Path Workbench/de: Difference between revisions
| Line 69: | Line 69: | ||
* [[Image:Path-Engrave.png|32px]] [[Path_Engrave|Engrave]]: Erzeugt einen Pfad für Gravuren |
* [[Image:Path-Engrave.png|32px]] [[Path_Engrave|Engrave]]: Erzeugt einen Pfad für Gravuren |
||
* [[Image:Path-Face.png|32px]] [[Path_MillFace|Mill Face]]: |
* [[Image:Path-Face.png|32px]] [[Path_MillFace|Mill Face]]: Erzeugt einen Pfad zum Planen von Oberflächen |
||
* [[Image:Path-Helix.png|32px]] [[Path_Helix|Helix]]: Creates a helical path |
* [[Image:Path-Helix.png|32px]] [[Path_Helix|Helix]]: Creates a helical path |
||
Revision as of 21:09, 17 March 2018
Einleitung
Im Path Arbeitsbereich können zum Betrieb von CNC Maschinen benötigte Befehlssätze erstellt werden. Unterstützt werden, Stand März 2018, Fräsen, Lasercutter, Graviermaschinen und ähnliche, 3 achsige CNC Maschinen deren Steuerung auf G-Code basiert. Die Path Postprozessoren erstellen G-Code in vielen verbreiteten Varianten, z.B. für Maschinencontroller von Centroid, Grbl, LinuCNC, Philips.
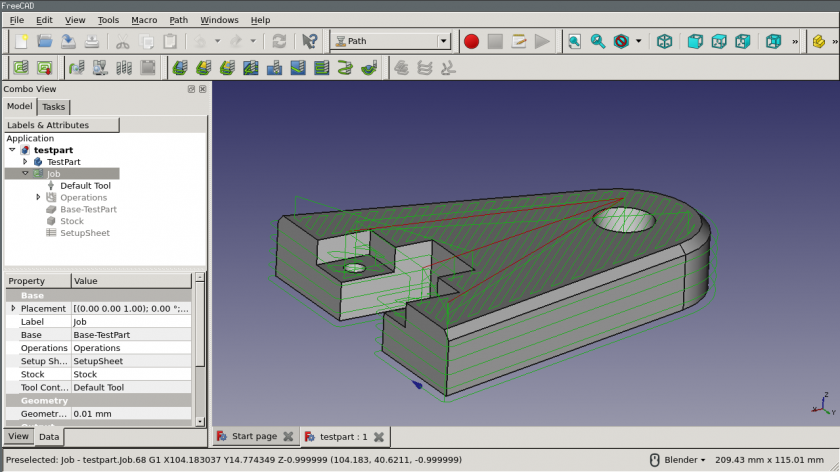
The FreeCAD Path Workbench workflow creates these machine instructions as follows:
- A 3D model is the base object, typically created using one or more of the Part Design, Part or Draft Workbenches.
- A Job is created in Path Workbench. This contains all the information required to generate the necessary G-Code to process the Job on a CNC mill: there is Stock material, the mill has a certain set of tools and it follows certain commands controlling speed and movements (usually G-Code).
- Tools are selected as required by the Job Operations.
- Milling paths are created using e.g. Contour and Pocket Operations. These Path objects use internal FreeCAD G-Code dialect, independent of the CNC machine.
Links für den schnellen Einstieg
- If you are a new new user trying to get familiar with Path, you might be interested in a fast walk-through tutorial.
- If you have a special machine which cannot use one of the available postprocessors you may want to learn about post-processor customization
- As an experienced user you may want to write a macro or automate a process might need to learn about scripting
- Power users who want to streamline their workflow can learn about customization.
- New developers who want to contribute to path might want to understand core concepts.
General concepts
The Path Workbench generates G-Code defining the paths required to mill the Project represented by the 3D model on the target mill—in [the Path Job Operations FreeCAD G-Code dialect ], which is later translated to the appropriate dialect for the target CNC controller by selecting the appropriate Postprocessor.
The G-Code is generated from directives and Operations contained in a Path Job. The Job Workflow lists these in the order they will be executed. The list is populated by adding Path Operations, Path Dressups, Path Partial Commands, and Path Modifications—from the Path Menu, or GUI buttons.
The Path Workbench provides a Tool Manager (Library, Tool-Table), and G-Code Inspection, and Simulation tools. It links the Postprocessor, and allows importing and exporting Job Templates.
The Path Workbench has external dependencies including:
- The FreeCAD 3D model units are defined in the Edit-> Preference...->General->Units tab's Units settings. The Postprocessor configuration defines the final G-Code units.
- The Macro file path, and Geometric tolerances, are defined in the Edit->Preferences...->Path->Job Preferences tab.
- Colors are defined in the Edit->Preferences...->Path->Path colors tab.
- Holding tag parameters are defined in the Edit->Preferences...->Path->Dressups tab.
- That the Base 3D model quality supports the Path WB requirements—passes Check Geometry.
FreeCAD Path Workbench internal G-Code dialect represents Feed rates in Units/Second—what the G-Code Inspection tool will show. The Postprocessor is configured to generate the appropriate Feed rates—either in Units/Second or Units/Minute for the target mill.
Path Kommandos
These commands are used for seting up a CNC project and manage your templates.
 Job: Erstellt einen neuen CNC Job
Job: Erstellt einen neuen CNC Job
 Post Process: Erstellt aus einem Job eine G-code Datei
Post Process: Erstellt aus einem Job eine G-code Datei
 Export Template: Speichert den ausgewählten Job als Vorlage
Export Template: Speichert den ausgewählten Job als Vorlage
 G-Code Inspector: Zeigt den G-code zur Überprüfung
G-Code Inspector: Zeigt den G-code zur Überprüfung
 Simulator: Zeigt eine Simulation des Fräsvorgangs wie er auf der Maschine ausgeführt wird.
Simulator: Zeigt eine Simulation des Fräsvorgangs wie er auf der Maschine ausgeführt wird.
 Tool Manager: Aufruf der Werkzeugtabelle
Tool Manager: Aufruf der Werkzeugtabelle
 Complete Loop: Erstellt aus 2 ausgewählten Kanten einen geschlossenen Ring
Complete Loop: Erstellt aus 2 ausgewählten Kanten einen geschlossenen Ring
- File:Path Contour.png Contour: Erzeugt einen Fräspfad aus der Kontur des Basisobjekts
- File:Path-Profile-Face.png Profile from Face: Erzeugt einen Kontur- Fräspfad um eine ausgewälte Fläche
- File:Path-Profile-Edges.png Profile from Edges: Erzeugt einen Kontur- Fräspfad von ausgewählten Kanten
 Pocket: Erzeugt einen Fräspfad für eine Tasche aus einer oder mehreren ausgewählten Taschen
Pocket: Erzeugt einen Fräspfad für eine Tasche aus einer oder mehreren ausgewählten Taschen
 Drilling: Erzeugt den Pfad für eine oder mehrere Bohrungen
Drilling: Erzeugt den Pfad für eine oder mehrere Bohrungen
 Engrave: Erzeugt einen Pfad für Gravuren
Engrave: Erzeugt einen Pfad für Gravuren
 Mill Face: Erzeugt einen Pfad zum Planen von Oberflächen
Mill Face: Erzeugt einen Pfad zum Planen von Oberflächen
 Helix: Creates a helical path
Helix: Creates a helical path
 3D Pocket: Creates a path for a 3D pocket
3D Pocket: Creates a path for a 3D pocket
Path Dressup
 Dogbone Dressup: Adds a dogbone dressup modification to a selected path
Dogbone Dressup: Adds a dogbone dressup modification to a selected path
 Dragknife Dressup: Adds a dragknife dressup modification to a selected path
Dragknife Dressup: Adds a dragknife dressup modification to a selected path
 Lead In Dressup: Adds a lead-in and/or lead-out point to a selected path
Lead In Dressup: Adds a lead-in and/or lead-out point to a selected path
 Ramp Entry Dressup: Adds ramp entry dressup modification to a selected path
Ramp Entry Dressup: Adds ramp entry dressup modification to a selected path
 Tag Dressup: Adds a holding tag dressup modification to a selected path
Tag Dressup: Adds a holding tag dressup modification to a selected path
Partial Commands
- File:Path SelectionPlane.png Plane: Changes the working plane of the machine
 Fixture: Changes the fixture position
Fixture: Changes the fixture position
- File:Path ToolLenthOffset.png Tool Length Offset: Changes the offset of the current tool
 Comment: Inserts a comment in the G-code of a path
Comment: Inserts a comment in the G-code of a path
 Stop: Inserts a full stop of the machine
Stop: Inserts a full stop of the machine
 Custom: Inserts custom G-code
Custom: Inserts custom G-code
 Gcode From a Shape: Creates a path object from a selected Part object
Gcode From a Shape: Creates a path object from a selected Part object
Path Modification
 Copy: Creates a parametric Copie of a selected path object
Copy: Creates a parametric Copie of a selected path object
 Array: Creates an array by duplicating a selected path
Array: Creates an array by duplicating a selected path
 Simple Copy: Creates a non-parametric copy of a selected path object
Simple Copy: Creates a non-parametric copy of a selected path object
Other
 3D Surface: Creates a path for a 3D surface
3D Surface: Creates a path for a 3D surface
 Feature area: Creates a feature area from selected objects
Feature area: Creates a feature area from selected objects
 Feature area workplane: Creates a feature area workplane
Feature area workplane: Creates a feature area workplane
 Path Errors: Checks the selected Job for missing values
Path Errors: Checks the selected Job for missing values
Scripting
The Path workbench offers a broad python scripting API. With it, you can create and modify paths from python scripts, or extend the available functionality of the workbench.
FAQ
The Path Workbench shares many concepts with other CAM software packages but has its own peculiarities. If something seems wrong, this might be a good place to start.