Robot Workbench/tr: Difference between revisions
(Updating to match new version of source page) |
No edit summary |
||
| (35 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
<languages/> |
|||
[[Image:KukaKR16FreeCAD.jpg|right|400px]] |
|||
{{Docnav |
|||
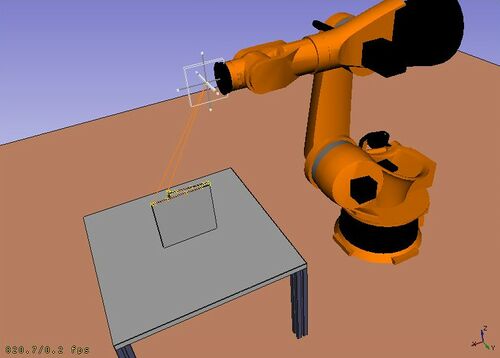
The robot workbench is a tool to simulate industrial grade [[Robot_6-Axis|Robot 6-Axis]], like e.g. [http://kuka.com/ Kuka]. |
|||
|[[Reverse_Engineering_Workbench|Reverse Engineering Workbench]] |
|||
You can do the following tasks: |
|||
|[[Sketcher_Workbench|Sketcher Workbench]] |
|||
* set up a simulation environment with a robot and work pieces |
|||
|IconL=Workbench_Reverse_Engineering.svg |
|||
* create and fill up trajectories |
|||
|IconR=Workbench_Sketcher.svg |
|||
* decompose features of an CAD part to a trajectory |
|||
}} |
|||
* simulate the robot movement and reachability |
|||
* export the trajectory to a robot program file |
|||
{{VeryImportantMessage|The Robot Workbench is unmaintained. If you have experience with the topic and are interested in maintaining it, please state your intention in the developer's section of the [https://forum.freecadweb.org/index.php FreeCAD forum]. |
|||
You can find an example here: |
|||
[https://github.com/FreeCAD/FreeCAD_sf_master/blob/master/src/Mod/Robot/RobotExample.py Example files] or try |
|||
the [[Robot tutorial]]. |
|||
The reason this workbench is still in the master source code is because this workbench is programmed in C++. If this workbench could be programmed in Python, then it could be made an [[external_workbenches|external workbench]] and it could be moved to a separate repository. |
|||
== Tools == |
|||
}} |
|||
Here the principal commands you can use to create a robot set-up. |
|||
== Giriş == |
|||
The tools to create and manage the 6-Axis robots |
|||
[[Image:Workbench_Robot.svg|thumb|128px|Robot workbench icon]] |
|||
* [[Image:Robot_CreateRobot.png|30px]] [[Robot_CreateRobot|Create a robot]]: Insert a new robot into the scene |
|||
* [[Image:Robot_Simulate.png|30px]] [[Robot_Simulate|Simulate a trajectory]]: Opens the simulation dialog and lets you simulate |
|||
* [[Image:Robot_Export.png|30px]] [[Robot_Export|Export a trajectory]]: Export a robot program file |
|||
* [[Image:Robot_SetHomePos.png|30px]] [[Robot_SetHomePos|Set home positon]]: Set the home position of a robot |
|||
* [[Image:Robot_RestoreHomePos.png|30px]] [[Robot_RestoreHomePos|Restore home positon]]: move the robot to its home position |
|||
<div class="mw-translate-fuzzy"> |
|||
=== Trajectories === |
|||
[[Robot Workbench/tr|Robot Tezgahı]], [http://kuka.com/ Kuka] gibi bir standart [[Robot_6-Axis|6 eksenli endüstriyel robot]] 'u simüle etmek için kullanılan bir araçtır. |
|||
Tools to create and manipulate trajectories. There are two kinds, the parametric and non parametric ones. |
|||
</div> |
|||
Aşağıdaki görevleri yapabilirsiniz: |
|||
==== non parametric trajectories ==== |
|||
* Bir robot ve iş parçaları ile bir simülasyon ortamı kurun. |
|||
* [[Image:Robot_CreateTrajectory.png|30px]] [[Robot_CreateTrajectory|Create a trajectory]]: Inserts a new empty trajectory-object into the scene |
|||
* Hareket yörüngelerini oluşturun ve doldurun. |
|||
* [[Image:Robot_SetDefaultOrientation.png|30px]] [[Robot_SetDefaultOrientation|Set the default orientation]]: Set the orientation way-points gets created by default |
|||
* Bir CAD parçasının özelliklerini bir yörüngeye ayırın. |
|||
* [[Image:Robot_SetDefaultValues.png|30px]] [[Robot_SetDefaultValues|Set the default speed parameter]]: Set the default values for way-point creation |
|||
* Robot hareketini simüle edin ve mesafeye ulaşın. |
|||
* [[Image:Robot_InsertWaypoint.png|30px]] [[Robot_InsertWaypoint|Insert a waypoint]]: Insert a way-point from the current robot position into a trajectory |
|||
* Yörüngeyi bir robot program dosyasına aktarın. |
|||
* [[Image:Robot_InsertWaypointPre.png|30px]] [[Robot_InsertWaypointPre|Insert a waypoint]]: Insert a way-point from the current mouse position into a trajectory |
|||
<div class="mw-translate-fuzzy"> |
|||
==== parametric trajectories ==== |
|||
Başlamak için [[Robot tutorial/tr|Robot klavuzunu]] deneyin ve [https://github.com/FreeCAD/FreeCAD_sf_master/blob/master/src/Mod/Robot/RobotExample.py RobotExample.py] örneğindeki programlama arayüzünü görün. |
|||
* [[Image:Robot_Edge2Trac.png|30px]] [[Robot_Edge2Trac|Create a trajectory out of edges]]: Insert a new object which decompose edges to a trajectory |
|||
</div> |
|||
* [[Image:Robot_TrajectoryDressUp.png|30px]] [[Robot_TrajectoryDressUp|Dress-up a trajectory]]: Lets you override one or more properties of a trajectory |
|||
* [[Image:Robot_TrajectoryCompound.png|30px]] [[Robot_TrajectoryCompound|Trajectory compound]]: Create a compound out of some single trajectories |
|||
{{TOCright}} |
|||
== Scripting == |
|||
[[Image:Robot_Workbench_example.jpg|500px]] |
|||
This section is generated out of: https://github.com/FreeCAD/FreeCAD_sf_master/blob/master/src/Mod/Robot/RobotExample.py |
|||
You can use this file directly if you want. |
|||
== Araçlar == |
|||
Example how to use the basic robot class Robot6Axis which represents a 6-axis |
|||
Burada bir robot kurulumu oluşturmak için kullanabileceğiniz temel komutlar. |
|||
industrial robot. The Robot module is dependent on Part but not on other modules. |
|||
It works mostly with the basic types Placement, Vector and Matrix. So we need |
|||
only: |
|||
{{Code|code= |
|||
from Robot import * |
|||
from Part import * |
|||
from FreeCAD import * |
|||
}} |
|||
=== Basic robot stuff === |
|||
create the robot. If you do not specify another kinematic it becomes a Puma 560 |
|||
{{Code|code= |
|||
rob = Robot6Axis() |
|||
print rob |
|||
}} |
|||
accessing the axis and the Tcp. Axes go from 1-6 and are in degree: |
|||
{{Code|code= |
|||
Start = rob.Tcp |
|||
print Start |
|||
print rob.Axis1 |
|||
}} |
|||
move the first axis of the robot: |
|||
{{Code|code= |
|||
rob.Axis1 = 5.0 |
|||
}} |
|||
the Tcp has changed (forward kinematic) |
|||
{{Code|code= |
|||
print rob.Tcp |
|||
}} |
|||
move the robot back to start position (reverse kinematic): |
|||
{{Code|code= |
|||
rob.Tcp = Start |
|||
print rob.Axis1 |
|||
}} |
|||
the same with axis 2: |
|||
{{Code|code= |
|||
rob.Axis2 = 5.0 |
|||
print rob.Tcp |
|||
rob.Tcp = Start |
|||
print rob.Axis2 |
|||
}} |
|||
Waypoints: |
|||
{{Code|code= |
|||
w = Waypoint(Placement(),name="Pt",type="LIN") |
|||
print w.Name,w.Type,w.Pos,w.Cont,w.Velocity,w.Base,w.Tool |
|||
}} |
|||
generate more. The trajectory always finds automatically a unique name for the waypoints |
|||
{{Code|code= |
|||
l = [w] |
|||
for i in range(5): |
|||
l.append(Waypoint(Placement(Vector(0,0,i*100),Vector(1,0,0),0),"LIN","Pt")) |
|||
}} |
|||
create a trajectory |
|||
{{Code|code= |
|||
t = Trajectory(l) |
|||
print t |
|||
for i in range(7): |
|||
t.insertWaypoints(Waypoint(Placement(Vector(0,0,i*100+500),Vector(1,0,0),0),"LIN","Pt")) |
|||
}} |
|||
see a list of all waypoints: |
|||
{{Code|code= |
|||
print t.Waypoints |
|||
del rob,Start,t,l,w |
|||
}} |
|||
=== Working with the document objects === |
|||
=== Robotlar === |
|||
Working with the robot document objects: |
|||
6 Eksenli robotları oluşturma ve yönetme araçları |
|||
first create a robot in the active document |
|||
{{Code|code= |
|||
if(App.activeDocument() == None):App.newDocument() |
|||
App.activeDocument().addObject("Robot::RobotObject","Robot") |
|||
}} |
|||
Define the visual representation and the kinematic definition (see [[Robot_6-Axis|Robot 6-Axis]] and [[VRML Preparation for Robot Simulation|VRML Preparation for Robot Simulation]] for details about that) |
|||
{{Code|code= |
|||
App.activeDocument().Robot.RobotVrmlFile = App.getResourceDir()+"Mod/Robot/Lib/Kuka/kr500_1.wrl" |
|||
App.activeDocument().Robot.RobotKinematicFile = App.getResourceDir()+"Mod/Robot/Lib/Kuka/kr500_1.csv" |
|||
}} |
|||
start positon of the Axis (only that which differ from 0) |
|||
{{Code|code= |
|||
App.activeDocument().Robot.Axis2 = -90 |
|||
App.activeDocument().Robot.Axis3 = 90 |
|||
}} |
|||
retrieve the Tcp position |
|||
{{Code|code= |
|||
pos = FreeCAD.getDocument("Unnamed").getObject("Robot").Tcp |
|||
}} |
|||
move the robot |
|||
{{Code|code= |
|||
pos.move(App.Vector(-10,0,0)) |
|||
FreeCAD.getDocument("Unnamed").getObject("Robot").Tcp = pos |
|||
}} |
|||
create an empty Trajectory object in the active document |
|||
{{Code|code= |
|||
App.activeDocument().addObject("Robot::TrajectoryObject","Trajectory") |
|||
}} |
|||
get the Trajectory |
|||
{{Code|code= |
|||
t = App.activeDocument().Trajectory.Trajectory |
|||
}} |
|||
add the actual TCP position of the robot to the trajectory |
|||
{{Code|code= |
|||
StartTcp = App.activeDocument().Robot.Tcp |
|||
t.insertWaypoints(StartTcp) |
|||
App.activeDocument().Trajectory.Trajectory = t |
|||
print App.activeDocument().Trajectory.Trajectory |
|||
}} |
|||
insert some more Waypoints and the start point at the end again: |
|||
{{Code|code= |
|||
for i in range(7): |
|||
t.insertWaypoints(Waypoint(Placement(Vector(0,1000,i*100+500),Vector(1,0,0),i),"LIN","Pt")) |
|||
<div class="mw-translate-fuzzy"> |
|||
t.insertWaypoints(StartTcp) # end point of the trajectory |
|||
* [[Image: Robot_CreateRobot.png | 30px]] [[Robot_CreateRobot/tr |Robot Oluştur]]: Sahneye yeni bir robot yerleştirin |
|||
App.activeDocument().Trajectory.Trajectory = t |
|||
* [[Image: Robot_Simulate.png | 30px]] [[Robot_Simulate/tr | Robot Simülasyon]] : Simülasyon iletişim kutusunu açar ve simüle etmenizi sağlar |
|||
print App.activeDocument().Trajectory.Trajectory |
|||
* [[Image: Robot_Export.png | 30px]] [[Robot_Export/tr| Robot Dışa aktar]]: Bir robot program dosyasını dışa aktarın |
|||
}} |
|||
* [[Image: Robot_SetHomePos.png | 30px]] [[ Robot_SetHomePos/tr | Ana konum ayarla]]: Bir robotun ana konumunu ayarlayın |
|||
* [[Image: Robot_RestoreHomePos.png | 30px]] [[Robot_RestoreHomePos | Ana konuma dön]]: robotu ana konumuna getirir. |
|||
</div> |
|||
=== |
=== Yörüngeler === |
||
Yörüngeleri oluşturmak ve değiştirmek için araçlar. Parametrik ve parametrik olmayan iki tür vardır. |
|||
To be done..... |
|||
=== Exporting the trajectory === |
|||
The trajectory is exported by Python. That means for every control cabinet type there is a post-processor |
|||
Python module. Here is in detail the Kuka post-processor described |
|||
{{Code|code= |
|||
from KukaExporter import ExportCompactSub |
|||
<div class="mw-translate-fuzzy"> |
|||
ExportCompactSub(App.activeDocument().Robot,App.activeDocument().Trajectory,'D:/Temp/TestOut.src') |
|||
==== Parametrik olmayan yörüngeler ==== |
|||
}} |
|||
* [[Image: Robot_CreateTrajectory.png | 30px]] [[Robot_CreateTrajectory/tr |Yörünge oluştur]]: Sahneye yeni bir boş yörünge nesnesi ekler |
|||
* [[Image: Robot_SetDefaultOrientation.png | 30px]] [[Robot_SetDefaultOrientation/tr | Varsayılan yönlendirmeyi ayarla]]: Oryantasyon yol noktalarını varsayılan olarak oluşturulacak şekilde ayarlayın |
|||
and that's kind of how it's done: |
|||
* [[Image: Robot_SetDefaultValues.png | 30px]] [[Robot_SetDefaultValues/tr|Varsayılan değerleri ayarla]] Yol noktası oluşturma için varsayılan değerleri ayarlayın. |
|||
{{Code|code= |
|||
* [[Image: Robot_InsertWaypoint.png | 30px]] [[Robot_InsertWaypoint/tr| Bir yol noktası ekleyin]]: Geçerli robot konumundan bir yörüngeye bir yol noktası ekleyin |
|||
for w in App.activeDocument().Trajectory.Trajectory.Waypoints: |
|||
* [[Image: Robot_InsertWaypointPre.png | 30px]] [[Robot_InsertWaypointPre/tr | Bir yol noktası ekle]]: Geçerli fare konumundan bir yörüngeye bir yol noktası ekleyin |
|||
(A,B,C) = (w.Pos.Rotation.toEuler()) |
|||
</div> |
|||
print ("LIN {X %.3f,Y %.3f,Z %.3f,A %.3f,B %.3f,C %.3f} ; %s"%(w.Pos.Base.x,w.Pos.Base.y,w.Pos.Base.z,A,B,C,w.Name)) |
|||
<div class="mw-translate-fuzzy"> |
|||
}} |
|||
==== Parametrik yörüngeler ==== |
|||
== Tutorials == |
|||
* [[Image: Robot_Edge2Trac.png | 30px]] [[Robot_Edge2Trac | Kenarlardan bir yörünge oluşturun]]: Kenarları yörüngeye çeviren yeni bir nesne yerleştirin |
|||
* [[Robot 6-Axis|Robot 6-Axis]] |
|||
* [[Image: Robot_TrajectoryDressUp.png | 30px]] [[Robot_TrajectoryDressUp | Bir yörüngeyi giydir]]: Yörüngenin bir veya daha fazla özelliğini geçersiz kılmanıza izin verir |
|||
* [[VRML Preparation for Robot Simulation|VRML Preparation for Robot Simulation]] |
|||
* [[Image: Robot_TrajectoryCompound.png | 30px]] [[Robot_TrajectoryCompound | Trajectory ...]]: Bazı tek yörüngelerin dışında bir bileşik oluşturun |
|||
</div> |
|||
== Betik == |
|||
<div class="mw-translate-fuzzy"> |
|||
{{docnav|FEM Module|Standard Menu}} |
|||
Robot yer değiştirmelerini modellemek için kullanılan işlevlerin açıklaması için [[Robot API example/tr|Robot API örneği]] bölümüne bakınız. |
|||
</div> |
|||
== Kılavuzlar == |
|||
[[Category:User_Documentation/tr]] |
|||
* [[Robot 6-Axis/tr | Robot 6 Eksen]] |
|||
* [[VRML Preparation for Robot Simulation/tr| Robot Simülasyonu için VRML Hazırlığı]] |
|||
<div class="mw-translate-fuzzy"> |
|||
<languages/> |
|||
{{docnav/tr|[[FEM Workbench/tr|FEM tezgahı]]|[[Standard Menu/tr|Standart Menü]]}} |
|||
{{Robot Tools navi/tr}} |
|||
{{Userdocnavi/tr}} |
|||
[[Category:Workbenches/tr]] |
|||
</div> |
|||
{{Robot Tools navi{{#translation:}}}} |
|||
{{Userdocnavi{{#translation:}}}} |
|||
[[Category:Workbenches{{#translation:}}]] |
|||
Latest revision as of 10:28, 27 August 2021
The reason this workbench is still in the master source code is because this workbench is programmed in C++. If this workbench could be programmed in Python, then it could be made an external workbench and it could be moved to a separate repository.
Giriş

Robot Tezgahı, Kuka gibi bir standart 6 eksenli endüstriyel robot 'u simüle etmek için kullanılan bir araçtır.
Aşağıdaki görevleri yapabilirsiniz:
- Bir robot ve iş parçaları ile bir simülasyon ortamı kurun.
- Hareket yörüngelerini oluşturun ve doldurun.
- Bir CAD parçasının özelliklerini bir yörüngeye ayırın.
- Robot hareketini simüle edin ve mesafeye ulaşın.
- Yörüngeyi bir robot program dosyasına aktarın.
Başlamak için Robot klavuzunu deneyin ve RobotExample.py örneğindeki programlama arayüzünü görün.
Araçlar
Burada bir robot kurulumu oluşturmak için kullanabileceğiniz temel komutlar.
Robotlar
6 Eksenli robotları oluşturma ve yönetme araçları
 Robot Oluştur: Sahneye yeni bir robot yerleştirin
Robot Oluştur: Sahneye yeni bir robot yerleştirin Robot Simülasyon : Simülasyon iletişim kutusunu açar ve simüle etmenizi sağlar
Robot Simülasyon : Simülasyon iletişim kutusunu açar ve simüle etmenizi sağlar Robot Dışa aktar: Bir robot program dosyasını dışa aktarın
Robot Dışa aktar: Bir robot program dosyasını dışa aktarın Ana konum ayarla: Bir robotun ana konumunu ayarlayın
Ana konum ayarla: Bir robotun ana konumunu ayarlayın Ana konuma dön: robotu ana konumuna getirir.
Ana konuma dön: robotu ana konumuna getirir.
Yörüngeler
Yörüngeleri oluşturmak ve değiştirmek için araçlar. Parametrik ve parametrik olmayan iki tür vardır.
Parametrik olmayan yörüngeler
 Yörünge oluştur: Sahneye yeni bir boş yörünge nesnesi ekler
Yörünge oluştur: Sahneye yeni bir boş yörünge nesnesi ekler Varsayılan yönlendirmeyi ayarla: Oryantasyon yol noktalarını varsayılan olarak oluşturulacak şekilde ayarlayın
Varsayılan yönlendirmeyi ayarla: Oryantasyon yol noktalarını varsayılan olarak oluşturulacak şekilde ayarlayın Varsayılan değerleri ayarla Yol noktası oluşturma için varsayılan değerleri ayarlayın.
Varsayılan değerleri ayarla Yol noktası oluşturma için varsayılan değerleri ayarlayın. Bir yol noktası ekleyin: Geçerli robot konumundan bir yörüngeye bir yol noktası ekleyin
Bir yol noktası ekleyin: Geçerli robot konumundan bir yörüngeye bir yol noktası ekleyin Bir yol noktası ekle: Geçerli fare konumundan bir yörüngeye bir yol noktası ekleyin
Bir yol noktası ekle: Geçerli fare konumundan bir yörüngeye bir yol noktası ekleyin
Parametrik yörüngeler
 Kenarlardan bir yörünge oluşturun: Kenarları yörüngeye çeviren yeni bir nesne yerleştirin
Kenarlardan bir yörünge oluşturun: Kenarları yörüngeye çeviren yeni bir nesne yerleştirin Bir yörüngeyi giydir: Yörüngenin bir veya daha fazla özelliğini geçersiz kılmanıza izin verir
Bir yörüngeyi giydir: Yörüngenin bir veya daha fazla özelliğini geçersiz kılmanıza izin verir Trajectory ...: Bazı tek yörüngelerin dışında bir bileşik oluşturun
Trajectory ...: Bazı tek yörüngelerin dışında bir bileşik oluşturun
Betik
Robot yer değiştirmelerini modellemek için kullanılan işlevlerin açıklaması için Robot API örneği bölümüne bakınız.
Kılavuzlar
- Trajectories, non parametric: Create a trajectory, Set default orientation, Set default values, Insert waypoint, Insert waypoint (mouse)
- Trajectories, parametric: Create a trajectory from edges, Dress-up trajectory, Trajectory compound
- Getting started
- Installation: Download, Windows, Linux, Mac, Additional components, Docker, AppImage, Ubuntu Snap
- Basics: About FreeCAD, Interface, Mouse navigation, Selection methods, Object name, Preferences, Workbenches, Document structure, Properties, Help FreeCAD, Donate
- Help: Tutorials, Video tutorials
- Workbenches: Std Base, Assembly, BIM, CAM, Draft, FEM, Inspection, Mesh, OpenSCAD, Part, PartDesign, Points, Reverse Engineering, Robot, Sketcher, Spreadsheet, Surface, TechDraw, Test Framework
- Hubs: User hub, Power users hub, Developer hub
- Trajectories, non parametric: Create a trajectory, Set default orientation, Set default values, Insert waypoint, Insert waypoint (mouse)
- Trajectories, parametric: Create a trajectory from edges, Dress-up trajectory, Trajectory compound
- Getting started
- Installation: Download, Windows, Linux, Mac, Additional components, Docker, AppImage, Ubuntu Snap
- Basics: About FreeCAD, Interface, Mouse navigation, Selection methods, Object name, Preferences, Workbenches, Document structure, Properties, Help FreeCAD, Donate
- Help: Tutorials, Video tutorials
- Workbenches: Std Base, Assembly, BIM, CAM, Draft, FEM, Inspection, Mesh, OpenSCAD, Part, PartDesign, Points, Reverse Engineering, Robot, Sketcher, Spreadsheet, Surface, TechDraw, Test Framework
- Hubs: User hub, Power users hub, Developer hub