Developing FreeCAD with GitKraken/pl: Difference between revisions
(Created page with "Więcej informacji można znaleźć w podręczniku GitKraken [https://support.gitkraken.com/start-here/guide/ Przewodnik dla początkujących].") |
(Created page with "{| class="wikitable" |- |+ ''Local'' wskazuje komputer lokalny |- | Local master || Lokalna gałąź głównej gałęzi FreeCAD, oznaczona ''niebieską'' linią na zrzucie ekranu.") |
||
| Line 69: | Line 69: | ||
{| class="wikitable" |
{| class="wikitable" |
||
|- |
|- |
||
|+ ''Local'' |
|+ ''Local'' wskazuje komputer lokalny |
||
|- |
|- |
||
| Local master || |
| Local master || Lokalna gałąź głównej gałęzi FreeCAD, oznaczona ''niebieską'' linią na zrzucie ekranu. |
||
The item is highlighted in '''green''', meaning that the branch is currently active ({{incode|git checkout}}). |
The item is highlighted in '''green''', meaning that the branch is currently active ({{incode|git checkout}}). |
||
Revision as of 10:35, 12 November 2023
Przedmowa
FreeCAD używa Git do zarządzania swoim kodem źródłowym. Niniejszy dokument stanowi pobieżne wprowadzenie do GitKraken, graficznego interfejsu użytkownika Git. GitKraken jest zastrzeżonym oprogramowaniem, które jest bezpłatne do użytku niekomercyjnego. Nie potrzebujesz GitKrakena do tworzenia kodu dla FreeCAD, ale wielu programistów lubi go i uważa za przydatny do zarządzania ich rozwojem. FreeCAD nie popiera GitKraken, ale mamy nadzieję, że przewodnik taki jak ten pokaże użytkownikom, jak łatwo jest skonfigurować środowisko programistyczne i zachęci więcej osób do wniesienia wkładu.
Więcej informacji na temat ogólnego korzystania z Git z linii poleceń można znaleźć na stronie Zarządzanie kodem źródłowym oraz w książce online Pro Git. Aby skompilować FreeCAD zobacz stronę Kompilacja.
Wprowadzenie
Git to potężny system kontroli wersji powszechnie używany do śledzenia rozwoju kodu komputerowego. Mimo że jest to złożony system, zwykle potrzebne są tylko podstawowe informacje na temat jego działania i znajomość kilku poleceń terminala. Graficzny interfejs użytkownika (GUI) ułatwia naukę. GitKraken to zastrzeżony program, który jest darmowy do użytku niekomercyjnego i działa na platformie Electron, co oznacza, że jest wieloplatformowy i może być używany tak samo w systemach Linux, MacOS i Windows.
Konfiguracja Git development
Istnieją różne sposoby pobrania GitKraken w zależności od systemu operacyjnego. W dystrybucjach Linuksa czasami można go pobrać z menedżera pakietów.
- Pobierz GitKraken.
- W przeglądarce internetowej przejdź do strony:
https://github.com/FreeCAD/FreeCAD.
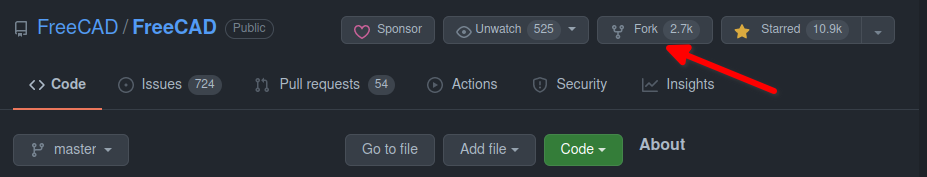
- Kiknij na Fork. Spowoduje to sklonowanie repozytorium
FreeCAD/FreeCADdo własnego konta. Innymi słowy, adres URL dostępu do forka będzie następujący:https://github.com/GITHUBUSERNAME/FreeCAD.git
- Otwórz GitKraken, przejdź do menu File → Clone Repo, kolejnie wprowadź adres.
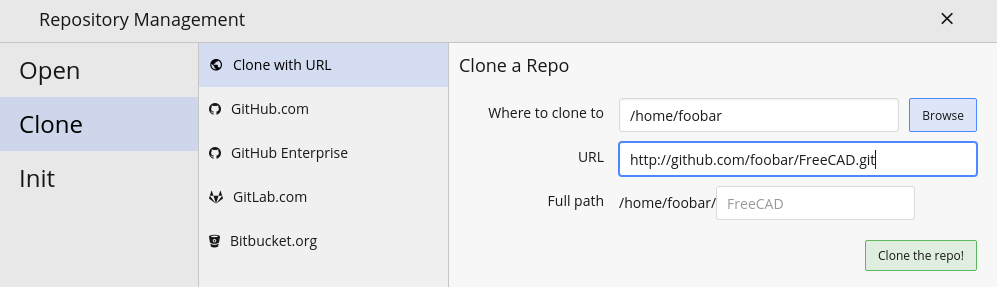
- GitKraken wykona teraz operację
git clonena twoim osobistym repozytorium. Zapoznaj się z różnicą między zdalnym repozytorium origin vs. upstream. Essentially, Twój fork FreeCAD jest repozytoriumorigin, podczas gdy oficjalne repozytorium FreeCAD jestupstream. Teraz musisz odpowiednio ustawić upstream. - Znajdź pasek boczny w Gitkraken. Znajduje się tam sekcja Lokalna i Zdalna. Sekcja Local odnosi się do lokalnych oddziałów. Sekcja Remote odnosi się do zdalnych repozytoriów i ich gałęzi. Dodajmy repozytorium FreeCAD jako zdalne. W sekcji Remote kliknij przycisk +. ( jak pokazano na poniższym obrazku)
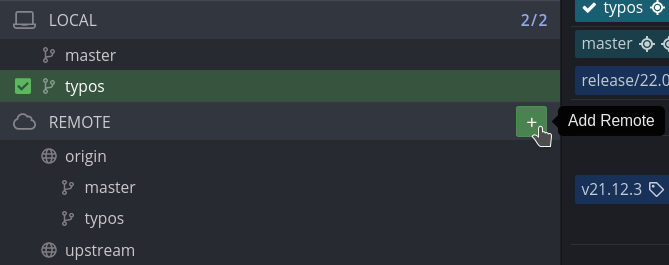
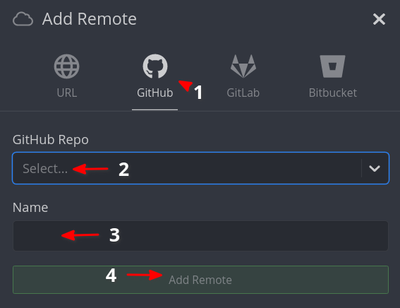
- Otworzy się okno dialogowe Add Remote. Kliknij symbol Github (1). W polu Github repo (2) znajdź
FreeCAD/FreeCADi kliknij na niego. W polu Name wpiszupstream. Następnie kliknij przycisk Add Button.
- Okno dialogowe zostanie zamknięte i nastąpi powrót do głównego interfejsu GitKrakena. Tym razem znajdź sekcję Local na pasku bocznym. Kliknij dwukrotnie gałąź
master, aby się do niej przełączyć. W wierszu poleceń jest to równoważnegit checkout master
- Kliknij ikonę "Push" w prawym górnym rogu interfejsu. Spowoduje to wypchnięcie Local master do Remote origin master
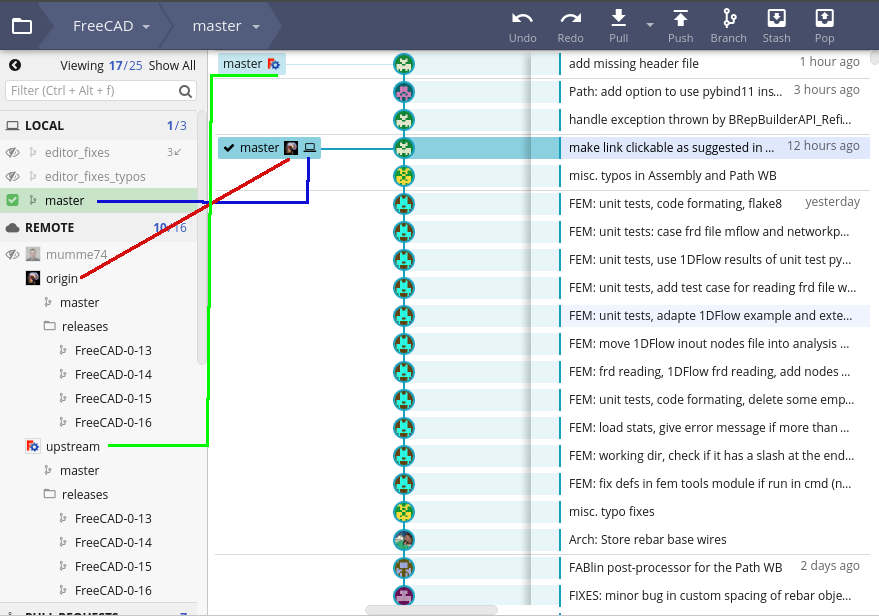
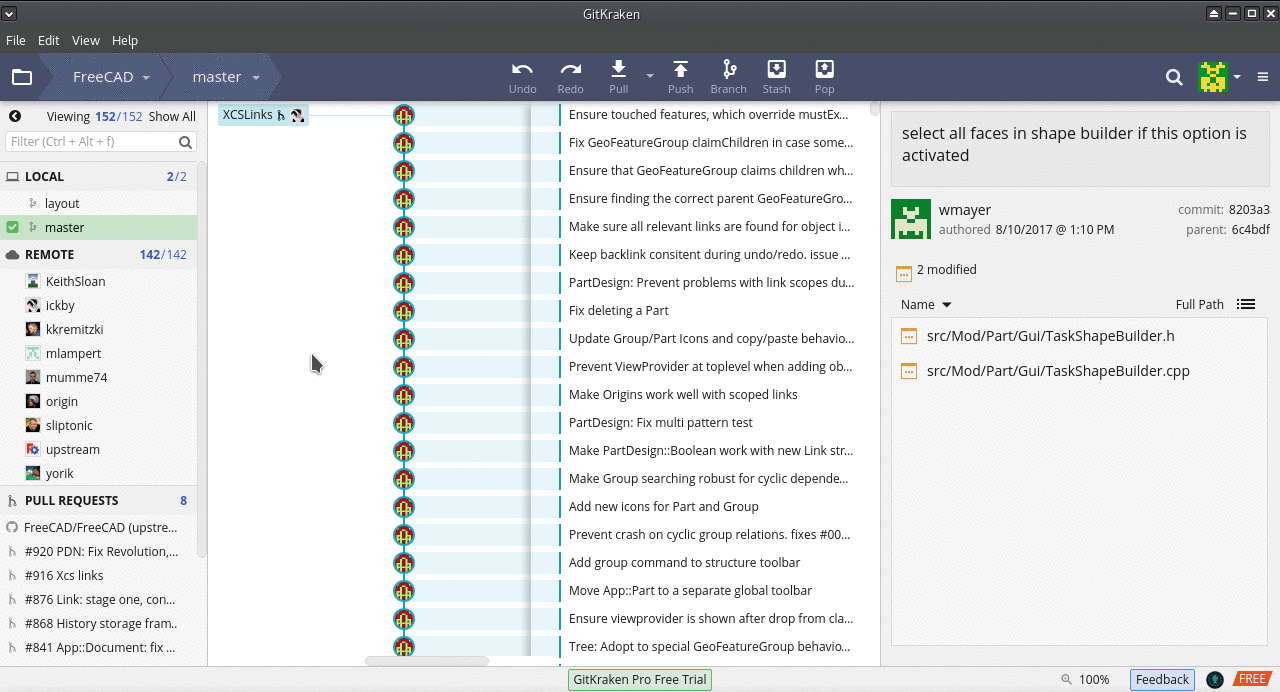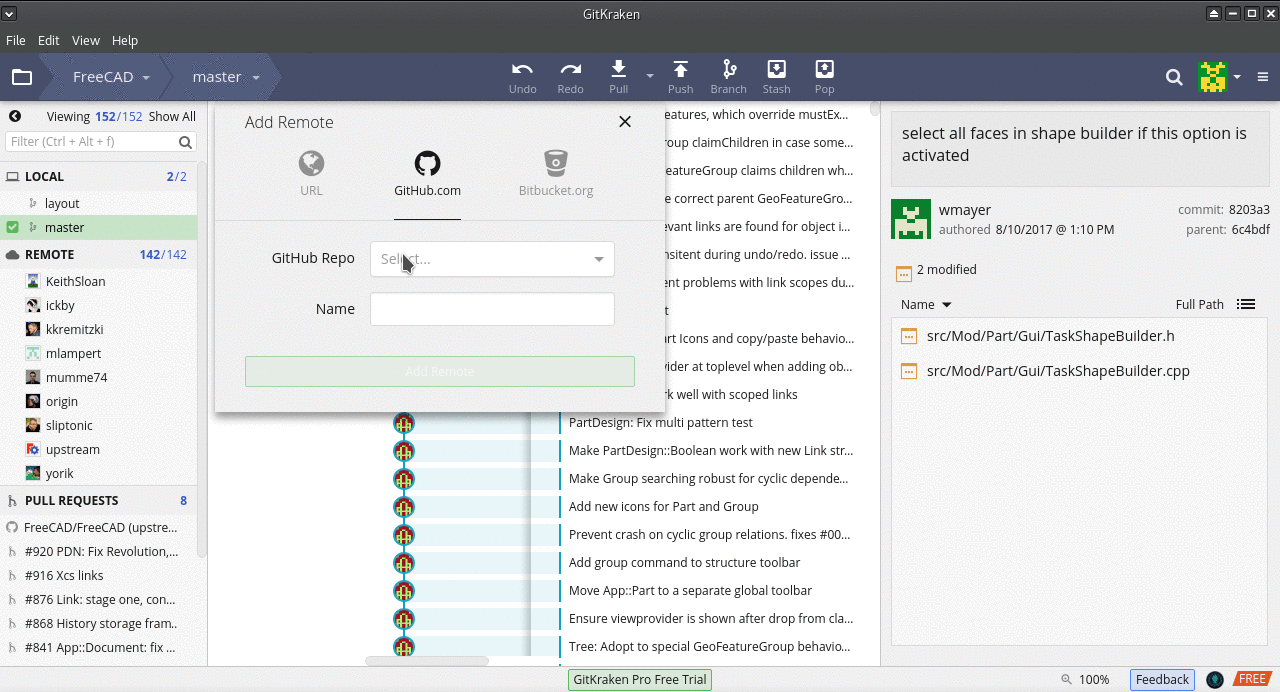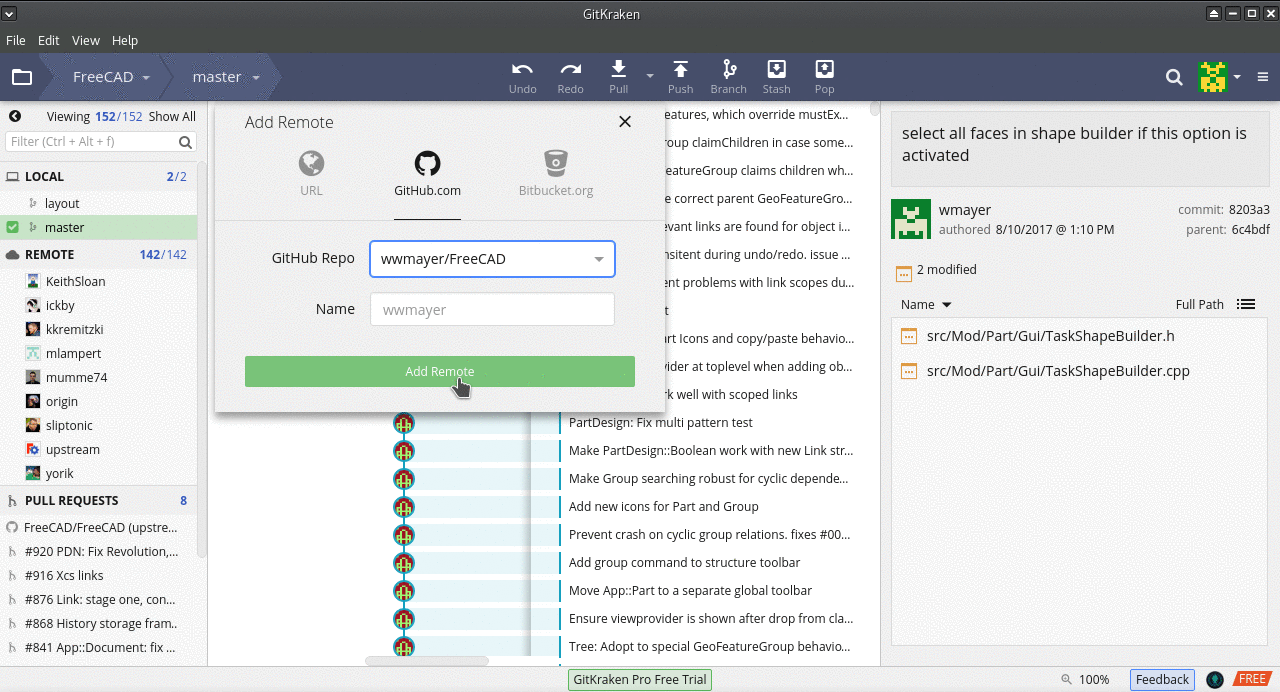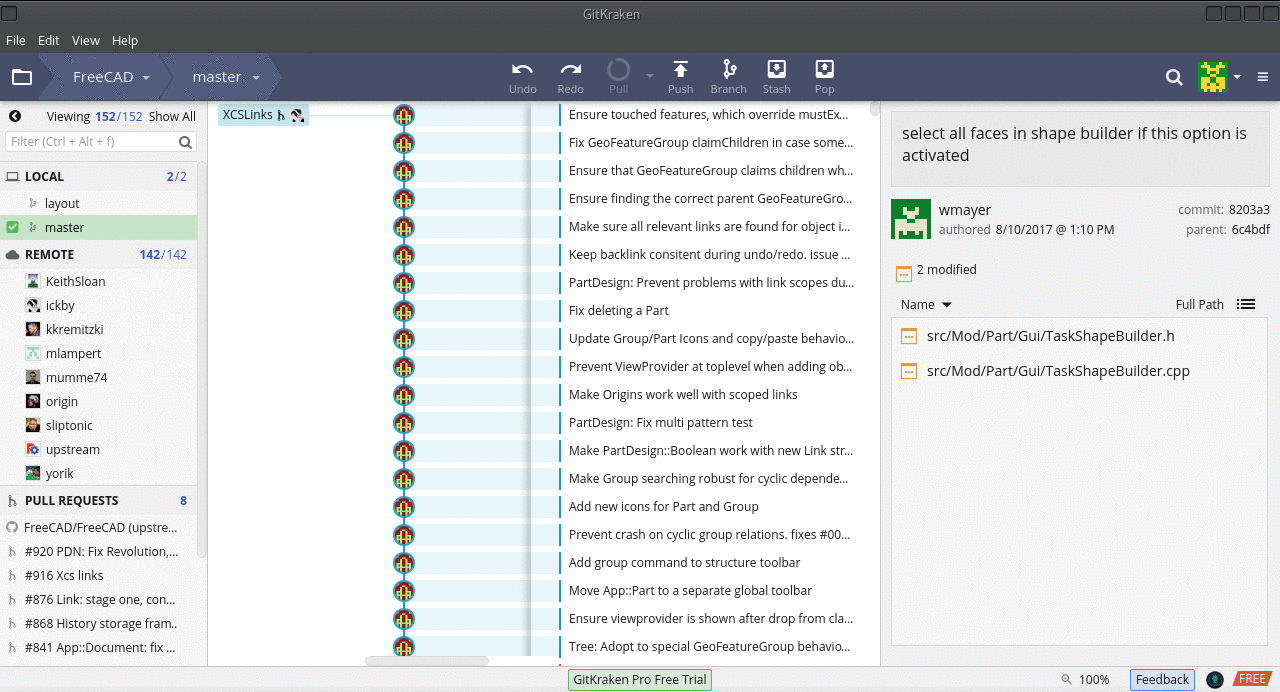
Interfejs GitKraken
Więcej informacji można znaleźć w podręczniku GitKraken Przewodnik dla początkujących.
| Local master | Lokalna gałąź głównej gałęzi FreeCAD, oznaczona niebieską linią na zrzucie ekranu.
The item is highlighted in green, meaning that the branch is currently active ( |
| Local <branch-name> | Any other branches on your local machine. In the screenshot you can see branches called editor_fixes and editor_fixes_typos
|
| Remote upstream | The official FreeCAD repository https://github.com/FreeCAD/FreeCAD, indicated by the green line in the screenshot.
|
| Remote origin | Your personal fork of FreeCAD, https://github.com/YourGitHubUsername/FreeCAD, indicated by the red line in the screenshot.
|
GitKraken interface showing three local branches including a local master, and remote origin and upstream repositories, each of which have a master and release branches.
In the image, the remote the Local master and Remote origin master branches are three commits behind the Remote upstream master, that is, the official FreeCAD source code. This is indicated by the icons being three steps behind in the chain that represents the commit history of the master branch. See Rebasing to update the branches that are behind.
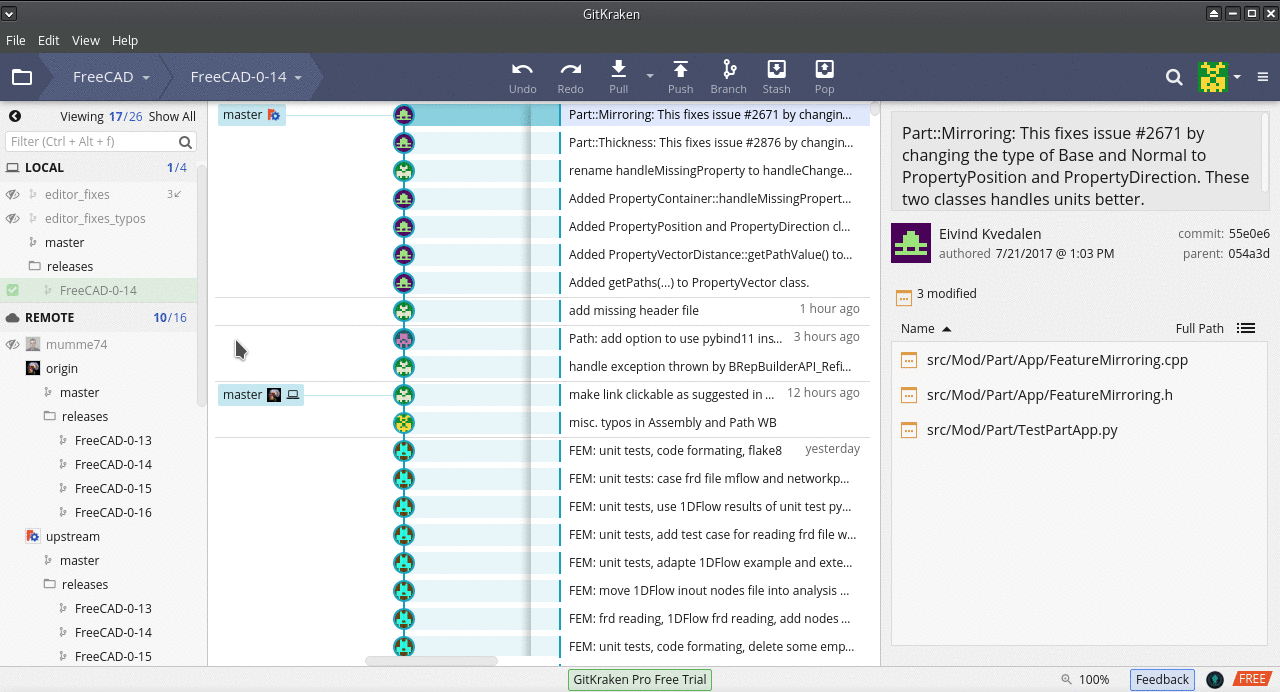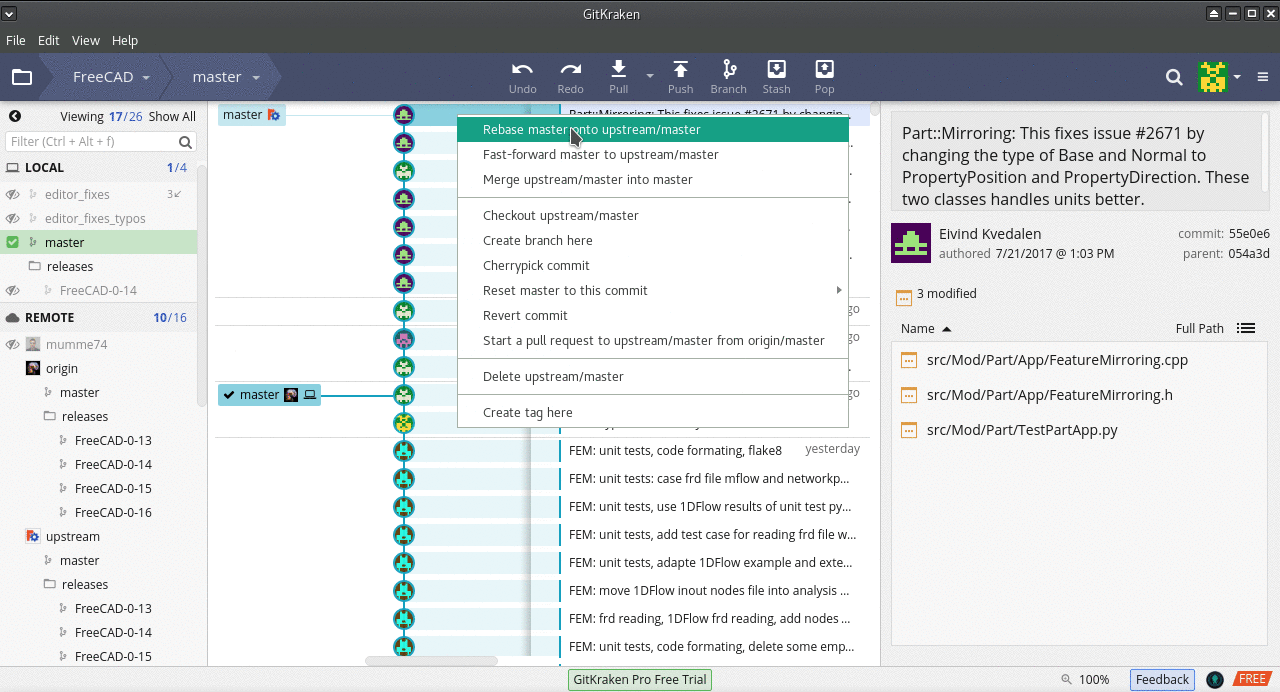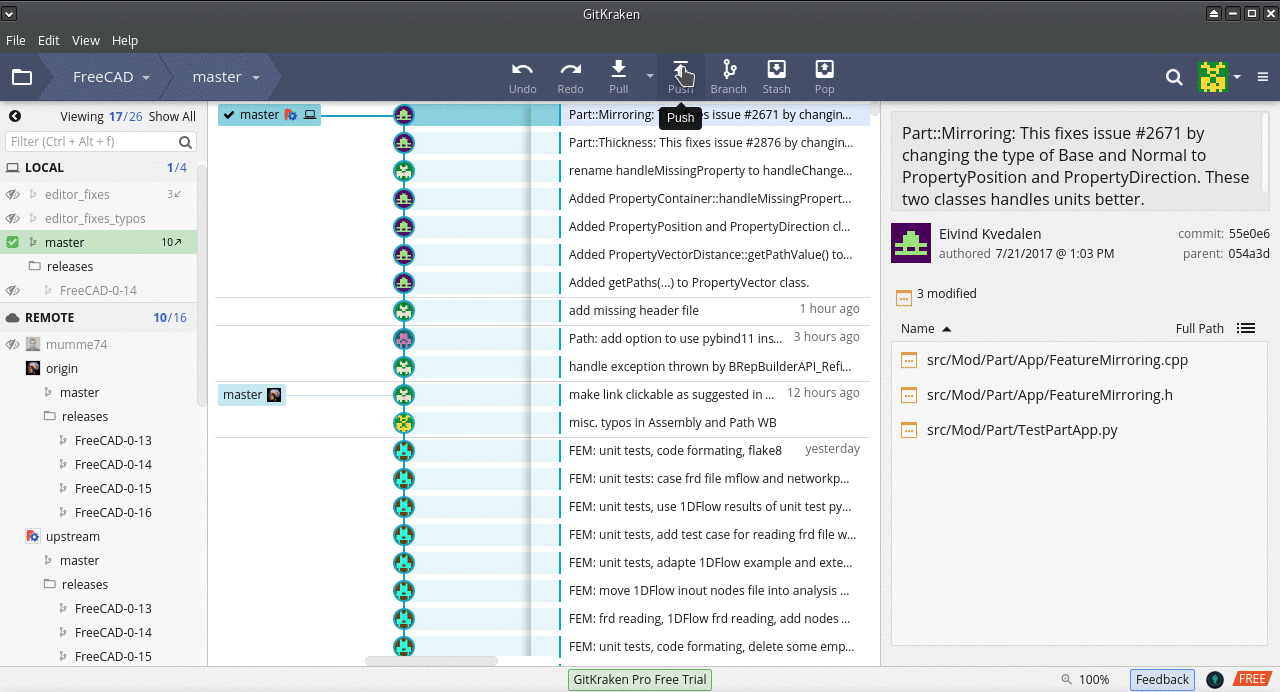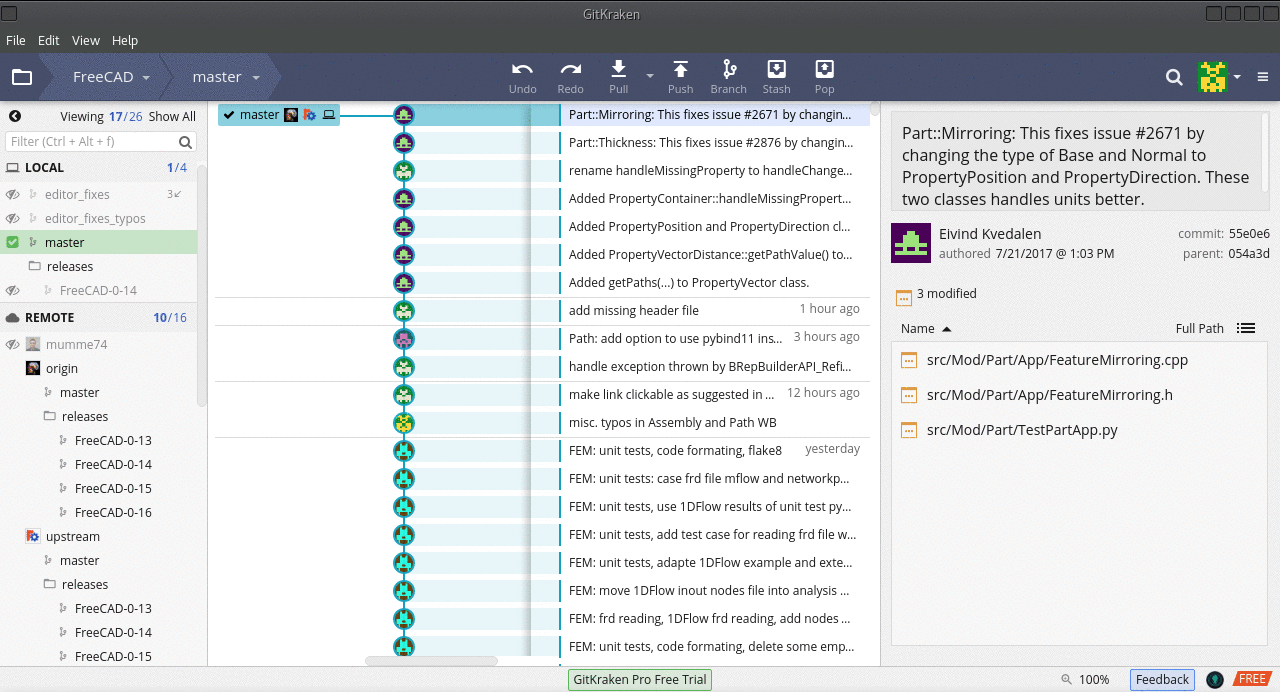
Rebasing
- Checkout the Local master branch by double clicking on it (
git checkout master) - Move the mouse to the last upstream commit, right click, and choose Rebase master onto upstream/master (
git pull upstream master) - Now press the Push button (
git push origin master). This pushes from your Local master to the Remote origin master.
Rebasing a local master updates it so that it matches the contents of the upstream master.
Branches
Branches are a feature that makes Git powerful compared to other revision systems. Branches aren't complete forks, but rather define snapshots where a version of the code starts diverging from the master branch. Whenever you want to modify the FreeCAD code, first create a branch, then make changes, and then merge your commits back to the master branch. With Git it is simple to create, merge and delete branches when you no longer need them. Please read Branching and Merging to understand more about this process in GitKraken.
- Make sure you currently have the master branch active (double click on it,
git checkout master). In GitKraken the Local master branch should be highlighted in green. - Click the Branch button to create a new branch and enter its new name (
git checkout -b new-name-of-your-branch).
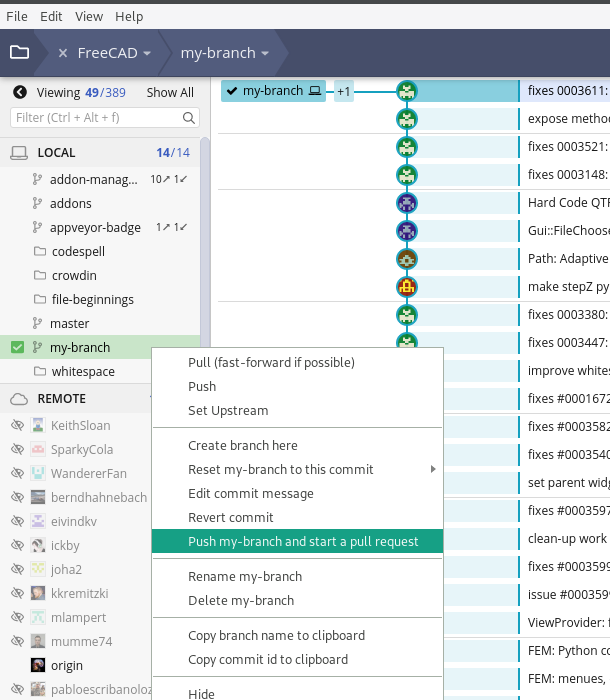
Making pull requests
Pull requests (PRs) are necessary to merge the code in a branch in your local repository with the code in the upstream repository. To summarize the process, once you've modified your branch, you need to push it to your GitHub fork (origin, https://github.com/GITHUBUSERNAME/FreeCAD.git), and from there make a pull request to upstream. GitKraken saves you some clicks to easily create pull requests instead of using GitHub's interface.
Steps in GitKraken:
- Find you local branch on the interface and make sure it's active (double click on it).
- Right click the branch name and find the option to Push <your-branch-name> and start a pull request.
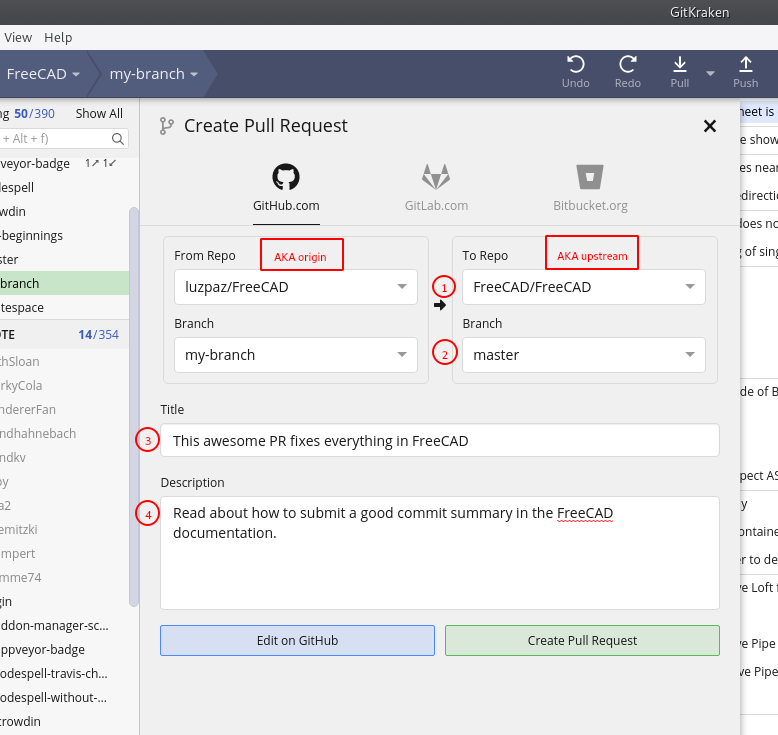
- GitKraken will open a dialog that asks you to confirm the repository which your branch will use to pull and push. It will then push your local branch to that remote repository.
- GitKraken will ask you what you want to call the remote branch. The default name is the same name that the branch has locally in your computer.
- GitKraken then opens up another dialog asking the repositories and branches to merge, and the direction (from and to).
- You normally want to merge from the remote origin <your-branch-name> (
GITHUBUSERNAME/FreeCAD) to the remote upstream master branch (FreeCAD/FreeCAD). Be sure to enter a good title for the pull request, and write a more descriptive paragraph if your changes are significant. Consult the official documentation of GitKraken for more information.
Resolving merge conflicts
GitKraken has a special merge conflict tool that is only accessible in the GitKraken Pro version. However, there are workarounds to use external tools for merging.
- GitKraken compatible external merge tools: Beyond Compare, FileMerge, Kaleidoscope, KDiff, Araxis, P4Merge
- If none of the above options work for you, it's possible to specify External merge and diff tools within the configuration file
~/.gitconfigin your user's home directory.
Squashing commits
As a revision control system Git encourages making many commits to keep track of your changes; however, if you have too many small changes the commit history may look a bit messy. Squashing is condensing various commits into only one commit. From the GitKraken manual, squashing is available for commits that meet the following requirements:
- You need to select at least two commits to squash.
- The youngest commit, by commit date, is also the current HEAD commit.
- Genealogically consecutive.
- Chronologically consecutive.
- The oldest commit in the list has a parent.
If all these conditions are met, the Squash option appears when you right click the commit node. See Squash.gif
Following other FreeCAD repositories
You can use GitKraken to follow the personal FreeCAD forks of other developers; in this way you can see how they write code and commit changes to their own branches before they submit pull requests to the upstream FreeCAD/FreeCAD repository.
- In the left side panel next to the Remote category, press the + sign.
- A dialogue will come up to enter the name of the repository that you want to add. Recommended remotes are from the main FreeCAD developers and known contributors: wmayer, yorikvanhavre, ickby, sliptonic, kkremitzki, etc.
- Press Add Remote.
Now whenever new commits are made, or branches are rebased, by the authors of those repositories, you will see their commit history in a graphical way.
Related
- Getting started
- Installation: Download, Windows, Linux, Mac, Additional components, Docker, AppImage, Ubuntu Snap
- Basics: About FreeCAD, Interface, Mouse navigation, Selection methods, Object name, Preferences, Workbenches, Document structure, Properties, Help FreeCAD, Donate
- Help: Tutorials, Video tutorials
- Workbenches: Std Base, Arch, Assembly, CAM, Draft, FEM, Inspection, Mesh, OpenSCAD, Part, PartDesign, Points, Reverse Engineering, Robot, Sketcher, Spreadsheet, Surface, TechDraw, Test Framework
- Hubs: User hub, Power users hub, Developer hub