Draft CircularArray: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
(Removed Preferences paragraph.) |
||
| (14 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{Page_in_progress}} |
|||
<languages/> |
<languages/> |
||
<translate> |
<translate> |
||
| Line 7: | Line 6: | ||
|[[Draft_PolarArray|PolarArray]] |
|[[Draft_PolarArray|PolarArray]] |
||
|[[Draft_PathArray|PathArray]] |
|[[Draft_PathArray|PathArray]] |
||
|[[ |
|[[Draft_Workbench|Draft]] |
||
|IconL=Draft_PolarArray.svg |
|IconL=Draft_PolarArray.svg |
||
|IconR=Draft_PathArray.svg |
|IconR=Draft_PathArray.svg |
||
| Line 17: | Line 16: | ||
|Name=Draft CircularArray |
|Name=Draft CircularArray |
||
|MenuLocation=Modification → Array tools → Circular array |
|MenuLocation=Modification → Array tools → Circular array |
||
|Workbenches=[[Draft |
|Workbenches=[[Draft_Workbench|Draft]], [[Arch_Workbench|Arch]] |
||
|Version=0.19 |
|Version=0.19 |
||
|SeeAlso=[[Draft_OrthoArray|Draft OrthoArray]], [[Draft_PolarArray|Draft PolarArray]], [[Draft_PathArray|Draft PathArray]], [[Draft_PathLinkArray|Draft PathLinkArray]], [[Draft_PointArray|Draft PointArray]], [[ |
|SeeAlso=[[Draft_OrthoArray|Draft OrthoArray]], [[Draft_PolarArray|Draft PolarArray]], [[Draft_PathArray|Draft PathArray]], [[Draft_PathLinkArray|Draft PathLinkArray]], [[Draft_PointArray|Draft PointArray]], [[Draft_PointLinkArray|Draft PointLinkArray]] |
||
}} |
}} |
||
| Line 25: | Line 24: | ||
<!--T:4--> |
<!--T:4--> |
||
The |
The [[Image:Draft_CircularArray.svg|24px]] '''Draft CircularArray''' command creates an array from a selected object by placing copies along concentric circumferences. The command can optionally create a [[App_Link|Link]] array, which is more efficient than a regular array. |
||
<!--T:5--> |
<!--T:5--> |
||
The command can be used on 2D objects created with the [[Draft_Workbench|Draft Workbench]] or [[Sketcher_Workbench|Sketcher Workbench]], but also on many 3D objects such as those created with the [[Part_Workbench|Part Workbench]], [[PartDesign_Workbench|PartDesign Workbench]] or [[Arch_Workbench|Arch Workbench]]. |
|||
| ⚫ | |||
* To create orthogonal or polar arrays, use the corresponding {{Button|[[File:Draft_OrthoArray.svg|16px]] [[Draft_OrthoArray|OrthoArray]]}} and {{Button|[[File:Draft_PolarArray.svg|16px]] [[Draft_PolarArray|PolarArray]]}} tools. |
|||
* To position copies along a path use {{Button|[[File:Draft_PathArray.svg|16px]] [[Draft_PathArray|PathArray]]}} or {{Button|[[File:Draft_PathLinkArray.svg|16px]] [[Draft_PathLinkArray|PathLinkArray]]}}. |
|||
* To position copies at specified points use {{Button|[[File:Draft_PointArray.svg|16px]] [[Draft_PointArray|PointArray]]}} or {{Button|[[File:Draft_PointLinkArray.svg|16px]] [[Draft_PointLinkArray|PointLinkArray]]}}. |
|||
* To create copies and manually place them use {{Button|[[File:Draft_Move.svg|16px]] [[Draft_Move|Move]]}} or {{Button|[[File:Draft_Rotate.svg|16px]] [[Draft_Rotate|Rotate]]}}. |
|||
* To create exact copies and manually place or scale them, use {{Button|[[File:Draft_Clone.svg|16px]] [[Draft_Clone|Clone]]}} or {{Button|[[File:Std_LinkMake.svg|16px]] [[Std_LinkMake|Std LinkMake]]}}. |
|||
</translate> |
</translate> |
||
| Line 41: | Line 33: | ||
<translate> |
<translate> |
||
<!--T:7--> |
<!--T:7--> |
||
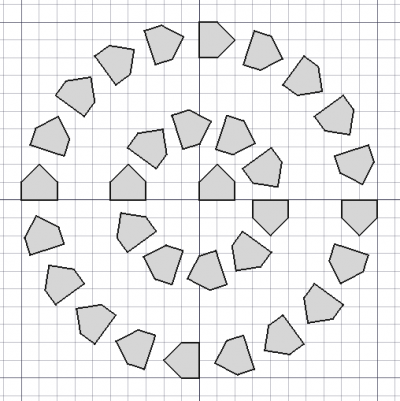
{{Caption| |
{{Caption|Draft CircularArray}} |
||
== Usage == <!--T:8--> |
== Usage == <!--T:8--> |
||
| ⚫ | |||
See also: [[Draft_Snap|Draft Snap]]. |
|||
<!--T:9--> |
<!--T:9--> |
||
# Optionally select one object. |
|||
# Select the object from which you wish to array. |
|||
# There are several ways to invoke the command: |
|||
# Press the {{Button|[[ |
#* Press the {{Button|[[Image:Draft_CircularArray.svg|16px]] [[Draft_CircularArray|Circular array]]}} button. |
||
# The [[task_panel|task panel]] is launched where you can select the radial distance, the tangential distance, the number of circular layers, the symmetry parameter, and the center of the axis of rotation. |
|||
#* Select the {{MenuCommand|Modification → Array tools → [[Image:Draft_CircularArray.svg|16px]] Circular array}} option from the menu. |
|||
# You can click on the [[3D_view|3D view]] to simultaneously set the position of the center of rotation, and complete the command. Otherwise, just press {{KEY|Enter}} or the {{Button|OK}} button to complete the operation. |
|||
# The {{MenuCommand|Circular array}} task panel opens. See [[#Options|Options]] for more information. |
|||
# If you have not yet selected an object: select one object. |
|||
# Enter the required parameters in the task panel. |
|||
# To finish the command do one of the following: |
|||
#* Pick a point in the [[3D_view|3D view]] for the {{MenuCommand|Center of rotation}}. |
|||
#* Press {{KEY|Enter}}. |
|||
#* Press the {{Button|OK}} button. |
|||
== Options == <!--T:11--> |
== Options == <!--T:11--> |
||
| Line 58: | Line 60: | ||
* Enter the {{MenuCommand|Number of circular layers}}. The element at the center counts as one layer. Must be at least {{Value|2}}. The maximum that can be entered in the task panel is {{Value|99}}, but higher values are possible by changing the {{PropertyData|Number Circles}} property of the array. |
* Enter the {{MenuCommand|Number of circular layers}}. The element at the center counts as one layer. Must be at least {{Value|2}}. The maximum that can be entered in the task panel is {{Value|99}}, but higher values are possible by changing the {{PropertyData|Number Circles}} property of the array. |
||
* Enter the {{MenuCommand|Symmetry}} value. This number determines how the elements are distributed. A value of {{Value|3}}, for example, results in a pattern with three equal 120° pie segments. Larger values for the {{MenuCommand|Symmetry}} and the {{MenuCommand|Tangential distance}} result in fewer or even no elements on the inner layers. |
* Enter the {{MenuCommand|Symmetry}} value. This number determines how the elements are distributed. A value of {{Value|3}}, for example, results in a pattern with three equal 120° pie segments. Larger values for the {{MenuCommand|Symmetry}} and the {{MenuCommand|Tangential distance}} result in fewer or even no elements on the inner layers. |
||
* Pick a point in the [[3D_view|3D view]] or type |
* Pick a point in the [[3D_view|3D view]], note that this will also finish the command, or type coordinates for the {{MenuCommand|Center of rotation}}. The rotation axis of the array will pass through this point. It is advisable to move the pointer out of the [[3D_view|3D view]] before entering coordinates. |
||
* Press the {{MenuCommand|Reset point}} button to reset the {{MenuCommand|Center of rotation}} to the origin. |
* Press the {{MenuCommand|Reset point}} button to reset the {{MenuCommand|Center of rotation}} to the origin. |
||
* If the {{MenuCommand|Fuse}} checkbox is checked overlapping elements in the array are fused. This does not work for Link arrays. |
* If the {{MenuCommand|Fuse}} checkbox is checked overlapping elements in the array are fused. This does not work for Link arrays. |
||
| Line 64: | Line 66: | ||
* Press {{KEY|Esc}} or the {{Button|Cancel}} button to abort the command. |
* Press {{KEY|Esc}} or the {{Button|Cancel}} button to abort the command. |
||
== |
==Notes== <!--T:29--> |
||
<!--T:10--> |
<!--T:10--> |
||
| Line 70: | Line 72: | ||
* A Draft CircularArray can be turned into a [[Draft_OrthoArray|Draft OrthoArray]] or a [[Draft_PolarArray|Draft PolarArray]] by changing its {{PropertyData|Array Type}} property. |
* A Draft CircularArray can be turned into a [[Draft_OrthoArray|Draft OrthoArray]] or a [[Draft_PolarArray|Draft PolarArray]] by changing its {{PropertyData|Array Type}} property. |
||
* A Link array cannot be turned into a regular array or vice versa. The type of array must be decided at creation time. |
* A Link array cannot be turned into a regular array or vice versa. The type of array must be decided at creation time. |
||
== Preferences == |
|||
See also: [[Preferences_Editor|Preferences Editor]] and [[Draft_Preferences|Draft Preferences]]. |
|||
* To change the number of decimals used for the input of coordinates and distances: {{MenuCommand|Edit → Preferences... → General → Units → Units settings → Number of decimals}}. |
|||
== Properties == <!--T:13--> |
== Properties == <!--T:13--> |
||
| Line 90: | Line 86: | ||
To create a circular array use the {{incode|make_array}} method ({{Version|0.19}}) of the Draft module. This method replaces the deprecated {{incode|makeArray}} method. The {{incode|make_array}} method can create [[Draft_OrthoArray|Draft OrthoArrays]], [[Draft_PolarArray|Draft PolarArrays]] and Draft CircularArrays. For each array type one or more wrappers are available. |
To create a circular array use the {{incode|make_array}} method ({{Version|0.19}}) of the Draft module. This method replaces the deprecated {{incode|makeArray}} method. The {{incode|make_array}} method can create [[Draft_OrthoArray|Draft OrthoArrays]], [[Draft_PolarArray|Draft PolarArrays]] and Draft CircularArrays. For each array type one or more wrappers are available. |
||
<!--T:33--> |
|||
The main method: |
The main method: |
||
| Line 98: | Line 95: | ||
<translate> |
<translate> |
||
<!--T:34--> |
|||
The wrapper for circular arrays is: |
The wrapper for circular arrays is: |
||
| Line 141: | Line 139: | ||
|[[Draft_PolarArray|PolarArray]] |
|[[Draft_PolarArray|PolarArray]] |
||
|[[Draft_PathArray|PathArray]] |
|[[Draft_PathArray|PathArray]] |
||
|[[ |
|[[Draft_Workbench|Draft]] |
||
|IconL=Draft_PolarArray.svg |
|IconL=Draft_PolarArray.svg |
||
|IconR=Draft_PathArray.svg |
|IconR=Draft_PathArray.svg |
||
Latest revision as of 19:49, 7 December 2023
|
|
| Menu location |
|---|
| Modification → Array tools → Circular array |
| Workbenches |
| Draft, Arch |
| Default shortcut |
| None |
| Introduced in version |
| 0.19 |
| See also |
| Draft OrthoArray, Draft PolarArray, Draft PathArray, Draft PathLinkArray, Draft PointArray, Draft PointLinkArray |
Description
The Draft CircularArray command creates an array from a selected object by placing copies along concentric circumferences. The command can optionally create a Link array, which is more efficient than a regular array.
The command can be used on 2D objects created with the Draft Workbench or Sketcher Workbench, but also on many 3D objects such as those created with the Part Workbench, PartDesign Workbench or Arch Workbench.
Draft CircularArray
Usage
See also: Draft Snap.
- Optionally select one object.
- There are several ways to invoke the command:
- Press the
Circular array button.
- Select the Modification → Array tools →
Circular array option from the menu.
- Press the
- The Circular array task panel opens. See Options for more information.
- If you have not yet selected an object: select one object.
- Enter the required parameters in the task panel.
- To finish the command do one of the following:
- Pick a point in the 3D view for the Center of rotation.
- Press Enter.
- Press the OK button.
Options
- Enter the Radial distance to specify the distance between the circular layers, and between the center and the first circular layer.
- Enter the Tangential distance to specify the distance between the elements on the same circular layer. Must be larger than zero.
- Enter the Number of circular layers. The element at the center counts as one layer. Must be at least
2. The maximum that can be entered in the task panel is99, but higher values are possible by changing the DataNumber Circles property of the array. - Enter the Symmetry value. This number determines how the elements are distributed. A value of
3, for example, results in a pattern with three equal 120° pie segments. Larger values for the Symmetry and the Tangential distance result in fewer or even no elements on the inner layers. - Pick a point in the 3D view, note that this will also finish the command, or type coordinates for the Center of rotation. The rotation axis of the array will pass through this point. It is advisable to move the pointer out of the 3D view before entering coordinates.
- Press the Reset point button to reset the Center of rotation to the origin.
- If the Fuse checkbox is checked overlapping elements in the array are fused. This does not work for Link arrays.
- If the Link array checkbox is checked a Link array instead of a regular array is created. A Link array is more efficient because its elements are App Link objects.
- Press Esc or the Cancel button to abort the command.
Notes
- The default rotation axis for the array is the positive Z axis. This can be changed by editing its DataAxis property.
- A Draft CircularArray can be turned into a Draft OrthoArray or a Draft PolarArray by changing its DataArray Type property.
- A Link array cannot be turned into a regular array or vice versa. The type of array must be decided at creation time.
Properties
See Draft OrthoArray.
Scripting
See also: Autogenerated API documentation and FreeCAD Scripting Basics.
To create a circular array use the make_array method (introduced in version 0.19) of the Draft module. This method replaces the deprecated makeArray method. The make_array method can create Draft OrthoArrays, Draft PolarArrays and Draft CircularArrays. For each array type one or more wrappers are available.
The main method:
array = make_array(base_object, arg1, arg2, arg3, arg4=None, arg5=None, arg6=None, use_link=True)
The wrapper for circular arrays is:
array = make_circular_array(base_object,
r_distance=100, tan_distance=50,
number=3, symmetry=1,
axis=App.Vector(0, 0, 1), center=App.Vector(0, 0, 0),
use_link=True)
base_objectis the object to be arrayed. It can also be theLabel(string) of an object in the current document.r_distanceandtan_distanceare the radial and tangential distances between the elements.numberis the number of circular layers in the pattern, the original object counts as the first layer.symmetryis an integer used in some calculations that affect the way the elements are distributed around the circumferences. Usual values are from 1 to 6. Higher values are not recommended and will make the elements in the inner layers disappear.axisandcenterare vectors that describe the direction of the axis of rotation, and a point through which that axis passes.- If
use_linkisTruethe created elements are App Links instead of regular copies. arrayis returned with the created array object.
Example:
import FreeCAD as App
import Draft
doc = App.newDocument()
tri = Draft.make_polygon(3, 600)
array = Draft.make_circular_array(tri, 1800, 1200, 4, 1)
doc.recompute()
- Drafting: Line, Polyline, Fillet, Arc, Arc by 3 points, Circle, Ellipse, Rectangle, Polygon, B-spline, Cubic Bézier curve, Bézier curve, Point, Facebinder, ShapeString, Hatch
- Annotation: Text, Dimension, Label, Annotation styles, Annotation scale
- Modification: Move, Rotate, Scale, Mirror, Offset, Trimex, Stretch, Clone, Array, Polar array, Circular array, Path array, Path link array, Point array, Point link array, Edit, Subelement highlight, Join, Split, Upgrade, Downgrade, Wire to B-spline, Draft to sketch, Set slope, Flip dimension, Shape 2D view
- Draft Tray: Select plane, Set style, Toggle construction mode, AutoGroup
- Snapping: Snap lock, Snap endpoint, Snap midpoint, Snap center, Snap angle, Snap intersection, Snap perpendicular, Snap extension, Snap parallel, Snap special, Snap near, Snap ortho, Snap grid, Snap working plane, Snap dimensions, Toggle grid
- Miscellaneous: Apply current style, Layer, Manage layers, Add a new named group, Move to group, Select group, Add to construction group, Toggle normal/wireframe display, Create working plane proxy, Heal, Show snap toolbar
- Additional: Constraining, Pattern, Preferences, Import Export Preferences, DXF/DWG, SVG, OCA, DAT
- Context menu:
- Layer container: Merge layer duplicates, Add new layer
- Layer: Activate this layer, Select layer contents
- Text: Open hyperlinks
- Wire: Flatten
- Working plane proxy: Write camera position, Write objects state
- Getting started
- Installation: Download, Windows, Linux, Mac, Additional components, Docker, AppImage, Ubuntu Snap
- Basics: About FreeCAD, Interface, Mouse navigation, Selection methods, Object name, Preferences, Workbenches, Document structure, Properties, Help FreeCAD, Donate
- Help: Tutorials, Video tutorials
- Workbenches: Std Base, Arch, Assembly, CAM, Draft, FEM, Inspection, Mesh, OpenSCAD, Part, PartDesign, Points, Reverse Engineering, Robot, Sketcher, Spreadsheet, Surface, TechDraw, Test Framework
- Hubs: User hub, Power users hub, Developer hub