Robot Workbench/sv: Difference between revisions
Renatorivo (talk | contribs) No edit summary |
(Updating to match new version of source page) |
||
| Line 19: | Line 19: | ||
* [[Image:Robot_CreateRobot.png|30px]] [[Robot_CreateRobot|Create a robot]]: Insert a new robot into the scene |
* [[Image:Robot_CreateRobot.png|30px]] [[Robot_CreateRobot|Create a robot]]: Insert a new robot into the scene |
||
* [[Image:Robot_Simulate.png|30px]] [[Robot_Simulate|Simulate a trajectory]]: Opens the simulation dialog and |
* [[Image:Robot_Simulate.png|30px]] [[Robot_Simulate|Simulate a trajectory]]: Opens the simulation dialog and lets you simulate |
||
* [[Image:Robot_Export.png|30px]] [[Robot_Export|Export a trajectory]]: Export a robot program file |
* [[Image:Robot_Export.png|30px]] [[Robot_Export|Export a trajectory]]: Export a robot program file |
||
* [[Image:Robot_SetHomePos.png|30px]] [[Robot_SetHomePos|Set home positon]]: Set the home position of |
* [[Image:Robot_SetHomePos.png|30px]] [[Robot_SetHomePos|Set home positon]]: Set the home position of a robot |
||
* [[Image:Robot_RestoreHomePos.png|30px]] [[Robot_RestoreHomePos|Restore home positon]]: move the robot to its home position |
* [[Image:Robot_RestoreHomePos.png|30px]] [[Robot_RestoreHomePos|Restore home positon]]: move the robot to its home position |
||
=== Trajectories === |
=== Trajectories === |
||
Tools to |
Tools to create and manipulate trajectories. There are two kinds, the parametric and non parametric ones. |
||
==== non parametric ==== |
==== non parametric trajectories ==== |
||
* [[Image:Robot_CreateTrajectory.png|30px]] [[Robot_CreateTrajectory|Create a trajectory]]: |
* [[Image:Robot_CreateTrajectory.png|30px]] [[Robot_CreateTrajectory|Create a trajectory]]: Inserts a new empty trajectory-object into the scene |
||
* [[Image:Robot_SetDefaultOrientation.png|30px]] [[Robot_SetDefaultOrientation|Set the default orientation]]: Set the orientation way-points gets created by default |
* [[Image:Robot_SetDefaultOrientation.png|30px]] [[Robot_SetDefaultOrientation|Set the default orientation]]: Set the orientation way-points gets created by default |
||
* [[Image:Robot_SetDefaultValues.png|30px]] [[Robot_SetDefaultValues|Set the default speed parameter]]: |
* [[Image:Robot_SetDefaultValues.png|30px]] [[Robot_SetDefaultValues|Set the default speed parameter]]: Set the default values for way-point creation |
||
* [[Image:Robot_InsertWaypoint.png|30px]] [[Robot_InsertWaypoint|Insert a waypoint]]: Insert a way-point from the current robot position into a trajectory |
* [[Image:Robot_InsertWaypoint.png|30px]] [[Robot_InsertWaypoint|Insert a waypoint]]: Insert a way-point from the current robot position into a trajectory |
||
* [[Image:Robot_InsertWaypointPre.png|30px]] [[Robot_InsertWaypointPre|Insert a waypoint]]: Insert a way-point from the current mouse position into a trajectory |
* [[Image:Robot_InsertWaypointPre.png|30px]] [[Robot_InsertWaypointPre|Insert a waypoint]]: Insert a way-point from the current mouse position into a trajectory |
||
==== parametric ==== |
==== parametric trajectories ==== |
||
* [[Image:Robot_Edge2Trac.png|30px]] [[Robot_Edge2Trac|Create a trajectory out of edges]]: Insert a new object which decompose edges to a trajectory |
* [[Image:Robot_Edge2Trac.png|30px]] [[Robot_Edge2Trac|Create a trajectory out of edges]]: Insert a new object which decompose edges to a trajectory |
||
* [[Image:Robot_TrajectoryDressUp.png|30px]] [[Robot_TrajectoryDressUp|Dress-up a trajectory]]: |
* [[Image:Robot_TrajectoryDressUp.png|30px]] [[Robot_TrajectoryDressUp|Dress-up a trajectory]]: Lets you override one or more properties of a trajectory |
||
* [[Image:Robot_TrajectoryCompound.png|30px]] [[Robot_TrajectoryCompound|Trajectory compound]]: |
* [[Image:Robot_TrajectoryCompound.png|30px]] [[Robot_TrajectoryCompound|Trajectory compound]]: Create a compound out of some single trajectories |
||
== Skript == |
== Skript == |
||
Revision as of 14:04, 10 March 2016
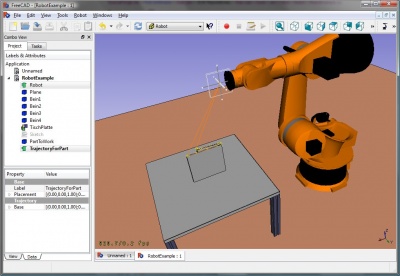
Robot arbetsbänken är ett verktyg för simulering av 6-axliga industrirobotar, som t.ex. Kuka. Denna arbetsbänk är ett pågående arbete för att implementera ett off-line programmeringsverktyg för Robot_6-Axis industrirobotar i FreeCAD. You can do following tasks:
- set up a simulation environment with a robot and work pieces
- create and fill up trajectories
- decompose features of an CAD part to a trajectory
- simulate the robot movement and reachability
- export the trajectory to a robot program file
Du kan hitta ett exempel här: Example files or try the Robot tutorial.
Tools
Here the principal commands you can use to create a robot set-up.
Robots
The tools to create and manage the 6-Axis robots
 Create a robot: Insert a new robot into the scene
Create a robot: Insert a new robot into the scene Simulate a trajectory: Opens the simulation dialog and lets you simulate
Simulate a trajectory: Opens the simulation dialog and lets you simulate Export a trajectory: Export a robot program file
Export a trajectory: Export a robot program file Set home positon: Set the home position of a robot
Set home positon: Set the home position of a robot Restore home positon: move the robot to its home position
Restore home positon: move the robot to its home position
Trajectories
Tools to create and manipulate trajectories. There are two kinds, the parametric and non parametric ones.
non parametric trajectories
 Create a trajectory: Inserts a new empty trajectory-object into the scene
Create a trajectory: Inserts a new empty trajectory-object into the scene Set the default orientation: Set the orientation way-points gets created by default
Set the default orientation: Set the orientation way-points gets created by default Set the default speed parameter: Set the default values for way-point creation
Set the default speed parameter: Set the default values for way-point creation Insert a waypoint: Insert a way-point from the current robot position into a trajectory
Insert a waypoint: Insert a way-point from the current robot position into a trajectory Insert a waypoint: Insert a way-point from the current mouse position into a trajectory
Insert a waypoint: Insert a way-point from the current mouse position into a trajectory
parametric trajectories
 Create a trajectory out of edges: Insert a new object which decompose edges to a trajectory
Create a trajectory out of edges: Insert a new object which decompose edges to a trajectory Dress-up a trajectory: Lets you override one or more properties of a trajectory
Dress-up a trajectory: Lets you override one or more properties of a trajectory Trajectory compound: Create a compound out of some single trajectories
Trajectory compound: Create a compound out of some single trajectories
Skript
Detta avsnitt är genererat från: https://github.com/FreeCAD/FreeCAD_sf_master/blob/master/src/Mod/Robot/RobotExample.py Du kan använda den filen direkt, om du vill.
Exempel på hur man använder klassen Robot6Axis, vilken representerar en 6-axlig industrirobot. Robot modulen beror på Delmodulen, men inte på andra modulen. Den arbetar mest med enkla typer som Placering, Vektor och Matris. Så vi behöver bara:
from Robot import *
from Part import *
from FreeCAD import *
Grundläggande robotsaker
Skapa roboten. Om du inte specificerar någon annan kinematik så blir det en Puma 560
rob = Robot6Axis()
print rob
komma åt axlarna och tcp (verktygets centrumpunkt). Axlarna är 1-6 och värdena uttrycks i grader:
Start = rob.Tcp
print Start
print rob.Axis1
flytta robotens första axel:
rob.Axis1 = 5.0
Tcp har ändrats (framåtgående kinematik)
print rob.Tcp
flytta tillbaka roboten till startpositionen (bakåtgående kinematik):
rob.Tcp = Start
print rob.Axis1
samma med axel 2:
rob.Axis2 = 5.0
print rob.Tcp
rob.Tcp = Start
print rob.Axis2
Banpunkter:
w = Waypoint(Placement(),name="Pt",type="LIN")
print w.Name,w.Type,w.Pos,w.Cont,w.Velocity,w.Base,w.Tool
generera mer. Banan hittar alltid automatiskt på ett unikt namn för banpunkterna
l = [w]
for i in range(5):
l.append(Waypoint(Placement(Vector(0,0,i*100),Vector(1,0,0),0),"LIN","Pt"))
Skapa en bana
t = Trajectory(l)
print t
for i in range(7):
t.insertWaypoints(Waypoint(Placement(Vector(0,0,i*100+500),Vector(1,0,0),0),"LIN","Pt"))
se en lista på alla banpunkter:
print t.Waypoints
del rob,Start,t,l,w
Working with the document objects
Arbeta med robotdokument objekten: skapa först en robot i det aktiva dokumentet
if(App.activeDocument() == None):App.newDocument()
App.activeDocument().addObject("Robot::RobotObject","Robot")
Definiera den visuella representationen och den kinematiska definitionen (se Robot_6-Axis för detaljer om det)
App.activeDocument().Robot.RobotVrmlFile = App.getResourceDir()+"Mod/Robot/Lib/Kuka/kr500_1.wrl"
App.activeDocument().Robot.RobotKinematicFile = App.getResourceDir()+"Mod/Robot/Lib/Kuka/kr500_1.csv"
Axelns startpositon (endast om det skiljer sig från 0)
App.activeDocument().Robot.Axis2 = -90
App.activeDocument().Robot.Axis3 = 90
hämta Tcp positionen
pos = FreeCAD.getDocument("Unnamed").getObject("Robot").Tcp
flytta roboten
pos.move(App.Vector(-10,0,0))
FreeCAD.getDocument("Unnamed").getObject("Robot").Tcp = pos
skapa ett tomt banobjekt i det aktiva dokumentet
App.activeDocument().addObject("Robot::TrajectoryObject","Trajectory")
hämta banan
t = App.activeDocument().Trajectory.Trajectory
lägg till robotens aktuella TCP position till banan
StartTcp = App.activeDocument().Robot.Tcp
t.insertWaypoints(StartTcp)
App.activeDocument().Trajectory.Trajectory = t
print App.activeDocument().Trajectory.Trajectory
sätt in några fler banpunkter och startpunkten i slutet igen:
for i in range(7):
t.insertWaypoints(Waypoint(Placement(Vector(0,1000,i*100+500),Vector(1,0,0),i),"LIN","Pt"))
t.insertWaypoints(StartTcp) # end point of the trajectory
App.activeDocument().Trajectory.Trajectory = t
print App.activeDocument().Trajectory.Trajectory
Simulation
ska göras.....
Exportera banan
Banan exporteras av Python. Det innebär att för varje robotkontroll typ så finns det en post-processor Python modul. Här är Kuka post-processorn beskriven i detalj
from KukaExporter import ExportCompactSub
ExportCompactSub(App.activeDocument().Robot,App.activeDocument().Trajectory,'D:/Temp/TestOut.src')
och det är ungefär så här det görs:
for w in App.activeDocument().Trajectory.Trajectory.Waypoints:
(A,B,C) = (w.Pos.Rotation.toEuler())
print ("LIN {X %.3f,Y %.3f,Z %.3f,A %.3f,B %.3f,C %.3f} ; %s"%(w.Pos.Base.x,w.Pos.Base.y,w.Pos.Base.z,A,B,C,w.Name))
Tutorials