|9}}. |
* {{PropertyData|Maximum Segments|Integer}}: maximum number of segments, it defaults to {{Value|9}}. |
||
<span id="View"></span> |
|||
=== |
===Widok=== |
||
{{TitleProperty|Base}} |
{{TitleProperty|Base}} |
||
Revision as of 13:53, 23 January 2024
|
|
| Menu location |
|---|
| Surface → Filling |
| Workbenches |
| Powierzchnia 3D |
| Default shortcut |
| None |
| Introduced in version |
| 0.17 |
| See also |
| None |
Opis
Polecenie Wypełnianie tworzy powierzchnię z serii połączonych krawędzi granicznych. Krzywizna powierzchni może być dodatkowo kontrolowana przez krawędzie i wierzchołki, które nie są krawędziami granicznymi, oraz powierzchnię podpierającą.
Geometria bazowa może należeć do krzywych utworzonych za pomocą środowiska Rysunek Roboczy lub Szkicownik, ale może również należeć do obiektów bryłowych, takich jak te utworzone za pomocą środowiska Część lub Projekt Części.
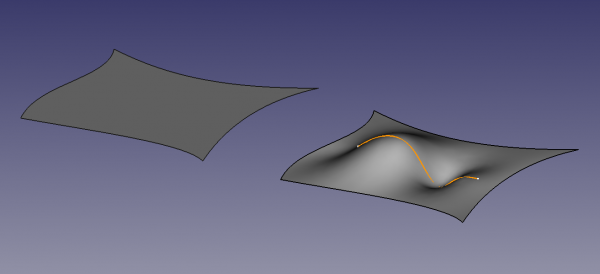
Dwie wypełnione powierzchnie ograniczone czterema krawędziami znajdującymi się na płaszczyźnie XY. Powierzchnia po prawej stronie jest dodatkowo kontrolowana przez krawędź niebędącą granicą.
Użycie
- Naciśnij przycisk
Wypełnianie.
- Otworzy się panel zadań Granice. Zobacz dostępne Opcje.
- Wybierz dwie lub więcej krawędzi w oknie widoku 3D:
- W tym momencie nie ma potrzeby naciskania przycisku Dodaj krawędź w sekcji Granice.
- Krawędzie muszą być wybrane w odpowiedniej kolejności.
- Krawędzie muszą być połączone, ale cała granica nie musi być zamknięta.
- Kompletna granica nie powinna się przecinać.
- W przypadku okrągłej granicy 360° można wybrać dwie półokrągłe krawędzie.
- Podgląd ostatecznego kształtu zostanie wyświetlony po wybraniu wystarczającej ilości prawidłowej geometrii.
- Opcjonalnie wybierz Powierzchnia pomocnicza. Zobacz Przykład.
- Opcjonalnie wybierz jedno lub więcej Wiązania krawędziowe.
- Opcjonalnie wybierz jedno lub więcej Wiązań wierzchołków.
- Naciśnij przycisk OK.
Opcje
- In the Boundaries section a support surface and boundary edges can specified:
- Press the Support surface button and select a face in the 3D view to add a support surface.
- Press the Add edge button once to start selecting boundary edges in the 3D view.
- There are several ways to deselect boundary edges:
- Press the Remove edge button once to start deselecting edges in the 3D view.
- Select an edge in the list and press Delete.
- Right-click an edge in the list and select Remove from the context menu.
- In the Edge constraints section non-boundary edges can be specified:
- The selection options are similar to those for boundary edges.
- In the Vertex constraints section non-boundary vertices can be specified:
- The selection options are similar to those for boundary edges.
- Press Esc or the Cancel button to abort the operation.
Example
The Support surface acts as an additional constraint for the surface. The following simple example will give you an idea how this works:
- In the
Part Workbench create a
cylinder and set its DANEAngle to
180°. - Switch to the
Surface Workbench and press the
Filling button.
- Select the two semi-circular edges and the two straight edges that connect them.
- The result matches the four boundary edges, but the inner shape is quite different from the cylindrical face.
- Edit the Surface object and for the Support surface select the cylindrical face.
- The modified shape matches the cylindrical face much more closely.
Properties
A Surface Filling (Surface::Filling class) is derived from the basic Part Feature (Part::Feature class, through the Part::Spline subclass), therefore it shares all the latter's properties.
In addition to the properties described in Part Feature, the Surface Filling has the following properties in the property editor.
Data
Filling
- DANEBoundary Edges (
LinkSubList): boundary edges; C0 is required for edges without a corresponding face. - DANEBoundary Faces (
StringList): - DANEBoundary Order (
IntegerList): order of constraint on boundary faces;0,1, and2are possible. - DANEUnbound Edges (
LinkSubList): unbound constraint edges; C0 is required for edges without a corresponding face. - DANEUnbound Faces (
StringList): - DANEUnbound Order (
IntegerList): order of constraint on unbound faces;0,1, and2are possible. - DANEFree Faces (
LinkSubList): free constraint on a face. - DANEFree Order (
IntegerList): order of constraint on free faces. - DANEPoints (
LinkSubList): constraint points on surface. - DANEInitial Face (
LinkSub): initial surface to use. - DANEDegree (
Integer): starting degree, it defaults to3. - DANEPoints On Curve (
Integer): number of points on an edge for constraint. - DANEIterations (
Integer): number of iterations, it defaults to2. - DANEAnisotropy (
Bool): it defaults tofalse. - DANETolerance2d (
Float): 2D tolerance, it defaults to0.0. - DANETolerance3d (
Float): 3D tolerance, it defaults to0.0. - DANETol Angular (
Float): G1 tolerance, it defaults to0.01. - DANETol Curvature (
Float): G2 tolerance, it defaults to0.10. - DANEMaximum Degree (
Integer): maximum curve degree, it defaults to8. - DANEMaximum Segments (
Integer): maximum number of segments, it defaults to9.
Widok
Base
- WIDOKPunkty kontrolne (
Bool): wartość domyślna toFAŁSZ, Jeśli ustawionoPRAWDA, wyświetlona zostanie nakładka z punktami kontrolnymi krzywej.
Tworzenie skryptów
Zobacz również: FreeCAD podstawy tworzenia skryptów.
Narzędzie Wypełnienie powierzchni może być używane w makrodefinicjach i z konsoli Python poprzez dodanie obiektu Surface::Filling.
- Krawędzie, które mają być użyte do zdefiniowania powierzchni, muszą być przypisane jako LinkSubList do właściwości
BoundaryEdgesobiektu. - Pomocnicze krawędzie i wierzchołki muszą być przypisane jako LinkSubLists do właściwości
UnboundEdgesiPointsobiektu. - Wszystkie obiekty z krawędziami muszą zostać obliczone, zanim będą mogły zostać użyte jako dane wejściowe dla właściwości obiektu Filling.
import FreeCAD as App
import Draft
doc = App.newDocument()
a = App.Vector(-20, -20, 0)
b = App.Vector(-18, 25, 0)
c = App.Vector(60, 26, 0)
d = App.Vector(33, -20, 0)
points1 = [a, App.Vector(-20, -8, 0), App.Vector(-17, 7, 0), b]
obj1 = Draft.make_bspline(points1)
points2 = [b, App.Vector(0, 25, 0), c]
obj2 = Draft.make_bspline(points2)
points3 = [c, App.Vector(37, 4, 0), d]
obj3 = Draft.make_bspline(points3)
points4 = [d, App.Vector(-2, -18, 0), a]
obj4 = Draft.make_bspline(points4)
doc.recompute()
surf = doc.addObject("Surface::Filling", "Surface")
surf.BoundaryEdges = [(obj1, "Edge1"),
(obj2, "Edge1"),
(obj3, "Edge1"),
(obj4, "Edge1")]
doc.recompute()
# ---------------------------------------------------------
points_spl = [App.Vector(-10, 0, 2),
App.Vector(4, 0, 7),
App.Vector(18, 0, -5),
App.Vector(25, 0, 0),
App.Vector(30, 0, 0)]
aux_edge = Draft.make_bspline(points_spl)
doc.recompute()
surf.UnboundEdges = [(aux_edge, "Edge1")]
doc.recompute()
# ---------------------------------------------------------
aux_v1 = Draft.make_line(App.Vector(-13, -12, 5),
App.Vector(-13, -12, -5))
aux_v2 = Draft.make_line(App.Vector(-3, 18, 5),
App.Vector(-3, 18, -5))
doc.recompute()
surf.Points = [(aux_v1, "Vertex2"),
(aux_v2, "Vertex1")]
doc.recompute()
- Jak zacząć
- Instalacja: Pobieranie programu, Windows, Linux, Mac, Dodatkowych komponentów, Docker, AppImage, Ubuntu Snap
- Podstawy: Informacje na temat FreeCAD, Interfejs użytkownika, Profil nawigacji myszką, Metody wyboru, Nazwa obiektu, Edytor ustawień, Środowiska pracy, Struktura dokumentu, Właściwości, Pomóż w rozwoju FreeCAD, Dotacje
- Pomoc: Poradniki, Wideo poradniki
- Środowiska pracy: Strona Startowa, Architektura, Assembly, CAM, Rysunek Roboczy, MES, Inspekcja, Siatka, OpenSCAD, Część, Projekt Części, Punkty, Inżynieria Wsteczna, Robot, Szkicownik, Arkusz Kalkulacyjny, Powierzchnia 3D, Rysunek Techniczny, Test Framework