Robot Workbench: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
|||
| (88 intermediate revisions by 20 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
<languages/> |
|||
The robot workbench is a tool to simulate industrial grade 6-axis robots, like e.g. [http://kuka.com/ Kuka]. |
|||
<translate> |
|||
<!--T:40--> |
|||
== General use == |
|||
{{Docnav |
|||
[[Image:KukaKR16FreeCAD.jpg|right|400px]] |
|||
|[[Reverse_Engineering_Workbench|Reverse Engineering Workbench]] |
|||
|[[Sketcher_Workbench|Sketcher Workbench]] |
|||
|IconL=Workbench_Reverse_Engineering.svg |
|||
|IconR=Workbench_Sketcher.svg |
|||
}} |
|||
<!--T:42--> |
|||
This workbench is an ongoing effort to implement an off-line programming tool for 6-axis industrial robots into FreeCAD. |
|||
{{VeryImportantMessage|The Robot Workbench is unmaintained. If you have experience with the topic and are interested in maintaining it, please state your intention in the developer's section of the [https://forum.freecadweb.org/index.php FreeCAD forum]. |
|||
<!--T:47--> |
|||
An examples you can find here: |
|||
The reason this workbench is still in the master source code is because this workbench is programmed in C++. If this workbench could be programmed in Python, then it could be made an [[external_workbenches|external workbench]] and it could be moved to a separate repository. |
|||
}} |
|||
== Introduction == <!--T:37--> |
|||
http://www.freecad-project.de/svn/ExampleData/Examples/RobotSimulation/ |
|||
</translate> |
|||
== Tools == |
|||
[[Image:Workbench_Robot.svg|thumb|128px|<translate><!--T:46--> Robot workbench icon</translate>]] |
|||
<translate> |
|||
<!--T:2--> |
|||
The [[Image:Workbench_Robot.svg|24px]] [[Robot_Workbench|Robot Workbench]] is a tool to simulate a standard [[Robot_6-Axis|6-axis industrial robot]], like [http://kuka.com/ Kuka]. |
|||
<!--T:38--> |
|||
== Scripting == |
|||
You can do the following tasks: |
|||
* Set up a simulation environment with a robot and work pieces. |
|||
* Create and fill up movement trajectories. |
|||
* Decompose features of a CAD part to a trajectory. |
|||
* Simulate the robot movement and reaching distance. |
|||
* Export the trajectory to a robot program file. |
|||
<!--T:3--> |
|||
This section is generated out of: http://free-cad.svn.sourceforge.net/viewvc/free-cad/trunk/src/Mod/Robot/RobotExample.py?view=markup |
|||
To get started try the [[Robot_tutorial|Robot tutorial]], and see the programming interface in the [https://github.com/FreeCAD/FreeCAD_sf_master/blob/master/src/Mod/Robot/RobotExample.py RobotExample.py] example file. |
|||
You can use this file directly if you want. |
|||
</translate> |
|||
Example how to use the basic robot class Robot6Axis which represents a 6-axis |
|||
{{TOCright}} |
|||
industrial robot. The Robot module is dependent on Part but not on other modules. |
|||
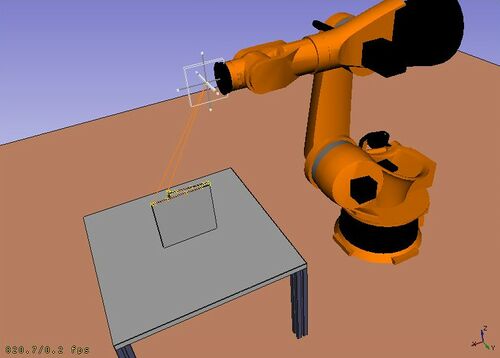
[[Image:Robot_Workbench_example.jpg|500px]] |
|||
It works mostly with the basic types Placement, Vector and Matrix. So we need |
|||
<translate> |
|||
only: |
|||
from Robot import * |
|||
from Part import * |
|||
from FreeCAD import * |
|||
=== Basic robot stuff === |
|||
create the robot. If you do not specify another kinematic it becomes a Puma 560 |
|||
rob = Robot6Axis() |
|||
print rob |
|||
accessing the axis and the Tcp. Axes go from 1-6 and are in degree: |
|||
Start = rob.Tcp |
|||
print Start |
|||
print rob.Axis1 |
|||
move the first axis of the robot: |
|||
rob.Axis1 = 5.0 |
|||
the Tcp has changed (forward kinematic) |
|||
print rob.Tcp |
|||
move the robot back to start position (reverse kinematic): |
|||
rob.Tcp = Start |
|||
print rob.Axis1 |
|||
the same with axis 2: |
|||
rob.Axis2 = 5.0 |
|||
print rob.Tcp |
|||
rob.Tcp = Start |
|||
print rob.Axis2 |
|||
Waypoints: |
|||
w = Waypoint(Placement(),name="Pt",type="LIN") |
|||
print w.Name,w.Type,w.Pos,w.Cont,w.Velocity,w.Base,w.Tool |
|||
generate more. The trajectory always finds automatically a unique name for the waypoints |
|||
l = [w] |
|||
for i in range(5): |
|||
l.append(Waypoint(Placement(Vector(0,0,i*100),Vector(1,0,0),0),"LIN","Pt")) |
|||
create a trajectory |
|||
t = Trajectory(l) |
|||
print t |
|||
for i in range(7): |
|||
t.insertWaypoints(Waypoint(Placement(Vector(0,0,i*100+500),Vector(1,0,0),0),"LIN","Pt")) |
|||
see a list of all waypoints: |
|||
print t.Waypoints |
|||
del rob,Start,t,l,w |
|||
=== working with the document === |
|||
== Tools == <!--T:4--> |
|||
Working with the robot document objects: |
|||
Here the principal commands you can use to create a robot set-up. |
|||
if(App.activeDocument() == None):App.newDocument() |
|||
=== Robots === <!--T:5--> |
|||
The tools to create and manage the 6-Axis robots |
|||
App.activeDocument().addObject("Robot::RobotObject","Robot") |
|||
Define the visual representation and the kinematic definition (see [[6-Axis Robot]] for details about that) |
|||
<!--T:6--> |
|||
App.activeDocument().Robot.RobotVrmlFile = App.getResourceDir()+"Mod/Robot/Lib/Kuka/kr500_1.wrl" |
|||
* [[Image:Robot_CreateRobot.svg|30px]] [[Robot_CreateRobot|Create a robot]]: Insert a new robot into the scene |
|||
App.activeDocument().Robot.RobotKinematicFile = App.getResourceDir()+"Mod/Robot/Lib/Kuka/kr500_1.csv" |
|||
* [[Image:Robot_Simulate.svg|30px]] [[Robot_Simulate|Simulate a trajectory]]: Opens the simulation dialog and lets you simulate |
|||
start positon of the Axis (only that which differ from 0) |
|||
* [[Image:Robot_Export.svg|30px]] [[Robot_Export|Export a trajectory]]: Export a robot program file |
|||
App.activeDocument().Robot.Axis2 = -90 |
|||
* [[Image:Robot_SetHomePos.svg|30px]] [[Robot_SetHomePos|Set home position]]: Set the home position of a robot |
|||
App.activeDocument().Robot.Axis3 = 90 |
|||
* [[Image:Robot_RestoreHomePos.svg|30px]] [[Robot_RestoreHomePos|Restore home position]]: move the robot to its home position |
|||
retrieve the Tcp position |
|||
=== Trajectories === <!--T:7--> |
|||
pos = FreeCAD.getDocument("Unnamed").getObject("Robot").Tcp |
|||
Tools to create and manipulate trajectories. There are two kinds, the parametric and non parametric ones. |
|||
move the robot |
|||
pos.move(App.Vector(-10,0,0)) |
|||
==== Non parametric trajectories ==== <!--T:8--> |
|||
FreeCAD.getDocument("Unnamed").getObject("Robot").Tcp = pos |
|||
* [[Image:Robot_CreateTrajectory.svg|30px]] [[Robot_CreateTrajectory|Create a trajectory]]: Inserts a new empty trajectory-object into the scene |
|||
* [[Image:Robot_SetDefaultOrientation.svg|30px]] [[Robot_SetDefaultOrientation|Set the default orientation]]: Set the orientation way-points gets created by default |
|||
create an empty Trajectory object in the active document |
|||
* [[Image:Robot_SetDefaultValues.svg|30px]] [[Robot_SetDefaultValues|Set the default speed parameter]]: Set the default values for way-point creation |
|||
App.activeDocument().addObject("Robot::TrajectoryObject","Trajectory") |
|||
* [[Image:Robot_InsertWaypoint.svg|30px]] [[Robot_InsertWaypoint|Insert a waypoint]]: Insert a way-point from the current robot position into a trajectory |
|||
get the Trajectory |
|||
* [[Image:Robot_InsertWaypointPre.svg|30px]] [[Robot_InsertWaypointPre|Insert a waypoint preselected]]: Insert a way-point from the current mouse position into a trajectory |
|||
t = App.activeDocument().Trajectory.Trajectory |
|||
add the actual TCP position of the robot to the trajectory |
|||
==== Parametric trajectories ==== <!--T:9--> |
|||
StartTcp = App.activeDocument().Robot.Tcp |
|||
* [[Image:Robot_Edge2Trac.svg|30px]] [[Robot_Edge2Trac|Create a trajectory out of edges]]: Insert a new object which decompose edges to a trajectory |
|||
t.insertWaypoints(StartTcp) |
|||
* [[Image:Robot_TrajectoryDressUp.svg|30px]] [[Robot_TrajectoryDressUp|Dress-up a trajectory]]: Lets you override one or more properties of a trajectory |
|||
App.activeDocument().Trajectory.Trajectory = t |
|||
* [[Image:Robot_TrajectoryCompound.svg|30px]] [[Robot_TrajectoryCompound|Trajectory compound]]: Create a compound out of some single trajectories |
|||
print App.activeDocument().Trajectory.Trajectory |
|||
== Scripting == <!--T:10--> |
|||
insert some more Waypoints and the start point at the end again: |
|||
for i in range(7): |
|||
<!--T:39--> |
|||
t.insertWaypoints(Waypoint(Placement(Vector(0,1000,i*100+500),Vector(1,0,0),i),"LIN","Pt")) |
|||
See the [[Robot_API_example|Robot API example]] for a description of the functions used to model the robot displacements. |
|||
t.insertWaypoints(StartTcp) # end point of the trajectory |
|||
== Tutorials == <!--T:34--> |
|||
App.activeDocument().Trajectory.Trajectory = t |
|||
* [[Robot 6-Axis|Robot 6-Axis]] |
|||
print App.activeDocument().Trajectory.Trajectory |
|||
* [[VRML Preparation for Robot Simulation|VRML Preparation for Robot Simulation]] |
|||
=== Simulation === |
|||
To be done..... ;-) |
|||
<!--T:35--> |
|||
{{Docnav |
|||
=== Exporting the trajectory === |
|||
|[[Reverse_Engineering_Workbench|Reverse Engineering Workbench]] |
|||
The trajectory is exported by Python. That means for every control cabinet type there is a post-processor |
|||
|[[Sketcher_Workbench|Sketcher Workbench]] |
|||
Python module. Here is in detail the Kuka post-processor described |
|||
|IconL=Workbench_Reverse_Engineering.svg |
|||
from KukaExporter import ExportCompactSub |
|||
|IconR=Workbench_Sketcher.svg |
|||
}} |
|||
ExportCompactSub(App.activeDocument().Robot,App.activeDocument().Trajectory,'D:/Temp/TestOut.src') |
|||
</translate> |
|||
and that's kind of how it's done: |
|||
{{Robot Tools navi{{#translation:}}}} |
|||
for w in App.activeDocument().Trajectory.Trajectory.Waypoints: |
|||
{{Userdocnavi{{#translation:}}}} |
|||
(A,B,C) = (w.Pos.Rotation.toEuler()) |
|||
[[Category:Workbenches{{#translation:}}]] |
|||
print ("LIN {X %.3f,Y %.3f,Z %.3f,A %.3f,B %.3f,C %.3f} ; %s"%(w.Pos.Base.x,w.Pos.Base.y,w.Pos.Base.z,A,B,C,w.Name)) |
|||
Latest revision as of 20:49, 3 December 2020
The reason this workbench is still in the master source code is because this workbench is programmed in C++. If this workbench could be programmed in Python, then it could be made an external workbench and it could be moved to a separate repository.
Introduction

The Robot Workbench is a tool to simulate a standard 6-axis industrial robot, like Kuka.
You can do the following tasks:
- Set up a simulation environment with a robot and work pieces.
- Create and fill up movement trajectories.
- Decompose features of a CAD part to a trajectory.
- Simulate the robot movement and reaching distance.
- Export the trajectory to a robot program file.
To get started try the Robot tutorial, and see the programming interface in the RobotExample.py example file.
Tools
Here the principal commands you can use to create a robot set-up.
Robots
The tools to create and manage the 6-Axis robots
Create a robot: Insert a new robot into the scene
Simulate a trajectory: Opens the simulation dialog and lets you simulate
Export a trajectory: Export a robot program file
Set home position: Set the home position of a robot
Restore home position: move the robot to its home position
Trajectories
Tools to create and manipulate trajectories. There are two kinds, the parametric and non parametric ones.
Non parametric trajectories
Create a trajectory: Inserts a new empty trajectory-object into the scene
Set the default orientation: Set the orientation way-points gets created by default
Set the default speed parameter: Set the default values for way-point creation
Insert a waypoint: Insert a way-point from the current robot position into a trajectory
Insert a waypoint preselected: Insert a way-point from the current mouse position into a trajectory
Parametric trajectories
Create a trajectory out of edges: Insert a new object which decompose edges to a trajectory
Dress-up a trajectory: Lets you override one or more properties of a trajectory
Trajectory compound: Create a compound out of some single trajectories
Scripting
See the Robot API example for a description of the functions used to model the robot displacements.
Tutorials
- Trajectories, non parametric: Create a trajectory, Set default orientation, Set default values, Insert waypoint, Insert waypoint (mouse)
- Trajectories, parametric: Create a trajectory from edges, Dress-up trajectory, Trajectory compound
- Getting started
- Installation: Download, Windows, Linux, Mac, Additional components, Docker, AppImage, Ubuntu Snap
- Basics: About FreeCAD, Interface, Mouse navigation, Selection methods, Object name, Preferences, Workbenches, Document structure, Properties, Help FreeCAD, Donate
- Help: Tutorials, Video tutorials
- Workbenches: Std Base, Arch, Assembly, CAM, Draft, FEM, Inspection, Mesh, OpenSCAD, Part, PartDesign, Points, Reverse Engineering, Robot, Sketcher, Spreadsheet, Start, Surface, TechDraw, Test Framework, Web
- Hubs: User hub, Power users hub, Developer hub