Tree view/fr: Difference between revisions
(Created page with "=== Sélection du document ===") |
|||
| Line 39: | Line 39: | ||
** {{MenuCommand|Make Link group}}: [[Std_LinkMakeGroup|Simple group]], [[Std_LinkMakeGroup|Group with links]], [[Std_LinkMakeGroup|Group with transform links]]. |
** {{MenuCommand|Make Link group}}: [[Std_LinkMakeGroup|Simple group]], [[Std_LinkMakeGroup|Group with links]], [[Std_LinkMakeGroup|Group with transform links]]. |
||
=== |
=== Sélection du document === |
||
If you select the active document and right click, in addition to {{MenuCommand|Expression actions}} and {{MenuCommand|Link actions}}, the following commands appear: |
If you select the active document and right click, in addition to {{MenuCommand|Expression actions}} and {{MenuCommand|Link actions}}, the following commands appear: |
||
Revision as of 11:43, 17 December 2019
Introduction
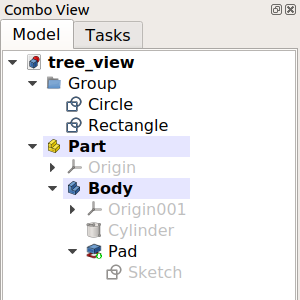
La vue en arborescence apparaît dans l'onglet Model de Vue combinée, l'un des panneaux les plus importants de l'interface. Elle montre tous les objets définis par l'utilisateur qui font partie d'un document FreeCAD. L'arborescence est une représentation de la Structure d'un document et indique quelles informations sont enregistrées sur le disque.
Ces objets ne doivent pas nécessairement être des formes géométriques visibles dans la Vue 3D mais peuvent également prendre en charge des objets de données créés avec l'un des ateliers.
L'arborescence montrant divers éléments du document.
Travailler avec la vue en arborescence
Par défaut, chaque fois qu'un nouvel objet est créé, il est ajouté à la fin de la liste dans l'arborescence. L'arborescence permet de gérer les objets pour les garder organisés. Elle permet de créer des groupes, de déplacer des objets à l'intérieur de groupes, de déplacer des groupes à l'intérieur d'autres groupes, de renommer des objets, de copier des objets, de supprimer des objets et d'autres opérations dans le menu contextuel qui dépend également du plan de travail actuellement actif.
De nombreuses opérations créent des objets qui dépendent d'un objet déjà existant. Dans ce cas, l'arborescence montre cette relation en absorbant l'objet plus ancien à l'intérieur du nouvel objet. Le développement et la réduction des objets dans l'arborescence montrent l'historique paramétrique de cet objet. Les objets qui sont plus profondément à l'intérieur des autres sont plus anciens, tandis que les objets qui sont à l'extérieur sont plus récents et sont dérivés des objets plus anciens. En modifiant les objets intérieurs, les opérations paramétriques se propagent jusqu'au sommet, générant un nouveau résultat.
L'objet au sommet est créé en effectuant des opérations paramétriques sur des objets qui ont eux-mêmes été créés par des opérations précédentes. L'élargissement de l'arbre à plusieurs niveaux révèle les éléments originaux qui ont été utilisés pour créer les solides partiels.
Actions
Remarque: des expressions et des actions de liaison ont été ajoutées dans la version 0.19.
Étant donné que l'arborescence répertorie les objets pouvant être visibles dans la vue 3D, de nombreuses actions sont identiques à celles qui peuvent être exécutées à partir de la vue 3D.
Lorsque l'application démarre, la valeur par défaut de l'Atelier Start est active, aucun document n'a été créé, un clic droit sur la vue en arborescence affiche une seule commande:
- Expression actions: Copy selected, Copy active document, Copy all documents, Coller. Celles-ci permettent de travailler avec divers documents mais sont désactivées si aucun document n'est présent.
Une fois un nouveau document créé, les éléments suivants deviennent actifs:
- Expression actions: Copy active document, Copy all documents.
De plus, les actions Liens sont disponibles.
- Link actions: Make Link.
- Make Link group: Simple group, Group with links, Group with transform links.
Sélection du document
If you select the active document and right click, in addition to Expression actions and Link actions, the following commands appear:
- Show hidden items: if active, the tree view will show hidden items.
- Search: shows an input field to search objects inside the selected document.
- Close document: closes the selected document by calling the application's
closeDocument()method. - Skip recomputes: if active, the document's objects will not recompute automatically.
- Allow partial recomputes: if active, the document will allow recompute of only some objects.
- Mark to recompute: marks all objects of the document as touched, and ready for recompute.
- Create group: creates a group in the selected document by using the document's
addObject()method.
Selecting objects
Once objects are added to the document then in addition to the previous actions, right clicking on an empty part of the tree view will show additional commands; these depend on the type of object and the active workbench.
For example, with the Draft Workbench active, first select an object, then right click on an empty place in the tree view:
- Toggle visibility: makes the object visible or invisible in the 3D view.
- Show selection: makes the selected objects visible.
- Hide selection: makes the selected objects invisible.
- Toggle selectability: makes the object no longer selectable in the 3D view; use again this command to cancel its effect. It sets the object's
Selectableattribute totrueorfalse. Change the property by toggling VueSelectable in the property editor. - Select all instances: selects all instances of this object in the tree view.
- Appearance: launches the dialog to change color and sizes of lines and vertices, and color of faces.
- Random color: assigns a random color to the object. It sets the object's
ShapeColorattribute to a tuple(r,g,b)with tree random floats between 0 and 1. Change the property by modifying VueShape Color in the property editor. - Cut: disabled if the right-click is not on the object.
- Copy: copies an object into memory.
- Paste: pastes the copied object into the document; the copy is added to the end of the tree view.
- Delete: removes the object from the document, and from the tree view, by calling the document's
removeObject()method. - Utilities: (optional) additional contextual commands provided by the Draft Workbench.
If an object is selected, for example, a Draft Line, and a right click is made in the same object additional commands may be available:
- Transform: launches the transform widget to move or rotate the object.
- Set colors: sets the colors of the object.
- Flatten this wire: (Draft) specific command for a Draft Line.
- Hide item: if active, the selected object will be set as hidden.
- Mark to recompute: marks the selected object as touched, and ready for recompute.
- Recompute: recomputes the selected object.
- Rename: starts editing the name of the selected object. This allows changing the
Labelattribute, but not theNameattribute, as the latter is read-only.
- Getting started
- Installation: Download, Windows, Linux, Mac, Additional components, Docker, AppImage, Ubuntu Snap
- Basics: About FreeCAD, Interface, Mouse navigation, Selection methods, Object name, Preferences, Workbenches, Document structure, Properties, Help FreeCAD, Donate
- Help: Tutorials, Video tutorials
- Workbenches: Std Base, Arch, Assembly, CAM, Draft, FEM, Inspection, Mesh, OpenSCAD, Part, PartDesign, Points, Reverse Engineering, Robot, Sketcher, Spreadsheet, Surface, TechDraw, Test Framework
- Hubs: User hub, Power users hub, Developer hub