Property editor/de: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| (15 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 8: | Line 8: | ||
{{TOCright}} |
{{TOCright}} |
||
<span id="Introduction"></span> |
|||
== Einführung == |
== Einführung == |
||
Der [[property editor/de|Eigenschafteneditor]] erscheint wenn der {{MenuCommand|Modell}} |
Der [[property editor/de|Eigenschafteneditor]] erscheint wenn der Reiter {{MenuCommand|Modell}} der |
||
[[combo_view/de|Combo |
[[combo_view/de|Combo-Ansicht]] auf der [[interface/de|Oberfläche]] aktiv ist; er ermöglicht die Verwaltung der öffentlich zugänglichen Eigenschaften der Objekte im Dokument. |
||
Generell ist der Eigenschafteneditor dazu gedacht, ein Objekt |
Generell ist der Eigenschafteneditor dazu gedacht, nur ein Objekt zur Zeit zu behandeln. Die im Eigenschafteneditor angezeigten Werte gehören zum ausgewählten Objekt des aktiven Dokuments. Es gibt jedoch einige Eigenschaften, wie Farben, die für viele ausgewählte Objekte gleichzeitig gesetzt werden können. Wenn kein Element ausgewählt wurde, bleibt der Eigenschafteneditor leer. |
||
Nicht alle Eigenschaften können immer geändert werden; je nach dem spezifischen Status der Eigenschaft sind einige von ihnen unsichtbar (nicht aufgeführt) oder schreibgeschützt (nicht bearbeitbar). |
Nicht alle Eigenschaften können immer geändert werden; je nach dem spezifischen Status der Eigenschaft sind einige von ihnen unsichtbar (nicht aufgeführt) oder schreibgeschützt (nicht bearbeitbar). |
||
{{TOCright}} |
{{TOCright}} |
||
[[File:FreeCAD_Property_editor_empty.png]] |
[[File:FreeCAD_Property_editor_empty.png]] |
||
{{Caption|Leerer |
{{Caption|Leerer Eigenschafteneditor, wenn kein Objekt ausgewählt ist.}} |
||
<span id="Property_types"></span> |
|||
==Eigenschaftentypen== |
==Eigenschaftentypen== |
||
Eine Eigenschaft ist eine Information wie eine Zahl oder eine Textzeichenfolge, die an ein FreeCAD |
Eine Eigenschaft ist eine Information wie eine Zahl oder eine Textzeichenfolge, die an ein FreeCAD-Dokument oder ein Objekt im Dokument angehängt ist. |
||
Benutzerdefinierte [[Scripted objects/de| |
Benutzerdefinierte [[Scripted objects/de|skriptgenerierte Objekte]] können jeden der im Basissystem definierten Eigenschaftstypen verwenden. Die vollständige Liste findet man unter [[Property/de|Objekteigenschaften]]. |
||
Einige der am häufigsten verwendeten Eigenschaftstypen sind: |
Einige der am häufigsten verwendeten Eigenschaftstypen sind: |
||
{{Code|code= |
{{Code|code= |
||
App::PropertyBool |
App::PropertyBool |
||
| Line 41: | Line 45: | ||
}} |
}} |
||
Verschiedene Objekte können unterschiedliche Typen von Eigenschaften haben. Viele Objekte haben jedoch die gleichen Typen, weil sie von der gleichen internen Klasse abgeleitet sind. Zum Beispiel haben die meisten Objekte, die geometrische Formen beschreiben (Linien, Kreise, Rechtecke, Volumenkörper, importierte Teile usw.), die Eigenschaft "Platzierung", die ihre Position in der [[3D view/de|3D |
Verschiedene Objekte können unterschiedliche Typen von Eigenschaften haben. Viele Objekte haben jedoch die gleichen Typen, weil sie von der gleichen internen Klasse abgeleitet sind. Zum Beispiel haben die meisten Objekte, die geometrische Formen beschreiben (Linien, Kreise, Rechtecke, Volumenkörper, importierte Teile usw.), die Eigenschaft "Platzierung", die ihre Position in der [[3D view/de|3D-Ansicht]] definiert. |
||
<span id="View_and_Data_properties"></span> |
|||
== Ansichts und Dateneigenschaften == |
|||
== Ansicht- und Daten-Eigenschaften == |
|||
There are two classes of feature properties accessible through tabs in the property editor: |
There are two classes of feature properties accessible through tabs in the property editor: |
||
| Line 51: | Line 56: | ||
For this reason, {{MenuCommand|Data}} properties are considered to be more "real", as they truly define the geometry of a shape. On the other hand, {{MenuCommand|View}} properties are less important because they only affect the superficial appearance of the geometry. For example, a circle of 10 mm radius is different from a circle of 5 mm radius; the color of the circle (view property) doesn't affect its shape, but the radius does (data property). In many instances in this documentation, the word "property" is understood to refer to a "Data property" and not to a "View property". |
For this reason, {{MenuCommand|Data}} properties are considered to be more "real", as they truly define the geometry of a shape. On the other hand, {{MenuCommand|View}} properties are less important because they only affect the superficial appearance of the geometry. For example, a circle of 10 mm radius is different from a circle of 5 mm radius; the color of the circle (view property) doesn't affect its shape, but the radius does (data property). In many instances in this documentation, the word "property" is understood to refer to a "Data property" and not to a "View property". |
||
<span id="Basic_properties"></span> |
|||
=== Grundlegende Eigenschaften === |
=== Grundlegende Eigenschaften === |
||
{{Emphasis|Siehe auch: [[Object_name/de|Objektname]]}} |
{{Emphasis|Siehe auch: [[Object_name/de|Objektname]]}} |
||
The most basic [[ |
The most basic [[Scripted_objects|scripted object]] won't show any {{MenuCommand|Data}} property in the property editor, except for its {{incode|Label}} attribute. The {{incode|Label}} is a user editable string that identifies the object in the [[Tree_view|tree view]]. On the other hand, the {{incode|Name}} attribute of an object is assigned at the moment of its creation and cannot be changed; this attribute is read-only, and is not displayed in the property editor either. |
||
Ein grundlegendes parametrisches Objekt wird wie folgt erstellt |
Ein grundlegendes parametrisches Objekt wird wie folgt erstellt |
||
| Line 70: | Line 76: | ||
{{Caption|View and Data tabs of the property editor, for a basic "App::FeaturePython" scripted object.}} |
{{Caption|View and Data tabs of the property editor, for a basic "App::FeaturePython" scripted object.}} |
||
Most geometrical objects that can be created and displayed in the [[ |
Most geometrical objects that can be created and displayed in the [[3D_view|3D view]] are derived from a {{incode|Part::Feature}}. See [[Part_Feature|Part Feature]] for the most basic properties that these objects have. |
||
For 2D geometry, most objects are derived from {{incode|Part::Part2DObject}} (itself derived from {{incode|Part::Feature}}) which is the base of [[Sketch|Sketches]], and most [[ |
For 2D geometry, most objects are derived from {{incode|Part::Part2DObject}} (itself derived from {{incode|Part::Feature}}) which is the base of [[Sketch|Sketches]], and most [[Draft_Workbench|Draft elements]]. See [[Part_Part2DObject|Part Part2DObject]] for the most basic properties that these objects have. |
||
<span id="Actions"></span> |
|||
== Maßnahmen == |
== Maßnahmen == |
||
<div class="mw-translate-fuzzy"> |
|||
Aktionen in der Eigenschaftsansicht wurden in 0.19 implementiert. |
|||
</div> |
|||
Right clicking in an empty space of the view, or with a property selected, shows only one command: |
Right clicking in an empty space of the view, or with a property selected, shows only one command: |
||
| Line 87: | Line 90: | ||
When the {{MenuCommand|Show all}} option is active, and one property is selected, more actions are available with a second right click: |
When the {{MenuCommand|Show all}} option is active, and one property is selected, more actions are available with a second right click: |
||
* {{MenuCommand|Show all}}: deactivates the {{MenuCommand|Show all}} command, hiding the additional Data and View properties. |
* {{MenuCommand|Show all}}: deactivates the {{MenuCommand|Show all}} command, hiding the additional Data and View properties. |
||
* {{MenuCommand|Add Property}}: adds a dynamic property to the object; this works with both C++ defined objects, and Python [[ |
* {{MenuCommand|Add Property}}: adds a dynamic property to the object; this works with both C++ defined objects, and Python [[Scripted_objects|scripted objects]]. |
||
* {{MenuCommand|Expression...}}: brings up the formula editor, which allows using [[Expressions|expressions]] in the property value. |
* {{MenuCommand|Expression...}}: brings up the formula editor, which allows using [[Expressions|expressions]] in the property value. |
||
* {{MenuCommand|Hidden}}: if active, sets the property as hidden, meaning that it will only be displayed in the property editor if {{MenuCommand|Show all}} is active. |
* {{MenuCommand|Hidden}}: if active, sets the property as hidden, meaning that it will only be displayed in the property editor if {{MenuCommand|Show all}} is active. |
||
| Line 97: | Line 100: | ||
* {{MenuCommand|EvalOnRestore}}: if active, it is evaluated when the document is restored. |
* {{MenuCommand|EvalOnRestore}}: if active, it is evaluated when the document is restored. |
||
<span id="Example_of_the_properties_of_a_PartDesign_object"></span> |
|||
==Beispiel für die Eigenschaften eines PartDesign |
==Beispiel für die Eigenschaften eines PartDesign-Objekts== |
||
In this section we show some common properties that are visible for a [[ |
In this section we show some common properties that are visible for a [[PartDesign_Body|PartDesign Body]], and one [[PartDesign_Feature|PartDesign Feature]]. The specific properties of an object can found in the specific documentation page of that object. |
||
<span id="View"></span> |
|||
===Ansicht=== |
===Ansicht=== |
||
Most of these properties are inherited from the [[Part_Feature|Part Feature]] basic object. |
Most of these properties are inherited from the [[Part_Feature|Part Feature]] basic object. |
||
[[File:FreeCAD_Property_editor_View.png|490px|left]] |
[[File:FreeCAD_Property_editor_View.png|490px|frame|left]] |
||
{{TitleProperty|Base}} |
{{TitleProperty|Base}} |
||
* {{PropertyView|Angular Deflection}}: it is another way to specify how finely to generate the mesh for rendering on screen or when exporting. The default value is 28.5 degrees, or 0.5 radians. The smaller the value the smoother the appearance will be in the [[ |
* {{PropertyView|Angular Deflection}}: it is another way to specify how finely to generate the mesh for rendering on screen or when exporting. The default value is 28.5 degrees, or 0.5 radians. The smaller the value the smoother the appearance will be in the [[3D_view|3D view]], and the finer the mesh that will be exported. |
||
* {{PropertyView|Bounding Box}}: indicates if a box showing the overall extent of the object is displayed. |
* {{PropertyView|Bounding Box}}: indicates if a box showing the overall extent of the object is displayed. |
||
* {{PropertyView|Deviation}}: sets the accuracy of the polygonal representation of the model in the [[ |
* {{PropertyView|Deviation}}: sets the accuracy of the polygonal representation of the model in the [[3D_view|3D view]] (tessellation). Lower values indicate better quality. The value is in percent of object's size. |
||
* {{PropertyView|Display Mode}}: display mode of the entire Body, {{Value|Flat lines}} (default), {{Value|Shaded}}, {{Value|Wireframe}}, {{Value|Points}}. |
* {{PropertyView|Display Mode}}: display mode of the entire Body, {{Value|Flat lines}} (default), {{Value|Shaded}}, {{Value|Wireframe}}, {{Value|Points}}. |
||
* {{PropertyView|Display Mode Body}}: display mode of the Tip of the Body, {{Value|Through}} (default), {{Value|Tip}}. |
* {{PropertyView|Display Mode Body}}: display mode of the Tip of the Body, {{Value|Through}} (default), {{Value|Tip}}. |
||
* {{PropertyView|Draw Style}}: {{Value|Solid}}, {{Value|Dashed}}, {{Value|Dotted}}, {{Value|Dashdot}}; defines the style of the edges in the [[ |
* {{PropertyView|Draw Style}}: {{Value|Solid}}, {{Value|Dashed}}, {{Value|Dotted}}, {{Value|Dashdot}}; defines the style of the edges in the [[3D_view|3D view]]. |
||
* {{PropertyView|Lighting}}: {{Value|One side}}, {{Value|Two side}} (default). |
* {{PropertyView|Lighting}}: {{Value|One side}}, {{Value|Two side}} (default). |
||
* {{PropertyView|Line Color}}: the RGB color of the edges, it defaults to {{value|(25, 25, 25)}}. |
* {{PropertyView|Line Color}}: the RGB color of the edges, it defaults to {{value|(25, 25, 25)}}. |
||
| Line 125: | Line 131: | ||
* {{PropertyView|Show In Tree}}: if it is {{TRUE}}, the object appears in the tree view. Otherwise, it is set as invisible. |
* {{PropertyView|Show In Tree}}: if it is {{TRUE}}, the object appears in the tree view. Otherwise, it is set as invisible. |
||
* {{PropertyView|Transparency}}: the degree of transparency from {{value|0}} (default) to {{value|100}}. |
* {{PropertyView|Transparency}}: the degree of transparency from {{value|0}} (default) to {{value|100}}. |
||
* {{PropertyView|Visibility}}: whether the object is visible in the [[ |
* {{PropertyView|Visibility}}: whether the object is visible in the [[3D_view|3D view]] or not. Toggle with the {{KEY|Space}} bar in the keyboard. |
||
{{clear}} |
{{clear}} |
||
<span id="Data"></span> |
|||
===Daten=== |
===Daten=== |
||
In this case we observe the properties of the [[ |
In this case we observe the properties of the [[PartDesign_Revolution|PartDesign Revolution]] feature. |
||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
{{TitleProperty|Base}} |
{{TitleProperty|Base}} |
||
| Line 154: | Line 163: | ||
{{clear}} |
{{clear}} |
||
<span id="Scripting"></span> |
|||
== Skripten == |
== Skripten == |
||
| Line 161: | Line 171: | ||
Deine Übersetzung |
Deine Übersetzung |
||
Most properties that are visible in the property editor can be accessed from the [[ |
Most properties that are visible in the property editor can be accessed from the [[Python_console|Python console]]. These properties are just attributes of the class that defines the selected object. For example, if the property editor shows the {{PropertyData|Group}} property, this means that the object has the {{incode|Group}} attribute. |
||
{{Code|code= |
{{Code|code= |
||
print(obj.Group) |
print(obj.Group) |
||
| Line 167: | Line 178: | ||
These attributes (properties) are added with the {{incode|addProperty}} method of the base object. At least it is necessary to specify the type of [[property|property]], and its name. |
These attributes (properties) are added with the {{incode|addProperty}} method of the base object. At least it is necessary to specify the type of [[property|property]], and its name. |
||
{{Code|code= |
{{Code|code= |
||
obj.addProperty("App::PropertyFloat", "Custom") |
obj.addProperty("App::PropertyFloat", "Custom") |
||
| Line 181: | Line 193: | ||
[[File:FreeCAD_Property_editor_Custom.png]] |
[[File:FreeCAD_Property_editor_Custom.png]] |
||
{{Caption|Property editor showing the Data properties of a [[ |
{{Caption|Property editor showing the Data properties of a [[PartDesign_Body|PartDesign Body]], with two additional properties, "Custom" and "Custom Camel Property".}} |
||
In similar way the {{MenuCommand|View}} properties are added, not to the base object, but to its {{incode|ViewObject}}. Then, it follows that properties like {{PropertyView|Angular Deflection}}, {{PropertyView|Bounding Box}}, {{PropertyView|Display Mode}}, {{PropertyView|Display Mode Body}}, {{PropertyView|Line Color}}, and others, can be examined and changed from the [[ |
In similar way the {{MenuCommand|View}} properties are added, not to the base object, but to its {{incode|ViewObject}}. Then, it follows that properties like {{PropertyView|Angular Deflection}}, {{PropertyView|Bounding Box}}, {{PropertyView|Display Mode}}, {{PropertyView|Display Mode Body}}, {{PropertyView|Line Color}}, and others, can be examined and changed from the [[Python_console|Python console]]. |
||
{{Code|code= |
{{Code|code= |
||
| Line 194: | Line 206: | ||
Alle öffentlichen Eigenschaften des Objekts und seines Ansichtsanbieters sind in dem entsprechenden Attribut {{incode|PropertiesList}} enthalten. |
Alle öffentlichen Eigenschaften des Objekts und seines Ansichtsanbieters sind in dem entsprechenden Attribut {{incode|PropertiesList}} enthalten. |
||
{{Code|code= |
{{Code|code= |
||
print(obj.PropertiesList) |
print(obj.PropertiesList) |
||
Latest revision as of 10:37, 9 April 2024
Einführung
Der Eigenschafteneditor erscheint wenn der Reiter Modell der Combo-Ansicht auf der Oberfläche aktiv ist; er ermöglicht die Verwaltung der öffentlich zugänglichen Eigenschaften der Objekte im Dokument.
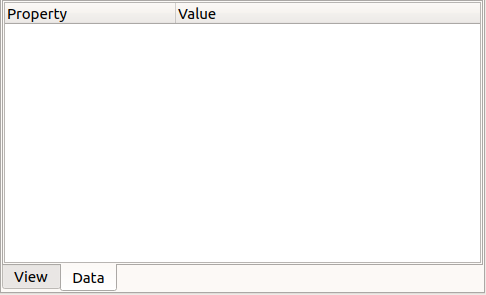
Generell ist der Eigenschafteneditor dazu gedacht, nur ein Objekt zur Zeit zu behandeln. Die im Eigenschafteneditor angezeigten Werte gehören zum ausgewählten Objekt des aktiven Dokuments. Es gibt jedoch einige Eigenschaften, wie Farben, die für viele ausgewählte Objekte gleichzeitig gesetzt werden können. Wenn kein Element ausgewählt wurde, bleibt der Eigenschafteneditor leer.
Nicht alle Eigenschaften können immer geändert werden; je nach dem spezifischen Status der Eigenschaft sind einige von ihnen unsichtbar (nicht aufgeführt) oder schreibgeschützt (nicht bearbeitbar).
Leerer Eigenschafteneditor, wenn kein Objekt ausgewählt ist.
Eigenschaftentypen
Eine Eigenschaft ist eine Information wie eine Zahl oder eine Textzeichenfolge, die an ein FreeCAD-Dokument oder ein Objekt im Dokument angehängt ist.
Benutzerdefinierte skriptgenerierte Objekte können jeden der im Basissystem definierten Eigenschaftstypen verwenden. Die vollständige Liste findet man unter Objekteigenschaften.
Einige der am häufigsten verwendeten Eigenschaftstypen sind:
App::PropertyBool
App::PropertyFloat
App::PropertyAngle
App::PropertyDistance
App::PropertyInteger
App::PropertyString
App::PropertyMatrix
App::PropertyVector
App::PropertyPlacement
Verschiedene Objekte können unterschiedliche Typen von Eigenschaften haben. Viele Objekte haben jedoch die gleichen Typen, weil sie von der gleichen internen Klasse abgeleitet sind. Zum Beispiel haben die meisten Objekte, die geometrische Formen beschreiben (Linien, Kreise, Rechtecke, Volumenkörper, importierte Teile usw.), die Eigenschaft "Platzierung", die ihre Position in der 3D-Ansicht definiert.
Ansicht- und Daten-Eigenschaften
There are two classes of feature properties accessible through tabs in the property editor:
- View properties, related to the "visual" appearance of the object. The View properties are tied to the ViewProvider (
ViewObjectattribute) of the object, and are only accessible when the graphical user interface (GUI) is loaded. They are not accessible when using FreeCAD in console mode, or as a headless library. - Data properties, related to the "physical" parameters of the object. The Data properties define the essential characteristics of the object; they exist at all times, even when FreeCAD is used in console mode, or as a library. This means that if you load a document in console mode, you can edit the radius of a circle or the length of a line, even if you cannot see the result on the screen.
For this reason, Data properties are considered to be more "real", as they truly define the geometry of a shape. On the other hand, View properties are less important because they only affect the superficial appearance of the geometry. For example, a circle of 10 mm radius is different from a circle of 5 mm radius; the color of the circle (view property) doesn't affect its shape, but the radius does (data property). In many instances in this documentation, the word "property" is understood to refer to a "Data property" and not to a "View property".
Grundlegende Eigenschaften
Siehe auch: Objektname
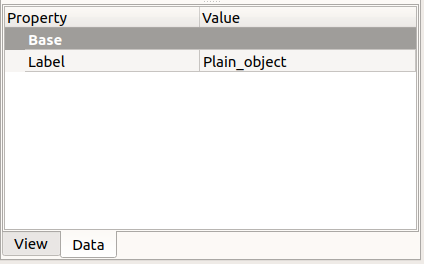
The most basic scripted object won't show any Data property in the property editor, except for its Label attribute. The Label is a user editable string that identifies the object in the tree view. On the other hand, the Name attribute of an object is assigned at the moment of its creation and cannot be changed; this attribute is read-only, and is not displayed in the property editor either.
Ein grundlegendes parametrisches Objekt wird wie folgt erstellt
obj = App.ActiveDocument.addObject("App::FeaturePython", "App__FeaturePython")
obj.Label = "Plain_object"
print(obj.Name)
print(obj.Label)
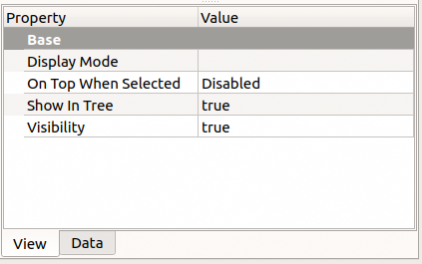
View and Data tabs of the property editor, for a basic "App::FeaturePython" scripted object.
Most geometrical objects that can be created and displayed in the 3D view are derived from a Part::Feature. See Part Feature for the most basic properties that these objects have.
For 2D geometry, most objects are derived from Part::Part2DObject (itself derived from Part::Feature) which is the base of Sketches, and most Draft elements. See Part Part2DObject for the most basic properties that these objects have.
Maßnahmen
Right clicking in an empty space of the view, or with a property selected, shows only one command:
- Show all: if active, in addition to the standard properties that appear already, it shows all the hidden Data and View properties in their respective tabs.
- Data: "Proxy", "Label2", "Expression Engine", and "Visibility".
- View: "Proxy".
When the Show all option is active, and one property is selected, more actions are available with a second right click:
- Show all: deactivates the Show all command, hiding the additional Data and View properties.
- Add Property: adds a dynamic property to the object; this works with both C++ defined objects, and Python scripted objects.
- Expression...: brings up the formula editor, which allows using expressions in the property value.
- Hidden: if active, sets the property as hidden, meaning that it will only be displayed in the property editor if Show all is active.
- Output: if active, sets the property as output.
- NoRecompute: if active, sets the property as not recomputed when the document is recomputed; this is useful when a property should be kept unaffected by other updates.
- ReadOnly: if active, sets the property to be read-only; it won't be editable in the property editor any more until this switch is turned off. The Expression... menu entry is no longer available. Note: It may be still possible to change the property via a dialog that updates the property.
- Transient: if active, sets the property as transient. The value of a transient property is not saved to file. When opening a file, it is instantiated with its default value.
- Touched: if active, it becomes touched, and ready for recompute.
- EvalOnRestore: if active, it is evaluated when the document is restored.
Beispiel für die Eigenschaften eines PartDesign-Objekts
In this section we show some common properties that are visible for a PartDesign Body, and one PartDesign Feature. The specific properties of an object can found in the specific documentation page of that object.
Ansicht
Most of these properties are inherited from the Part Feature basic object.

Base
- AnsichtAngular Deflection: it is another way to specify how finely to generate the mesh for rendering on screen or when exporting. The default value is 28.5 degrees, or 0.5 radians. The smaller the value the smoother the appearance will be in the 3D view, and the finer the mesh that will be exported.
- AnsichtBounding Box: indicates if a box showing the overall extent of the object is displayed.
- AnsichtDeviation: sets the accuracy of the polygonal representation of the model in the 3D view (tessellation). Lower values indicate better quality. The value is in percent of object's size.
- AnsichtDisplay Mode: display mode of the entire Body,
Flat lines(default),Shaded,Wireframe,Points. - AnsichtDisplay Mode Body: display mode of the Tip of the Body,
Through(default),Tip. - AnsichtDraw Style:
Solid,Dashed,Dotted,Dashdot; defines the style of the edges in the 3D view. - AnsichtLighting:
One side,Two side(default). - AnsichtLine Color: the RGB color of the edges, it defaults to
(25, 25, 25). - AnsichtLine Width: the thickness of the edges, it defaults to
2pixels. - AnsichtOn Top When Selected:
Disabled,Enabled,Object,Element. - AnsichtPoint Color: the RGB color of the vertices, it defaults to
(25, 25, 25). - AnsichtPoint Size: the size of the vertices, it defaults to
2pixels. - AnsichtSelectable: whether the object is selectable or not.
- AnsichtSelection Style:
Shape,BoundBox. - AnsichtShape Color: the RGB color of the shape, it defaults to
(204, 204, 204). - AnsichtShow In Tree: if it is
true, the object appears in the tree view. Otherwise, it is set as invisible. - AnsichtTransparency: the degree of transparency from
0(default) to100. - AnsichtVisibility: whether the object is visible in the 3D view or not. Toggle with the Space bar in the keyboard.
Daten
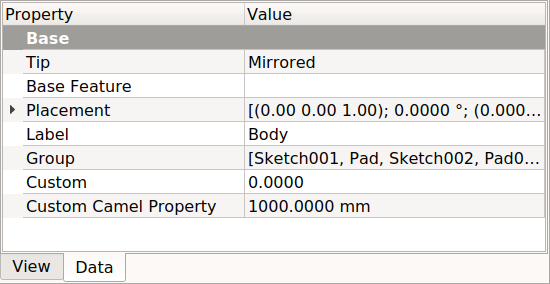
In this case we observe the properties of the PartDesign Revolution feature.

Base
- DatenLabel: the user defined name given to the object, this can be changed as desired.
Part Design
- DatenRefine: whether to refine the fusion done with other objects.
Revolution
- DatenBase: the point in space that specifies where the revolution takes place. It cannot be modified directly, only when editing the feature.
- DatenAxis: the axis around which the revolution will be performed. It cannot be modified directly, only when editing the feature.
- DatenAngle: the angle that specifies how much of the base element is rotated. By default it is
360 deg, but it can be any fraction of that.
Sketch Based
- DatenMidplane: if the base object is a Sketch, when this property is
true, it will perform the revolution with the sketch serving as a plane of symmetry. This is noticeable if the DatenAngle is different from360 deg. - DatenReversed: by default it is
true. Whether to perform the revolution in one direction or the other.
Skripten
Siehe auch: FreeCAD Grundlagen Skripten.
Siehe geskriptete Objekte für die vollständigen Informationen zum Hinzufügen von Eigenschaften zu Objekten, die über Python definiert wurden. Deine Übersetzung
Most properties that are visible in the property editor can be accessed from the Python console. These properties are just attributes of the class that defines the selected object. For example, if the property editor shows the DatenGroup property, this means that the object has the Group attribute.
print(obj.Group)
These attributes (properties) are added with the addProperty method of the base object. At least it is necessary to specify the type of property, and its name.
obj.addProperty("App::PropertyFloat", "Custom")
print(obj.Custom)
Properties follow the CapitalCamelCase or PascalCase convention, meaning that each word starts with a capital letter, and there are no underscores. When the property editor displays such names, it leaves a space between each capital letter, making it easier to read.
obj.addProperty("App::PropertyDistance", "CustomCamelProperty")
obj.CustomCamelProperty = 1000
print(obj.CustomCamelProperty)
Property editor showing the Data properties of a PartDesign Body, with two additional properties, "Custom" and "Custom Camel Property".
In similar way the View properties are added, not to the base object, but to its ViewObject. Then, it follows that properties like AnsichtAngular Deflection, AnsichtBounding Box, AnsichtDisplay Mode, AnsichtDisplay Mode Body, AnsichtLine Color, and others, can be examined and changed from the Python console.
print(obj.ViewObject.AngularDeflection)
print(obj.ViewObject.BoundingBox)
print(obj.ViewObject.DisplayMode)
print(obj.ViewObject.DisplayModeBody)
print(obj.ViewObject.LineColor)
Alle öffentlichen Eigenschaften des Objekts und seines Ansichtsanbieters sind in dem entsprechenden Attribut PropertiesList enthalten.
print(obj.PropertiesList)
print(obj.ViewObject.PropertiesList)
- Preferences Editor, Interface Customization
- Main window: Standard menu, Main view area, 3D view, Combo view (Tree view, Task panel, Property editor), Selection view, Report view, Python console, Status bar, DAG view, Workbench Selector
- Auxiliary windows: Scene inspector, Dependency graph
- File: New, Open, Close, Close All, Save, Save As, Save a Copy, Save All, Revert, Import, Export,Merge project, Project information, Print, Print preview, Export PDF, Recent files, Exit
- Edit: Undo, Redo, Cut, Copy, Paste, Duplicate selection, Refresh, Box selection, Box element selection, Select All, Delete, Send to Python Console, Placement, Transform, Alignment, Toggle Edit mode, Edit mode, Preferences
- View:
- Miscellaneous: Create new view, Orthographic view, Perspective view, Fullscreen, Bounding box, Toggle axis cross, Clipping plane, Texture mapping, Toggle navigation/Edit mode, Appearance, Random color, Workbench, Status bar
- Standard views: Fit all, Fit selection, Isometric, Dimetric, Trimetric, Home, Front, Top, Right, Rear, Bottom, Left, Rotate Left, Rotate Right
- Freeze display: Save views, Load views, Freeze view, Clear views
- Draw style: As is, Points, Wireframe, Hidden line, No shading, Shaded, Flat lines
- Stereo: Stereo red/cyan, Stereo quad buffer, Stereo Interleaved Rows, Stereo Interleaved Columns, Stereo Off, Issue camera position
- Zoom: Zoom In, Zoom Out, Box zoom
- Document window: Docked, Undocked, Fullscreen
- Visibility: Toggle visibility, Show selection, Hide selection, Select visible objects, Toggle all objects, Show all objects, Hide all objects, Toggle selectability, Toggle measurement, Clear measurement
- Toolbars: File, Edit, Clipboard, Workbench, Macro, View, Structure, Help
- Panels: Tree view, Property view, Selection view, Tasks, Python console, DAG view, Model, Report view
- Link navigation: Go to linked object, Go to the deepest linked object, Select all links
- Tree view actions: Sync view, Sync selection, Sync placement, Pre-selection, Record selection, Single document, Multi document, Collapse/Expand, Initiate dragging, Go to selection, Selection Back, Selection Forward
- Tools: Edit parameters, Save image, Load image, Scene inspector, Dependency graph, Project utility, Measure distance, Add text document, View turntable, Units calculator, Customize, Addon manager
- Macro: Macro recording, Macros, Recent macros, Execute macro, Attach to remote debugger, Debug macro, Stop debugging, Step over, Step into, Toggle breakpoint
- Help: Help, FreeCAD Website, Donate, Users documentation, Python scripting documentation, Automatic Python modules documentation, FreeCAD Forum, FreeCAD FAQ, Report a bug, About FreeCAD, What's This
- Erste Schritte
- Installation: Herunterladen, Windows, Linux, Mac, Zusätzlicher Komponenten, Docker, AppImage, Ubuntu Snap
- Grundlagen: Über FreeCAD, Graphische Oberfläche, Mausbedienung, Auswahlmethoden, Objektname, Programmeinstellungen, Arbeitsbereiche, Dokumentstruktur, Objekteigenschaften, Hilf FreeCAD, Spende
- Hilfe: Tutorien, Video Tutorien
- Arbeitsbereiche: Std Base, Arch, Assembly, CAM, Draft, FEM, Inspection, Mesh, OpenSCAD, Part, PartDesign, Points, Reverse Engineering, Robot, Sketcher, Spreadsheet, Surface, TechDraw, Test Framework