Part JoinConnect: Difference between revisions
Renatorivo (talk | contribs) mNo edit summary |
Renatorivo (talk | contribs) (Marked this version for translation) |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
<translate> |
<translate> |
||
<!--T:1--> |
|||
{{GuiCommand|Name=Part JoinConnect|MenuLocation=Part → Join → Connect Object|Workbenches=[[Part Module|Part]]|SeeAlso=[[Part_JoinConnect|Connect]], [[Part_JoinEmbed|Embed]], [[Part_JoinCutout|Cutout]], [[Part Booleans|Part Booleans]], [[Part Thickness|Part Thickness]]}} |
{{GuiCommand|Name=Part JoinConnect|MenuLocation=Part → Join → Connect Object|Workbenches=[[Part Module|Part]]|SeeAlso=[[Part_JoinConnect|Connect]], [[Part_JoinEmbed|Embed]], [[Part_JoinCutout|Cutout]], [[Part Booleans|Part Booleans]], [[Part Thickness|Part Thickness]]}} |
||
==Description== |
==Description== <!--T:2--> |
||
Connect tool connects interiors of two walled objects (e.g., pipes). |
Connect tool connects interiors of two walled objects (e.g., pipes). |
||
<!--T:3--> |
|||
[[image:JoinFeatures_Connect.png|600px]] |
[[image:JoinFeatures_Connect.png|600px]] |
||
==How to use== |
==How to use== <!--T:4--> |
||
# Select two objects to be connected. <br /> The order of selection is not important, since the action of the tool is symmetric. It is enough to select one sub-shape of each object (e.g., faces). |
# Select two objects to be connected. <br /> The order of selection is not important, since the action of the tool is symmetric. It is enough to select one sub-shape of each object (e.g., faces). |
||
# Invoke the Part JoinConnect command. |
# Invoke the Part JoinConnect command. |
||
<!--T:5--> |
|||
A Part JoinFeature object is created, with Mode set to 'Connect'. Original objects are hidden, and the result of conecting is shown in 3D view. |
A Part JoinFeature object is created, with Mode set to 'Connect'. Original objects are hidden, and the result of conecting is shown in 3D view. |
||
==Properties== |
==Properties== <!--T:6--> |
||
{{TitleProperty|Base}} |
{{TitleProperty|Base}} |
||
* {{PropertyData|Base}}: Reference to base object (one of the objects to be connected). The object should be a single solid. |
* {{PropertyData|Base}}: Reference to base object (one of the objects to be connected). The object should be a single solid. |
||
| Line 20: | Line 23: | ||
* {{PropertyData|Refine}}: Sets whether to apply [[Part RefineShape|Refine]] operation or not, to the final shape. The default value is determined by a 'Automatically refine shape after boolean operation' checkbox in PartDesign preferences. When Mode property is 'bypass', Refine is ignored (never applied). |
* {{PropertyData|Refine}}: Sets whether to apply [[Part RefineShape|Refine]] operation or not, to the final shape. The default value is determined by a 'Automatically refine shape after boolean operation' checkbox in PartDesign preferences. When Mode property is 'bypass', Refine is ignored (never applied). |
||
==Example== |
==Example== <!--T:7--> |
||
# Create a pipe by applying [[Part_Thickness|thickness]] to a [[Part_Cylinder|cylinder]]: <br />[[image:JoinFeatures_Example_step1.png|320px]] |
# Create a pipe by applying [[Part_Thickness|thickness]] to a [[Part_Cylinder|cylinder]]: <br />[[image:JoinFeatures_Example_step1.png|320px]] |
||
# Create another, smaller diameter pipe, and [[Placement|place]] it so that it pierces the wall of the first pipe: <br />[[image:JoinFeatures_Example_step2.png|320px]] |
# Create another, smaller diameter pipe, and [[Placement|place]] it so that it pierces the wall of the first pipe: <br />[[image:JoinFeatures_Example_step2.png|320px]] |
||
| Line 26: | Line 29: | ||
# Use some cross-section tool ([[Std_ClippingPlane|Clipping plane]], [[Arch_SectionPlane|Arch Section Plane]], [[Arch_CutPlane|Arch Cut Plane]]) to reveal internals. On the picture below, Arch Section Plane is used.<br />[[image:JoinFeatures_Example_step4_Connect.png|320px]] |
# Use some cross-section tool ([[Std_ClippingPlane|Clipping plane]], [[Arch_SectionPlane|Arch Section Plane]], [[Arch_CutPlane|Arch Cut Plane]]) to reveal internals. On the picture below, Arch Section Plane is used.<br />[[image:JoinFeatures_Example_step4_Connect.png|320px]] |
||
==Algorithm== |
==Algorithm== <!--T:8--> |
||
The algorithms behind Join tools are quite simple, and understanding them is important to use the tools correctly. The algorithm of Connect, in particular, is quite a bit more complex than others, but it's generally enough to think of it as a symmetric variant of [[Part_JoinEmbed#Algorithm|Embed algorithm]] |
The algorithms behind Join tools are quite simple, and understanding them is important to use the tools correctly. The algorithm of Connect, in particular, is quite a bit more complex than others, but it's generally enough to think of it as a symmetric variant of [[Part_JoinEmbed#Algorithm|Embed algorithm]] |
||
<!--T:9--> |
|||
1. Base object is [[Part Cut|boolean-cut]] with Tool object. The resulting shape is a set ([[Part MakeCompound|compound]]) of non-intersecting solids (typically, two). |
1. Base object is [[Part Cut|boolean-cut]] with Tool object. The resulting shape is a set ([[Part MakeCompound|compound]]) of non-intersecting solids (typically, two). |
||
<!--T:10--> |
|||
2. The resulting compound is filtered: only the largest solid is kept. |
2. The resulting compound is filtered: only the largest solid is kept. |
||
<!--T:11--> |
|||
3. Tool object is boolean-cut with Base object. |
3. Tool object is boolean-cut with Base object. |
||
<!--T:12--> |
|||
4. The resulting compound is filtered: only the largest solid is kept. |
4. The resulting compound is filtered: only the largest solid is kept. |
||
<!--T:13--> |
|||
5. [[Part_Common|Boolean-common]] is computed between Base and Tool |
5. [[Part_Common|Boolean-common]] is computed between Base and Tool |
||
<!--T:14--> |
|||
6. Results of 2, 4 and 5 are fused together. |
6. Results of 2, 4 and 5 are fused together. |
||
<!--T:15--> |
|||
7. If Refine property is true, the resulting shape is [[Part RefineShape|refined]]. |
7. If Refine property is true, the resulting shape is [[Part RefineShape|refined]]. |
||
<br /><br />[[image:JoinFeatures-Algo-Connect.png|800px]] |
<br /><br />[[image:JoinFeatures-Algo-Connect.png|800px]] |
||
===Notes=== |
===Notes=== <!--T:16--> |
||
* If at steps 1 and 3, the objects remains in one piece, the result of Connect will be equivalent to [[Part Fuse|fusion]] of Base and Tool, but taking much longer to compute. |
* If at steps 1 and 3, the objects remains in one piece, the result of Connect will be equivalent to [[Part Fuse|fusion]] of Base and Tool, but taking much longer to compute. |
||
* Now, the tool will produce unexpected result, if a compounds are supplied. This may be changed in the future. |
* Now, the tool will produce unexpected result, if a compounds are supplied. This may be changed in the future. |
||
| Line 50: | Line 60: | ||
* As of now, Connect does 5 boolean operations in a row, which makes it about 5 times slower than a regular boolean operation. |
* As of now, Connect does 5 boolean operations in a row, which makes it about 5 times slower than a regular boolean operation. |
||
==Scripting== |
==Scripting== <!--T:17--> |
||
<!--T:18--> |
|||
The Join tools can by used in [[macros]] and from the python console by using the following function: |
The Join tools can by used in [[macros]] and from the python console by using the following function: |
||
</translate> |
</translate> |
||
'''JoinFeatures.makePartJoinFeature(name = 'Connect', mode = 'Connect')''' |
'''JoinFeatures.makePartJoinFeature(name = 'Connect', mode = 'Connect')''' |
||
<translate> |
<translate> |
||
<!--T:19--> |
|||
* Creates an empty Connect feature (or other Join feature, depending on mode passed). The properties Base and Tool must be assigned explicitly, afterwards. |
* Creates an empty Connect feature (or other Join feature, depending on mode passed). The properties Base and Tool must be assigned explicitly, afterwards. |
||
* Returns the newly created object. |
* Returns the newly created object. |
||
<!--T:20--> |
|||
Example: |
Example: |
||
</translate> |
</translate> |
||
| Line 68: | Line 81: | ||
}} |
}} |
||
<translate> |
<translate> |
||
<!--T:21--> |
|||
The tool itself is implemented in Python, see /Mod/Part/JoinFeatures.py under where FreeCAD is installed. |
The tool itself is implemented in Python, see /Mod/Part/JoinFeatures.py under where FreeCAD is installed. |
||
==Version== |
==Version== <!--T:22--> |
||
The tool was introduced in FreeCAD v0.16.5069 |
The tool was introduced in FreeCAD v0.16.5069 |
||
Revision as of 20:21, 5 June 2015
|
|
| Menu location |
|---|
| Part → Join → Connect Object |
| Workbenches |
| Part |
| Default shortcut |
| None |
| Introduced in version |
| - |
| See also |
| Connect, Embed, Cutout, Part Booleans, Part Thickness |
Description
Connect tool connects interiors of two walled objects (e.g., pipes).
How to use
- Select two objects to be connected.
The order of selection is not important, since the action of the tool is symmetric. It is enough to select one sub-shape of each object (e.g., faces). - Invoke the Part JoinConnect command.
A Part JoinFeature object is created, with Mode set to 'Connect'. Original objects are hidden, and the result of conecting is shown in 3D view.
Properties
Base
- DataBase: Reference to base object (one of the objects to be connected). The object should be a single solid.
- DataTool: Reference to tool object (the other of the objects to be connected). The object should be a single solid.
- DataMode: The mode of operation, equals 'Connect' (Changing that will transform the tool into another Part_JoinXXX). The value of 'bypass' can be used to temporarily disable the long computations (a compound of Base and Tool will be created, which is a fast operation).
- DataRefine: Sets whether to apply Refine operation or not, to the final shape. The default value is determined by a 'Automatically refine shape after boolean operation' checkbox in PartDesign preferences. When Mode property is 'bypass', Refine is ignored (never applied).
Example
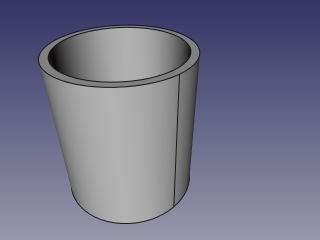
- Create a pipe by applying thickness to a cylinder:
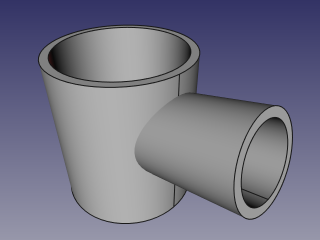
- Create another, smaller diameter pipe, and place it so that it pierces the wall of the first pipe:
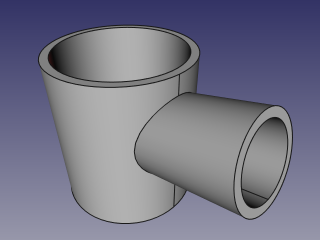
- Select the first pipe and the second pipe, and click the 'Connect objects' option from the Join tools dropdown toolbar button.
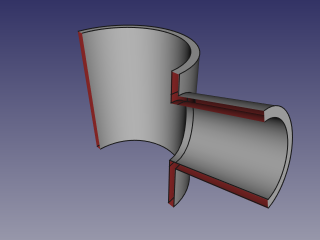
- Use some cross-section tool (Clipping plane, Arch Section Plane, Arch Cut Plane) to reveal internals. On the picture below, Arch Section Plane is used.
Algorithm
The algorithms behind Join tools are quite simple, and understanding them is important to use the tools correctly. The algorithm of Connect, in particular, is quite a bit more complex than others, but it's generally enough to think of it as a symmetric variant of Embed algorithm
1. Base object is boolean-cut with Tool object. The resulting shape is a set (compound) of non-intersecting solids (typically, two).
2. The resulting compound is filtered: only the largest solid is kept.
3. Tool object is boolean-cut with Base object.
4. The resulting compound is filtered: only the largest solid is kept.
5. Boolean-common is computed between Base and Tool
6. Results of 2, 4 and 5 are fused together.
7. If Refine property is true, the resulting shape is refined.
File:JoinFeatures-Algo-Connect.png
Notes
- If at steps 1 and 3, the objects remains in one piece, the result of Connect will be equivalent to fusion of Base and Tool, but taking much longer to compute.
- Now, the tool will produce unexpected result, if a compounds are supplied. This may be changed in the future.
- Because the largest piece is determined by comparing volumes of pieces, the tool can only work with solids. This may be changed in the future.
- As of now, Connect does 5 boolean operations in a row, which makes it about 5 times slower than a regular boolean operation.
Scripting
The Join tools can by used in macros and from the python console by using the following function:
JoinFeatures.makePartJoinFeature(name = 'Connect', mode = 'Connect')
- Creates an empty Connect feature (or other Join feature, depending on mode passed). The properties Base and Tool must be assigned explicitly, afterwards.
- Returns the newly created object.
Example:
import JoinFeatures
j = JoinFeatures.makePartJoinFeature(name = 'Connect', mode = 'Connect' )
j.Base = FreeCADGui.Selection.getSelection()[0]
j.Tool = FreeCADGui.Selection.getSelection()[1]
The tool itself is implemented in Python, see /Mod/Part/JoinFeatures.py under where FreeCAD is installed.
Version
The tool was introduced in FreeCAD v0.16.5069
