Draft SelectPlane/sv: Difference between revisions
(Updating to match new version of source page) |
(Updating to match new version of source page) |
||
| (28 intermediate revisions by 3 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
<languages/> |
|||
{{Docnav |
|||
|[[Draft_Shape2DView|Shape2DView]] |
|||
|[[Draft_SetStyle|SetStyle]] |
|||
|[[Draft_Workbench|Draft]] |
|||
|IconL=Draft_Shape2DView.svg |
|||
|IconR=Draft_SetStyle.svg |
|||
|IconC=Workbench_Draft.svg |
|||
}} |
|||
<div class="mw-translate-fuzzy"> |
<div class="mw-translate-fuzzy"> |
||
{{GuiCommand/sv|Name=Draft_Workingplane|Workbenches=[[ |
{{GuiCommand/sv|Name=Draft_Workingplane|Workbenches=[[Draft_Workbench/sv|Skiss]]|MenuLocation=Drafting → SelectPlane}} |
||
</div> |
</div> |
||
==Description== |
|||
<div class="mw-translate-fuzzy"> |
|||
====Beskrivning==== |
====Beskrivning==== |
||
Detta verktyg väntar på att användaren ska markera en existerande yta i 3D vyn eller att välja ett av de förinställda planen. Arbetsplanet kommer då att ställas in till det planet, och alla efterföljande 2D operationer kommer endast att hända på detta plan. |
Detta verktyg väntar på att användaren ska markera en existerande yta i 3D vyn eller att välja ett av de förinställda planen. Arbetsplanet kommer då att ställas in till det planet, och alla efterföljande 2D operationer kommer endast att hända på detta plan. |
||
</div> |
|||
{{Version|0.22}}: For each 3D view a separate working plane is stored. |
|||
[[Image:Workingplane_example.jpg]] |
|||
The [[Image:Draft_tray_button_plane.png]] button in the [[Draft_Tray|Draft Tray]] changes depending on the current working plane. {{Version|0.22}}: If the working plane is not set to {{MenuCommand|Auto}} an asterisk ({{MenuCommand|*}}) is appended to the button label if the origin of the working plane does not match the global origin. |
|||
<div class="mw-translate-fuzzy"> |
|||
====Bruk==== |
|||
[[Image:WorkingPlane_example.png|400px]] |
|||
* Välj en yta på ett existerande objekt i 3D vyn |
|||
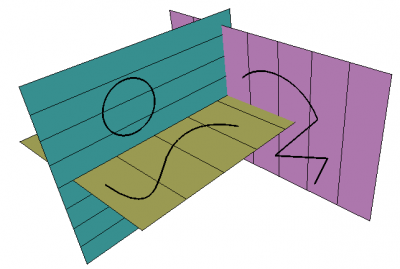
{{Caption|Shapes created on different working planes}} |
|||
* Alternativt, klicka på en av förvalsknapparna: {{KEY|XY}} (topp plan), {{KEY|XZ}} (fram plan) eller {{KEY|YZ}} (sido plan) |
|||
* Om du klickar på {{KEY|VIEW}} knappen så kommer arbetsplanet att bli samma som vyplanet, vinkelrätt till kameraaxeln och passerande genom origopunkten (0,0,0) |
|||
* Om du klickar på {{KEY|NONE}} så kommer arbetsplanet att tas bort. Nästa 2D operationer kommer att bli vyberoende. |
|||
* Du kan också specificera ett offsetvärde, vilket kommer att ställa in ditt arbetsplan till ett visst avstånd från det plan som du väljer. |
|||
</div> |
|||
==Usage with pre-selection== |
|||
==Options== |
|||
* To set the workplane to existing geometry: select a face of an existing object in the 3D view, or, {{Version|0.17}}, with CTRL pressed, 3 vertices on any object(s). Then press the {{KEY|[[Image:Draft SelectPlane.png|16px]] [[Draft SelectPlane|SelectPlane]]}} button |
|||
# Do one of the following: |
|||
* Pressing the {{KEY|'''VIEW'''}} button will set the working plane as the view plane, perpendicular to the camera axis and passing through the (0,0,0) origin point. |
|||
#* Select a single object. The following objects are supported: |
|||
* Pressing the {{KEY|'''AUTO'''}} will unset any current working plane. The next 2D operations will be view-dependent. |
|||
#** [[Draft_WorkingPlaneProxy|Draft WorkingPlaneProxies]]: the {{PropertyView|View Data}} (the camera position) and the {{PropertyView|Visibility Map}} (the saved visibility of objects) of the working plane proxy are also restored. |
|||
* You can also specify an offset value, which will set your working plane at a certain distance from the plane you select. |
|||
#** [[Arch_Axis|Arch Axes]] ({{Version|0.22}}) |
|||
* You can hide and show the grid with the shortcut {{KEY|'''G'''}}{{KEY|'''R'''}} |
|||
#** [[Arch_AxisSystem|Arch AxisSystems]] ({{Version|0.22}}) |
|||
#** [[Arch_BuildingPart|Arch BuildingParts]] |
|||
#** [[Arch_SectionPlane|Arch SectionPlanes]] |
|||
#** [[Std_Part|Std Parts]]: to avoid selecting subelements it is advisable to select these in the [[Tree_view|Tree view]]. |
|||
#** Non-solid objects that consist of a single flat face or a single curved edge, or ({{Version|0.22}}) that have three or more vertices. |
|||
#** Solid objects or objects without a shape that have a {{PropertyData|Placement}} property. ({{Version|0.22}}) |
|||
#* Select one or more subelements. You can select: |
|||
#** A flat face. |
|||
#** A curved edge. |
|||
#** Three vertices. |
|||
#** An edge and a vertex, or two edges. The combined vertices must define a plane. ({{Version|0.22}}) |
|||
# There are several ways to invoke the command: |
|||
#* Press the [[Image:Draft_tray_button_plane.png]] button in the [[Draft_Tray|Draft Tray]]. |
|||
#* Select the {{MenuCommand|Utilities → [[Image:Draft_SelectPlane.svg|16px]] Select plane}} option from the menu. |
|||
#* Use the keyboard shortcut: {{KEY|W}} then {{KEY|P}}. |
|||
# The working plane and the button in the [[Draft_Tray|Draft Tray]] are updated. |
|||
==Usage with post-selection== |
|||
# There are several ways to invoke the command: |
|||
#* Press the [[Image:Draft_tray_button_plane.png]] button in the [[Draft_Tray|Draft Tray]]. |
|||
#* Select the {{MenuCommand|Utilities → [[Image:Draft_SelectPlane.svg|16px]] Select plane}} option from the menu. |
|||
#* Use the keyboard shortcut: {{KEY|W}} then {{KEY|P}}. |
|||
# The {{MenuCommand|Working plane setup}} task panel opens. See [[#Options|Options]] for more information. |
|||
# Do one of the following: |
|||
#* Select a single object. See the [[#Usage_with_pre-selection|previous paragraph]]. |
|||
#* Select one or more subelements. See the [[#Usage_with_pre-selection|previous paragraph]]. |
|||
# Click anywhere in the [[3D_view|3D view]] to confirm the selection and finish the command. |
|||
# The working plane and the button in the [[Draft_Tray|Draft Tray]] are updated. |
|||
==Usage with presets== |
|||
# There are several ways to invoke the command: |
|||
#* Press the [[Image:Draft_tray_button_plane.png]] button in the [[Draft_Tray|Draft Tray]]. |
|||
#* Select the {{MenuCommand|Utilities → [[Image:Draft_SelectPlane.svg|16px]] Select plane}} option from the menu. |
|||
#* Use the keyboard shortcut: {{KEY|W}} then {{KEY|P}}. |
|||
# The {{MenuCommand|Working plane setup}} task panel opens. See [[#Options|Options]] for more information. |
|||
# Press any of the buttons to finish the command. |
|||
# The working plane and the button in the [[Draft_Tray|Draft Tray]] are updated. |
|||
==Options== |
|||
* Press the {{Button|[[Image:View-top.svg|16px]] Top (XY)}} button to align the working plane with the XY plane of the global coordinate system. |
|||
* Press the {{Button|[[Image:View-front.svg|16px]] Front (XZ)}} button to align the working plane with the XZ plane of the global coordinate system. |
|||
* Press the {{Button|[[Image:View-right.svg|16px]] Side (YZ)}} button to align the working plane with the YZ plane of the global coordinate system. |
|||
* Press the {{Button|[[Image:View-isometric.svg|16px]] Align to view}} button to align the working plane with the current [[3D_view|3D view]]. If the {{MenuCommand|Center plane on view}} checkbox is not checked the working plane origin will match the origin of the global coordinate system, else it will match the center of the current [[3D_view|3D view]]. |
|||
* Press the {{Button|[[Image:View-axonometric.svg|16px]] Automatic}} button to set the working plane to {{MenuCommand|Auto}}. A working plane set to {{MenuCommand|Auto}} will automatically align with the current [[3D_view|3D view]] whenever a Draft or [[Arch_Workbench|Arch]] command requiring point input is started. This is equivalent to pressing the {{Button|[[Image:View-isometric.svg|16px]] Align to view}} button before using the command. Additionally the working plane will align to planar faces that have been selected before starting the command, or when points on planar faces are picked during the command. |
|||
* The {{MenuCommand|Offset}} defines the perpendicular distance between the calculated plane and the actual working plane. |
|||
* Check the {{MenuCommand|Center plane on view}} checkbox to put the origin of the working plane in the center of to the current [[3D_view|3D view]]. This option can be useful in combination with the {{Button|[[Image:View-isometric.svg|16px]] Align to view}} button. |
|||
* Select a vertex in the [[3D_view|3D view]] and press the {{Button|[[Image:Draft_Move.svg|16px]] Move working plane}} button to move the working plane so that its origin matches the position of the selected vertex. |
|||
* The {{MenuCommand|Grid color}} button allows to quickly change the color of the grid. {{Version|0.22}} |
|||
* The {{MenuCommand|Grid spacing}} defines the distance between grid lines. |
|||
* The {{MenuCommand|Main line every}} value determines where main grid lines are drawn. Main grid lines are slightly thicker than normal grid lines. For example if the grid spacing is {{Value|0.5 m}} and there is a main line every {{Value|10 lines}}, such a line will occur every {{Value|5 m}}. |
|||
* The {{MenuCommand|Grid extension}} value determines the number of grid lines in the X and Y direction of the grid. |
|||
* The {{MenuCommand|Snapping radius}} is the maximum distance at which [[Draft_Snap_Grid|Draft Snap Grid]] detects the intersections of grid lines. |
|||
* Press the {{Button|[[Image:view-fullscreen.svg|16px]] Center view}} button to align the [[3D_view|3D view]] with the current working plane. |
|||
* Press the {{Button|[[Image:sel-back.svg|16px]] Previous}} button to reset the working plane to its previous position. |
|||
* Press the {{Button|Next [[Image:sel-forward.svg|16px]]}} button to reset the working plane to its next position. {{Version|0.22}} |
|||
* Press {{KEY|Esc}} or the {{Button|Close}} button to abort the command. |
|||
==Notes== |
|||
* It can be useful to align the [[3D_view|3D view]] with the selected Draft working plane. For example after switching the working plane to Front you may want to switch to the [[Std_ViewFront|Front view]] as well. |
|||
* The grid can be toggled with the [[Draft_ToggleGrid|Draft ToggleGrid]] command. |
|||
* By double-clicking [[Draft_WorkingPlaneProxy|Draft WorkingPlaneProxies]] in the [[Tree_view|Tree view]] you can quickly switch between working planes. |
|||
==Preferences== |
|||
See also: [[Preferences_Editor|Preferences Editor]] and [[Draft_Preferences|Draft Preferences]]. |
|||
* The grid settings in the task panel as well as several other grid settings are available as preferences: {{MenuCommand|Edit → Preferences... → Draft → Grid and snapping}}. |
|||
* The Snapping radius can also be changed on-the-fly (see [[Draft_Snap#Preferences|Draft Snap]]) or by changing: {{MenuCommand|Tools → Edit parameters... → BaseApp → Preferences → Mod → Draft → snapRange}}. |
|||
==Scripting== |
==Scripting== |
||
Working plane objects can easily be created and manipulated in scripts and [[macros]]. You can create your own, and use them independently of the current Draft working plane. |
|||
See also: [https://freecad.github.io/SourceDoc/ Autogenerated API documentation] and [[FreeCAD Scripting Basics|FreeCAD Scripting Basics]]. |
|||
Example: |
|||
{{Version|0.22}}: |
|||
The WorkingPlane module offers two classes to create working plane objects: the {{incode|PlaneBase}} class and the {{incode|PlaneGui}} class. The second class inherits from the first. Objects of the {{incode|PlaneGui}} class interact with the GUI (the [[Draft_Tray|Draft Tray]] button), the [[3D_view|3D view]] and the [[Draft_Snap_Grid|grid]]. {{incode|PlaneBase}} objects do not. |
|||
Use the {{incode|get_working_plane()}} method of the WorkingPlane module to get an instance of the {{incode|PlaneGui}} class linked to the current 3D view. The method either returns the existing working plane linked to the view or creates a new working plane if required. |
|||
{{Code|code= |
{{Code|code= |
||
import FreeCAD as App |
|||
import WorkingPlane |
import WorkingPlane |
||
myPlane = WorkingPlane.plane() |
|||
}} |
|||
wp = WorkingPlane.get_working_plane() |
|||
You can also access the current Draft working plane: |
|||
{{Code|code= |
|||
origin = App.Vector(0, 0, 0) |
|||
import FreeCAD |
|||
normal = App.Vector(1, 1, 1).normalize() |
|||
draftPlane = FreeCAD.DraftWorkingPlane |
|||
offset = 17 |
|||
wp.align_to_point_and_axis(origin, normal, offset) |
|||
point = App.Vector(10, 15, 2) |
|||
projection = wp.project_point(point) |
|||
print(projection) |
|||
}} |
}} |
||
The {{incode|PlaneBase}} class can be used to create working planes independent of the GUI: |
|||
To move or rotate the Draft working plane (see the [http://www.freecadweb.org/api/DraftWorkingPlane.html WorkingPlane API] page for available methods): |
|||
{{Code|code= |
{{Code|code= |
||
import |
import WorkingPlane |
||
from FreeCAD import Vector |
|||
wp = WorkingPlane.PlaneBase() |
|||
FreeCAD.DraftWorkingPlane.alignToPointAndAxis(Vector(0,0,0), Vector(1,1,1).normalize(), 17) |
|||
}} |
}} |
||
(note: a Draft command must have been issued to make grid adopt changes) |
|||
The working plane has a complete [http://www.freecadweb.org/api/DraftWorkingPlane.html scripting API] on its own, with convenience functions to position it and convert to/from placements. |
|||
{{ |
{{Docnav |
||
|[[Draft_Shape2DView|Shape2DView]] |
|||
<languages/> |
|||
|[[Draft_SetStyle|SetStyle]] |
|||
|[[Draft_Workbench|Draft]] |
|||
|IconL=Draft_Shape2DView.svg |
|||
|IconR=Draft_SetStyle.svg |
|||
|IconC=Workbench_Draft.svg |
|||
}} |
|||
{{Draft Tools navi{{#translation:}}}} |
|||
{{Userdocnavi{{#translation:}}}} |
|||
Revision as of 09:37, 28 March 2024
|
|
| Menyplacering |
|---|
| Drafting → SelectPlane |
| Arbetsbänkar |
| Skiss |
| Standard genväg |
| Ingen |
| Introducerad i version |
| - |
| Se även |
| Ingen |
Description
Beskrivning
Detta verktyg väntar på att användaren ska markera en existerande yta i 3D vyn eller att välja ett av de förinställda planen. Arbetsplanet kommer då att ställas in till det planet, och alla efterföljande 2D operationer kommer endast att hända på detta plan.
introduced in version 0.22: For each 3D view a separate working plane is stored.
The ![]() button in the Draft Tray changes depending on the current working plane. introduced in version 0.22: If the working plane is not set to Auto an asterisk (*) is appended to the button label if the origin of the working plane does not match the global origin.
button in the Draft Tray changes depending on the current working plane. introduced in version 0.22: If the working plane is not set to Auto an asterisk (*) is appended to the button label if the origin of the working plane does not match the global origin.
Shapes created on different working planes
Usage with pre-selection
- Do one of the following:
- Select a single object. The following objects are supported:
- Draft WorkingPlaneProxies: the VyView Data (the camera position) and the VyVisibility Map (the saved visibility of objects) of the working plane proxy are also restored.
- Arch Axes (introduced in version 0.22)
- Arch AxisSystems (introduced in version 0.22)
- Arch BuildingParts
- Arch SectionPlanes
- Std Parts: to avoid selecting subelements it is advisable to select these in the Tree view.
- Non-solid objects that consist of a single flat face or a single curved edge, or (introduced in version 0.22) that have three or more vertices.
- Solid objects or objects without a shape that have a DataPlacement property. (introduced in version 0.22)
- Select one or more subelements. You can select:
- A flat face.
- A curved edge.
- Three vertices.
- An edge and a vertex, or two edges. The combined vertices must define a plane. (introduced in version 0.22)
- Select a single object. The following objects are supported:
- There are several ways to invoke the command:
- Press the
 button in the Draft Tray.
button in the Draft Tray. - Select the Utilities →
Select plane option from the menu.
- Use the keyboard shortcut: W then P.
- Press the
- The working plane and the button in the Draft Tray are updated.
Usage with post-selection
- There are several ways to invoke the command:
- Press the
 button in the Draft Tray.
button in the Draft Tray. - Select the Utilities →
Select plane option from the menu.
- Use the keyboard shortcut: W then P.
- Press the
- The Working plane setup task panel opens. See Options for more information.
- Do one of the following:
- Select a single object. See the previous paragraph.
- Select one or more subelements. See the previous paragraph.
- Click anywhere in the 3D view to confirm the selection and finish the command.
- The working plane and the button in the Draft Tray are updated.
Usage with presets
- There are several ways to invoke the command:
- Press the
 button in the Draft Tray.
button in the Draft Tray. - Select the Utilities →
Select plane option from the menu.
- Use the keyboard shortcut: W then P.
- Press the
- The Working plane setup task panel opens. See Options for more information.
- Press any of the buttons to finish the command.
- The working plane and the button in the Draft Tray are updated.
Options
- Press the
Top (XY) button to align the working plane with the XY plane of the global coordinate system.
- Press the
Front (XZ) button to align the working plane with the XZ plane of the global coordinate system.
- Press the
Side (YZ) button to align the working plane with the YZ plane of the global coordinate system.
- Press the
Align to view button to align the working plane with the current 3D view. If the Center plane on view checkbox is not checked the working plane origin will match the origin of the global coordinate system, else it will match the center of the current 3D view.
- Press the
Automatic button to set the working plane to Auto. A working plane set to Auto will automatically align with the current 3D view whenever a Draft or Arch command requiring point input is started. This is equivalent to pressing the
Align to view button before using the command. Additionally the working plane will align to planar faces that have been selected before starting the command, or when points on planar faces are picked during the command.
- The Offset defines the perpendicular distance between the calculated plane and the actual working plane.
- Check the Center plane on view checkbox to put the origin of the working plane in the center of to the current 3D view. This option can be useful in combination with the
Align to view button.
- Select a vertex in the 3D view and press the
Move working plane button to move the working plane so that its origin matches the position of the selected vertex.
- The Grid color button allows to quickly change the color of the grid. introduced in version 0.22
- The Grid spacing defines the distance between grid lines.
- The Main line every value determines where main grid lines are drawn. Main grid lines are slightly thicker than normal grid lines. For example if the grid spacing is
0.5 mand there is a main line every10 lines, such a line will occur every5 m. - The Grid extension value determines the number of grid lines in the X and Y direction of the grid.
- The Snapping radius is the maximum distance at which Draft Snap Grid detects the intersections of grid lines.
- Press the
Center view button to align the 3D view with the current working plane.
- Press the
Previous button to reset the working plane to its previous position.
- Press the Next
button to reset the working plane to its next position. introduced in version 0.22
- Press Esc or the Close button to abort the command.
Notes
- It can be useful to align the 3D view with the selected Draft working plane. For example after switching the working plane to Front you may want to switch to the Front view as well.
- The grid can be toggled with the Draft ToggleGrid command.
- By double-clicking Draft WorkingPlaneProxies in the Tree view you can quickly switch between working planes.
Preferences
See also: Preferences Editor and Draft Preferences.
- The grid settings in the task panel as well as several other grid settings are available as preferences: Edit → Preferences... → Draft → Grid and snapping.
- The Snapping radius can also be changed on-the-fly (see Draft Snap) or by changing: Tools → Edit parameters... → BaseApp → Preferences → Mod → Draft → snapRange.
Scripting
See also: Autogenerated API documentation and FreeCAD Scripting Basics.
The WorkingPlane module offers two classes to create working plane objects: the PlaneBase class and the PlaneGui class. The second class inherits from the first. Objects of the PlaneGui class interact with the GUI (the Draft Tray button), the 3D view and the grid. PlaneBase objects do not.
Use the get_working_plane() method of the WorkingPlane module to get an instance of the PlaneGui class linked to the current 3D view. The method either returns the existing working plane linked to the view or creates a new working plane if required.
import FreeCAD as App
import WorkingPlane
wp = WorkingPlane.get_working_plane()
origin = App.Vector(0, 0, 0)
normal = App.Vector(1, 1, 1).normalize()
offset = 17
wp.align_to_point_and_axis(origin, normal, offset)
point = App.Vector(10, 15, 2)
projection = wp.project_point(point)
print(projection)
The PlaneBase class can be used to create working planes independent of the GUI:
import WorkingPlane
wp = WorkingPlane.PlaneBase()
- Drafting: Line, Polyline, Fillet, Arc, Arc by 3 points, Circle, Ellipse, Rectangle, Polygon, B-spline, Cubic Bézier curve, Bézier curve, Point, Facebinder, ShapeString, Hatch
- Annotation: Text, Dimension, Label, Annotation styles, Annotation scale
- Modification: Move, Rotate, Scale, Mirror, Offset, Trimex, Stretch, Clone, Array, Polar array, Circular array, Path array, Path link array, Point array, Point link array, Edit, Subelement highlight, Join, Split, Upgrade, Downgrade, Wire to B-spline, Draft to sketch, Set slope, Flip dimension, Shape 2D view
- Draft Tray: Select plane, Set style, Toggle construction mode, AutoGroup
- Snapping: Snap lock, Snap endpoint, Snap midpoint, Snap center, Snap angle, Snap intersection, Snap perpendicular, Snap extension, Snap parallel, Snap special, Snap near, Snap ortho, Snap grid, Snap working plane, Snap dimensions, Toggle grid
- Miscellaneous: Apply current style, Layer, Manage layers, Add a new named group, Move to group, Select group, Add to construction group, Toggle normal/wireframe display, Create working plane proxy, Heal, Show snap toolbar
- Additional: Constraining, Pattern, Preferences, Import Export Preferences, DXF/DWG, SVG, OCA, DAT
- Context menu:
- Layer container: Merge layer duplicates, Add new layer
- Layer: Activate this layer, Select layer contents
- Text: Open hyperlinks
- Wire: Flatten
- Working plane proxy: Write camera position, Write objects state
- Getting started
- Installation: Download, Windows, Linux, Mac, Additional components, Docker, AppImage, Ubuntu Snap
- Basics: About FreeCAD, Interface, Mouse navigation, Selection methods, Object name, Preferences, Workbenches, Document structure, Properties, Help FreeCAD, Donate
- Help: Tutorials, Video tutorials
- Workbenches: Std Base, Arch, Assembly, CAM, Draft, FEM, Inspection, Mesh, OpenSCAD, Part, PartDesign, Points, Reverse Engineering, Robot, Sketcher, Spreadsheet, Start, Surface, TechDraw, Test Framework, Web
- Hubs: User hub, Power users hub, Developer hub