Std Placement/ro: Difference between revisions
(Created page with "Std Placement") |
(Updating to match new version of source page) |
||
| (19 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
<languages/> |
<languages/> |
||
{{Docnav |
|||
|[[Std_SendToPythonConsole|SendToPythonConsole]] |
|||
|[[Std_TransformManip|TransformManip]] |
|||
|[[Std_Edit_Menu|Std Edit Menu]] |
|||
|IconL=Std_SendToPythonConsole.svg |
|||
|IconR=Std_TransformManip.svg |
|||
|IconC=Freecad.svg |
|||
}} |
|||
<div class="mw-translate-fuzzy"> |
|||
{{GuiCommand|Name=Std Placement|MenuLocation=[[Std Edit Menu|Edit]] → Placement...||Workbenches=All|Shortcut=|SeeAlso=[[Tasks Placement|Tasks Placement]], [[Placement|Placement]]}} |
{{GuiCommand|Name=Std Placement|MenuLocation=[[Std Edit Menu|Edit]] → Placement...||Workbenches=All|Shortcut=|SeeAlso=[[Tasks Placement|Tasks Placement]], [[Placement|Placement]]}} |
||
</div> |
|||
<span id="Description"></span> |
|||
==Descriere== |
|||
<div class="mw-translate-fuzzy"> |
|||
==Description== |
|||
| ⚫ | '''Placement''' este modul în care FreeCAD specifică locația și atitudinea (orientarea) unui obiect în spațiu. Placement can be specified in multiple forms and manipulated via [[Python_scripting_tutorial#Vectors_and_Placements|scripting]], the Properties panel or the '''Edit → Placement...''' dialog. |
||
</div> |
|||
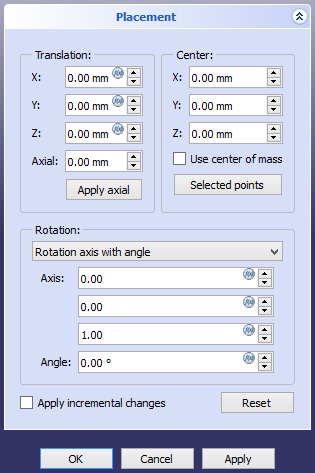
[[Image:Std_Placement_taskpanel.png]] |
|||
| ⚫ | |||
{{Caption|The Placement task panel}} |
|||
<span id="Usage"></span> |
|||
<div class="mw-translate-fuzzy"> |
|||
== |
==Utilizare== |
||
* Short description |
* Short description |
||
** Select an object in the tree view. |
** Select an object in the tree view. |
||
| Line 17: | Line 33: | ||
** Click {{KEY|OK}} or {{KEY|Apply}} |
** Click {{KEY|OK}} or {{KEY|Apply}} |
||
* For a full description see [[Tasks Placement|Tasks Placement]] and [[Placement|Placement]] |
* For a full description see [[Tasks Placement|Tasks Placement]] and [[Placement|Placement]] |
||
</div> |
|||
# Select a single object that has a {{PropertyData|Placement}} property in the [[Property_editor|property editor]]. |
|||
# Select the {{MenuCommand|Edit → Placement...}} option from the menu. |
|||
# Change one or more of the translation and rotation parameters. |
|||
# Do one of the following: |
|||
#* Press the {{Button|OK}} button to apply the changes and close the task panel. |
|||
#* Press the {{Button|Apply}} button to apply the changes, but keep the task panel open for further changes. |
|||
# Press {{KEY|Esc}} or the {{Button|Cancel}} button to abort the operation. This will undo any changes that have not been applied. |
|||
The dialog can also be launched by clicking on the ellipsis button {{Button|...}} that appears in the [[Property_editor|property editor]] when you click on the {{PropertyData|Placement}} property. |
|||
==Notes== |
|||
* For more information about the placement parameters see the [[Placement|Placement]] page, and the [[Aeroplane|Aeroplane]] tutorial. |
|||
* The rotation angle can be set in degrees in the GUI but is stored in radians internally so that angles usually have to be converted when used in scripts. |
|||
==Scripting== |
|||
{{Emphasis|See also:}} [[FreeCAD_Scripting_Basics|FreeCAD Scripting Basics]]. |
|||
See the [[Python_scripting_tutorial#Vectors_and_placements|Python scripting tutorial]]. |
|||
A placement is internally defined by a matrix; in many cases it is simpler to represent it by means of two components, a {{incode|Base}} point (vector), and a {{incode|Rotation}} value. The {{incode|Rotation}} itself has different representations; it can be entirely defined by the value of a "[https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Quaternion quaternion]" {{incode|(xi + yj + zk + w)}}, but it can also be described by a rotation {{incode|Axis}} (unit vector) and a rotation {{incode|Angle}} (radians). |
|||
{{Code|code= |
|||
import FreeCAD as App |
|||
doc = App.newDocument() |
|||
obj = doc.addObject("Part::Cylinder", "Cylinder") |
|||
print(obj.Placement) |
|||
# Placement [Pos=(0,0,0), Yaw-Pitch-Roll=(0,0,0)] |
|||
print(obj.Placement.Base) |
|||
# Vector (0.0, 0.0, 0.0) |
|||
print(obj.Placement.Rotation) |
|||
# Rotation (0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 1.0) |
|||
print(obj.Placement.Rotation.Angle) |
|||
# 0.0 |
|||
print(obj.Placement.Rotation.Axis) |
|||
# Vector (0.0, 0.0, 1.0) |
|||
print(obj.Placement.Rotation.Q) |
|||
# (0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 1.0) |
|||
}} |
|||
Move the base point of the object, then rotate the object 45 degrees around the X axis. |
|||
The math module supplies a method {{incode|radians()}} to easily convert degrees to radians and has to be imported at first. |
|||
{{Code|code= |
|||
==Links and Example== |
|||
import math |
|||
obj.Placement.Base = App.Vector(5, 3, 1) |
|||
obj.Placement.Rotation.Axis = App.Vector(1, 0, 0) |
|||
obj.Placement.Rotation.Angle = math.radians(45) |
|||
print(obj.Placement) |
|||
A practical example of using this command is in the tutorial [[Aeroplane| Aeroplane]]. |
|||
# Placement [Pos=(5,3,1), Yaw-Pitch-Roll=(0,0,45)] |
|||
print(obj.Placement.Rotation.Q) |
|||
# (0.3826834323650898, 0.0, 0.0, 0.9238795325112867) |
|||
print(obj.Placement.Matrix) |
|||
# Matrix ((1,0,0,5),(0,0.707107,-0.707107,3),(0,0.707107,0.707107,1),(0,0,0,1)) |
|||
}} |
|||
{{Docnav |
|||
|[[Std_SendToPythonConsole|SendToPythonConsole]] |
|||
|[[Std_TransformManip|TransformManip]] |
|||
|[[Std_Edit_Menu|Std Edit Menu]] |
|||
|IconL=Std_SendToPythonConsole.svg |
|||
|IconR=Std_TransformManip.svg |
|||
|IconC=Freecad.svg |
|||
}} |
|||
{{Std Base navi{{#translation:}}}} |
|||
{{clear}} |
|||
{{Userdocnavi{{#translation:}}}} |
|||
Latest revision as of 10:01, 20 September 2023
|
|
| Menu location |
|---|
| Edit → Placement... |
| Workbenches |
| All |
| Default shortcut |
| None |
| Introduced in version |
| - |
| See also |
| Tasks Placement, Placement |
Descriere
Placement este modul în care FreeCAD specifică locația și atitudinea (orientarea) unui obiect în spațiu. Placement can be specified in multiple forms and manipulated via scripting, the Properties panel or the Edit → Placement... dialog.
The Placement task panel
Utilizare
- Short description
- Select an object in the tree view.
- In the Edit menu, select Placements...
- Change the parameters for the translation or rotation, according to the desired action.
- Click OK or Apply
- For a full description see Tasks Placement and Placement
- Select a single object that has a DatePlacement property in the property editor.
- Select the Edit → Placement... option from the menu.
- Change one or more of the translation and rotation parameters.
- Do one of the following:
- Press the OK button to apply the changes and close the task panel.
- Press the Apply button to apply the changes, but keep the task panel open for further changes.
- Press Esc or the Cancel button to abort the operation. This will undo any changes that have not been applied.
The dialog can also be launched by clicking on the ellipsis button ... that appears in the property editor when you click on the DatePlacement property.
Notes
- For more information about the placement parameters see the Placement page, and the Aeroplane tutorial.
- The rotation angle can be set in degrees in the GUI but is stored in radians internally so that angles usually have to be converted when used in scripts.
Scripting
See also: FreeCAD Scripting Basics.
See the Python scripting tutorial.
A placement is internally defined by a matrix; in many cases it is simpler to represent it by means of two components, a Base point (vector), and a Rotation value. The Rotation itself has different representations; it can be entirely defined by the value of a "quaternion" (xi + yj + zk + w), but it can also be described by a rotation Axis (unit vector) and a rotation Angle (radians).
import FreeCAD as App
doc = App.newDocument()
obj = doc.addObject("Part::Cylinder", "Cylinder")
print(obj.Placement)
# Placement [Pos=(0,0,0), Yaw-Pitch-Roll=(0,0,0)]
print(obj.Placement.Base)
# Vector (0.0, 0.0, 0.0)
print(obj.Placement.Rotation)
# Rotation (0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 1.0)
print(obj.Placement.Rotation.Angle)
# 0.0
print(obj.Placement.Rotation.Axis)
# Vector (0.0, 0.0, 1.0)
print(obj.Placement.Rotation.Q)
# (0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 1.0)
Move the base point of the object, then rotate the object 45 degrees around the X axis.
The math module supplies a method radians() to easily convert degrees to radians and has to be imported at first.
import math
obj.Placement.Base = App.Vector(5, 3, 1)
obj.Placement.Rotation.Axis = App.Vector(1, 0, 0)
obj.Placement.Rotation.Angle = math.radians(45)
print(obj.Placement)
# Placement [Pos=(5,3,1), Yaw-Pitch-Roll=(0,0,45)]
print(obj.Placement.Rotation.Q)
# (0.3826834323650898, 0.0, 0.0, 0.9238795325112867)
print(obj.Placement.Matrix)
# Matrix ((1,0,0,5),(0,0.707107,-0.707107,3),(0,0.707107,0.707107,1),(0,0,0,1))
- File: New, Open, Close, Close All, Save, Save As, Save a Copy, Save All, Revert, Import, Export,Merge project, Project information, Print, Print preview, Export PDF, Recent files, Exit
- Edit: Undo, Redo, Cut, Copy, Paste, Duplicate selection, Refresh, Box selection, Box element selection, Select All, Delete, Send to Python Console, Placement, Transform, Alignment, Toggle Edit mode, Edit mode, Preferences
- View:
- Miscellaneous: Create new view, Orthographic view, Perspective view, Fullscreen, Bounding box, Toggle axis cross, Clipping plane, Texture mapping, Toggle navigation/Edit mode, Appearance, Random color, Workbench, Status bar
- Standard views: Fit all, Fit selection, Isometric, Dimetric, Trimetric, Home, Front, Top, Right, Rear, Bottom, Left, Rotate Left, Rotate Right
- Freeze display: Save views, Load views, Freeze view, Clear views
- Draw style: As is, Points, Wireframe, Hidden line, No shading, Shaded, Flat lines
- Stereo: Stereo red/cyan, Stereo quad buffer, Stereo Interleaved Rows, Stereo Interleaved Columns, Stereo Off, Issue camera position
- Zoom: Zoom In, Zoom Out, Box zoom
- Document window: Docked, Undocked, Fullscreen
- Visibility: Toggle visibility, Show selection, Hide selection, Select visible objects, Toggle all objects, Show all objects, Hide all objects, Toggle selectability, Toggle measurement, Clear measurement
- Toolbars: File, Edit, Clipboard, Workbench, Macro, View, Structure, Help
- Panels: Tree view, Property view, Selection view, Tasks, Python console, DAG view, Model, Report view
- Link navigation: Go to linked object, Go to the deepest linked object, Select all links
- Tree view actions: Sync view, Sync selection, Sync placement, Pre-selection, Record selection, Single document, Multi document, Collapse/Expand, Initiate dragging, Go to selection, Selection Back, Selection Forward
- Tools: Edit parameters, Save image, Load image, Scene inspector, Dependency graph, Project utility, Measure distance, Add text document, View turntable, Units calculator, Customize, Addon manager
- Macro: Macro recording, Macros, Recent macros, Execute macro, Attach to remote debugger, Debug macro, Stop debugging, Step over, Step into, Toggle breakpoint
- Help: Help, FreeCAD Website, Donate, Users documentation, Python scripting documentation, Automatic Python modules documentation, FreeCAD Forum, FreeCAD FAQ, Report a bug, About FreeCAD, What's This
- Getting started
- Installation: Download, Windows, Linux, Mac, Additional components, Docker, AppImage, Ubuntu Snap
- Basics: About FreeCAD, Interface, Mouse navigation, Selection methods, Object name, Preferences, Workbenches, Document structure, Properties, Help FreeCAD, Donate
- Help: Tutorials, Video tutorials
- Workbenches: Std Base, Arch, Assembly, CAM, Draft, FEM, Inspection, Mesh, OpenSCAD, Part, PartDesign, Points, Reverse Engineering, Robot, Sketcher, Spreadsheet, Surface, TechDraw, Test Framework
- Hubs: User hub, Power users hub, Developer hub