Std Placement/ru: Difference between revisions
(Updating to match new version of source page) |
(Updating to match new version of source page) |
||
| (17 intermediate revisions by 3 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
<languages/> |
<languages/> |
||
{{Docnav |
{{Docnav/ru |
||
|[[Std_SendToPythonConsole| |
|[[Std_SendToPythonConsole/ru|Команда "Отправить в консоль Python"]] |
||
|[[Std_TransformManip/ru|Команда "Преобразование"]] |
|||
|[[Std_Alignment|Std Alignment]] |
|||
|[[Std_Edit_Menu| |
|[[Std_Edit_Menu/ru|Меню "Правка"]] |
||
|IconL=Std_SendToPythonConsole.svg |
|IconL=Std_SendToPythonConsole.svg |
||
|IconR= |
|IconR=Std_TransformManip.svg |
||
|IconC=Freecad.svg |
|IconC=Freecad.svg |
||
}} |
}} |
||
{{GuiCommand/ru |
|||
<div class="mw-translate-fuzzy"> |
|||
|Name/ru=Расположение |
|||
{{GuiCommand/ru|Name=Std Placement|Name/ru=Std Placement|MenuLocation=[[Std Edit Menu/ru|Правка]] → Размещение...||Workbenches=All|Shortcut=|SeeAlso=[[Tasks Placement/ru|Tasks Placement]], [[Placement/ru|Placement]]}} |
|||
|Name=Std_Placement |
|||
</div> |
|||
|MenuLocation=Правка → Расположение... |
|||
|Workbenches=Все |
|||
|SeeAlso=[[Std_Alignment/ru|Выравнивание]], [[Placement/ru|Расположение]] |
|||
}} |
|||
= |
<span id="Description"></span> |
||
==Описание== |
|||
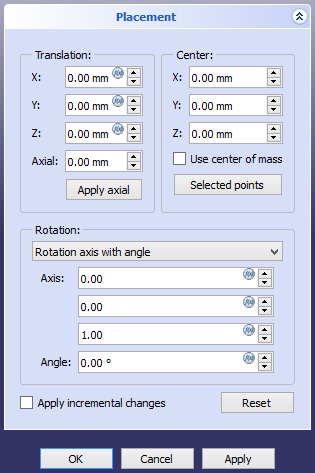
The '''Std Placement''' command displays the Placement [[Task_panel|task panel]] for a selected object. |
The '''Std Placement''' command displays the Placement [[Task_panel|task panel]] for a selected object. |
||
[[Image: |
[[Image:Std_Placement_taskpanel.png]] |
||
{{Caption|The Placement task panel}} |
{{Caption|The Placement task panel}} |
||
= |
<span id="Usage"></span> |
||
==Применение== |
|||
# Select a single object |
# Select a single object that has a {{PropertyData|Placement}} property in the [[Property_editor|property editor]]. |
||
# Select the {{MenuCommand|Edit → Placement...}} option from the menu. |
# Select the {{MenuCommand|Edit → Placement...}} option from the menu. |
||
# Change one or more of the translation and rotation parameters. |
# Change one or more of the translation and rotation parameters. |
||
| Line 29: | Line 35: | ||
#* Press the {{Button|OK}} button to apply the changes and close the task panel. |
#* Press the {{Button|OK}} button to apply the changes and close the task panel. |
||
#* Press the {{Button|Apply}} button to apply the changes, but keep the task panel open for further changes. |
#* Press the {{Button|Apply}} button to apply the changes, but keep the task panel open for further changes. |
||
| ⚫ | |||
The dialog can also be launched by clicking on the ellipsis button {{Button|...}} that appears in the [[Property_editor|property editor]] when you click on the {{PropertyData|Placement}} property. |
|||
==Options== |
|||
<span id="Notes"></span> |
|||
| ⚫ | |||
==Примечания== |
|||
| ⚫ | |||
==Notes== |
|||
* The rotation angle can be set in degrees in the GUI but is stored in radians internally so that angles usually have to be converted when used in scripts. |
|||
* The Placement task panel is also displayed when you select an object, click in the {{PropertyData|Placement}} field in the [[Property_editor|Property editor]] or the [[Combo_view|Combo view]], and then press the {{Button|...}} button that appears. |
|||
| ⚫ | |||
==Scripting== |
==Scripting== |
||
{{Emphasis| |
{{Emphasis|Смотрите так же:}} [[FreeCAD_Scripting_Basics/ru|Основы составления скриптов в FreeCAD]]. |
||
| ⚫ | |||
A placement is internally defined by a matrix; in many cases it is simpler to represent it by means of two components, a {{incode|Base}} point (vector), and a {{incode|Rotation}} value. The {{incode|Rotation}} itself has different representations; it can be entirely defined by the value of a "[https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Quaternion quaternion]" {{incode|(xi + yj + zk + w)}}, but it can also be described by a rotation {{incode|Axis}} (unit vector) and a rotation {{incode|Angle}} (radians). |
|||
{{Code|code= |
|||
import FreeCAD as App |
|||
doc = App.newDocument() |
|||
obj = doc.addObject("Part::Cylinder", "Cylinder") |
|||
print(obj.Placement) |
|||
# Placement [Pos=(0,0,0), Yaw-Pitch-Roll=(0,0,0)] |
|||
print(obj.Placement.Base) |
|||
# Vector (0.0, 0.0, 0.0) |
|||
print(obj.Placement.Rotation) |
|||
# Rotation (0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 1.0) |
|||
print(obj.Placement.Rotation.Angle) |
|||
# 0.0 |
|||
print(obj.Placement.Rotation.Axis) |
|||
# Vector (0.0, 0.0, 1.0) |
|||
print(obj.Placement.Rotation.Q) |
|||
# (0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 1.0) |
|||
}} |
|||
Move the base point of the object, then rotate the object 45 degrees around the X axis. |
|||
The math module supplies a method {{incode|radians()}} to easily convert degrees to radians and has to be imported at first. |
|||
{{Code|code= |
|||
import math |
|||
obj.Placement.Base = App.Vector(5, 3, 1) |
|||
obj.Placement.Rotation.Axis = App.Vector(1, 0, 0) |
|||
obj.Placement.Rotation.Angle = math.radians(45) |
|||
print(obj.Placement) |
|||
# Placement [Pos=(5,3,1), Yaw-Pitch-Roll=(0,0,45)] |
|||
print(obj.Placement.Rotation.Q) |
|||
# (0.3826834323650898, 0.0, 0.0, 0.9238795325112867) |
|||
print(obj.Placement.Matrix) |
|||
# Matrix ((1,0,0,5),(0,0.707107,-0.707107,3),(0,0.707107,0.707107,1),(0,0,0,1)) |
|||
}} |
|||
| ⚫ | |||
{{Docnav |
{{Docnav/ru |
||
|[[Std_SendToPythonConsole| |
|[[Std_SendToPythonConsole/ru|Команда "Отправить в консоль Python"]] |
||
|[[Std_TransformManip/ru|Команда "Преобразование"]] |
|||
|[[Std_Alignment|Std Alignment]] |
|||
|[[Std_Edit_Menu| |
|[[Std_Edit_Menu/ru|Меню "Правка"]] |
||
|IconL=Std_SendToPythonConsole.svg |
|IconL=Std_SendToPythonConsole.svg |
||
|IconR= |
|IconR=Std_TransformManip.svg |
||
|IconC=Freecad.svg |
|IconC=Freecad.svg |
||
}} |
}} |
||
| Line 56: | Line 105: | ||
{{Std Base navi{{#translation:}}}} |
{{Std Base navi{{#translation:}}}} |
||
{{Userdocnavi{{#translation:}}}} |
{{Userdocnavi{{#translation:}}}} |
||
{{clear}} |
|||
Latest revision as of 10:01, 20 September 2023
|
|
| Системное название |
|---|
| Std_Placement |
| Расположение в меню |
| Правка → Расположение... |
| Верстаки |
| Все |
| Быстрые клавиши |
| Нет |
| Представлено в версии |
| - |
| См. также |
| Выравнивание, Расположение |
Описание
The Std Placement command displays the Placement task panel for a selected object.
The Placement task panel
Применение
- Select a single object that has a ДанныеPlacement property in the property editor.
- Select the Edit → Placement... option from the menu.
- Change one or more of the translation and rotation parameters.
- Do one of the following:
- Press the OK button to apply the changes and close the task panel.
- Press the Apply button to apply the changes, but keep the task panel open for further changes.
- Press Esc or the Cancel button to abort the operation. This will undo any changes that have not been applied.
The dialog can also be launched by clicking on the ellipsis button ... that appears in the property editor when you click on the ДанныеPlacement property.
Примечания
- For more information about the placement parameters see the Placement page, and the Aeroplane tutorial.
- The rotation angle can be set in degrees in the GUI but is stored in radians internally so that angles usually have to be converted when used in scripts.
Scripting
Смотрите так же: Основы составления скриптов в FreeCAD.
See the Python scripting tutorial.
A placement is internally defined by a matrix; in many cases it is simpler to represent it by means of two components, a Base point (vector), and a Rotation value. The Rotation itself has different representations; it can be entirely defined by the value of a "quaternion" (xi + yj + zk + w), but it can also be described by a rotation Axis (unit vector) and a rotation Angle (radians).
import FreeCAD as App
doc = App.newDocument()
obj = doc.addObject("Part::Cylinder", "Cylinder")
print(obj.Placement)
# Placement [Pos=(0,0,0), Yaw-Pitch-Roll=(0,0,0)]
print(obj.Placement.Base)
# Vector (0.0, 0.0, 0.0)
print(obj.Placement.Rotation)
# Rotation (0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 1.0)
print(obj.Placement.Rotation.Angle)
# 0.0
print(obj.Placement.Rotation.Axis)
# Vector (0.0, 0.0, 1.0)
print(obj.Placement.Rotation.Q)
# (0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 1.0)
Move the base point of the object, then rotate the object 45 degrees around the X axis.
The math module supplies a method radians() to easily convert degrees to radians and has to be imported at first.
import math
obj.Placement.Base = App.Vector(5, 3, 1)
obj.Placement.Rotation.Axis = App.Vector(1, 0, 0)
obj.Placement.Rotation.Angle = math.radians(45)
print(obj.Placement)
# Placement [Pos=(5,3,1), Yaw-Pitch-Roll=(0,0,45)]
print(obj.Placement.Rotation.Q)
# (0.3826834323650898, 0.0, 0.0, 0.9238795325112867)
print(obj.Placement.Matrix)
# Matrix ((1,0,0,5),(0,0.707107,-0.707107,3),(0,0.707107,0.707107,1),(0,0,0,1))
- Стандартное меню: Файл, Правка, Вид, Инструменты, Макросы, Окна, Справка
- Структура: Std Part, Std Group, Std LinkMake
- Файл: Создать, Открыть, Закрыть, Закрыть всё, Сохранить, Сохранить как, Сохранить копию, Сохранить всё, Вернуться, Импортировать, Экспортировать, Объединить проект, Информация о проекте, Печать, Предварительный просмотр, Экспортировать в PDF, Недавние файлы, Выход
- Правка: Отменить, Вернуть, Вырезать, Копировать, Вставить, Дублировать выбранное, Обновить, Выделить область, Box element selection, Выбрать всё, Удалить, Расположение, Выравнивание, Редактировать/закончить редактирование, Настройки
- Вид: Создать новый вид, Ортогональная проекция, Перспективная проекция, На весь экран, Стандартные виды (Уместить всё, Уместить выделенное, Isometric, Dimetric, Trimetric, Спереди, Сверху, Справа, Сзади, Снизу, Слева, Повернуть влево, Повернуть вправо), Freeze display (Save views, Load views, Freeze view, Clear views), Стиль представления (Как есть, Плоские линии, Shaded, Каркас, Точки, Скрытые линии, Без затенения), Bounding box, Стерео (Стерео красный/голубой, Четверная буферизация стерео, Стерео с чередованием строк, Стерео с чередованием столбцов, Выключить стерео, Выводить положения камеры), Масштаб (Увеличить, Уменьшить, Увеличить область), Окно документа (Закреплённое, Откреплённое, На весь экран), Показать/скрыть оси координат, Плоскость сечения, Текстурирование, Видимость (Видимость, Показать выделенные, Скрыть выделенные, Выбрать видимые объекты, Инвертировать все видимости, Показать все объекты, Скрыть все объекты, Откл/вкл выделяемость, Показывать замеры, Удалить замер), Навигация/редактирование, Внешний вид, Случайный цвет, Верстак, Панели инструментов (Файл, Верстак, Макрос, Вид, Структура, Навигация), Панели (Отчёт, Иерархия документа, Окно свойств, Просмотр выделения, Комбо панель, Консоль Python, DAG view), Tree view actions (Sync view, Sync selection, Sync placement, Pre-selection, Record selection, Single document, Multi document, Collapse/expand, Initiate dragging, Go to selection), Строка состояния
- Инструменты: Редактор параметров, Сохранить изображение, Инспектор сцены, Граф зависимостей, Project utility, Измерить расстояние, Text document, Поворотный просмотр, Конвертор величин, Настройка, Addon manager
- Макросы: Запись макроса, Остановить запись макроса, Макрос, Выполнить макрос, Отладка макросов, Остановить отладку, Шаг с обходом, Шаг с заходом, Установить/снять точку останова
- Окна: Следующее, Предыдущее, Плиткой, Каскадом, Окна
- Справка: Справка, Сайт FreeCAD, Пользовательская документация, Документация по созданию скриптов на Python, Автоматически сгенерированная документация Python, Форум FreeCAD, FreeCAD ЧаВо, О FreeCAD, Что это?
- Начинающим
- Установка: Загрузка, Windows, Linux, Mac, Дополнительных компонентов, Docker, AppImage, Ubuntu Snap
- Базовая: О FreeCAD, Интерфейс, Навигация мыши, Методы выделения, Имя объекта, Настройки, Верстаки, Структура документа, Свойства, Помоги FreeCAD, Пожертвования
- Помощь: Учебники, Видео учебники
- Верстаки: Std Base, Arch, Assembly, CAM, Draft, FEM, Inspection, Mesh, OpenSCAD, Part, PartDesign, Points, Reverse Engineering, Robot, Sketcher, Spreadsheet, Surface, TechDraw, Test Framework