Funzionalità
Questa è una lista estesa, ma non comleta, delle caratteristiche già implementate in FreeCAD. Se siente interessati agli sviluppi futuri è possibile consultare la roadmap di sviluppo. Per avere un assaggio delle caratteristiche ci sono invece gli screenshot.
Note di sviluppo
Caratteristiche Generali
Di Base
- FreeCAD è multipiattaforma. È in grado di funzionare esattamente allo stesso modo su piattaforme Windows, Linux e Mac OSX.
- FreeCAD ha una interfaccia grafica completa. FreeCAD ha una [G.U.I.] completa basata sulla famosa piattaforma Qt, una interfaccia di visualizzazione 3D basata su Open Inventor, che garantisce un rendering rapido e permette di accedere facilmente alle varie proiezioni della scena.
- FreeCAD funziona anche da riga di comando, con il minimo utilizzo di memoria. Utilizzando la riga di comando FreeCAD si avvia senza l'interfaccia grafica, ma dispone comunque di tutte le sue funzioni, anche quelle più avanzate. Può, ad esempio, essere utilizzato come server per generare contenuti utilizzati in altre applicazioni.
- FreeCAD può essere importato come modulo Python all'interno di altre applicazioni in grado di gestire script in python, oppure direttamente all'interno di una console python. In questa modalità la G.U.I. non viene caricata, ma è comunque possibile utilizzare tutti gli strumenti di modellazione geometrica.
- Basato su plugins e moduli. FreeCAD è formato da una struttura di base, il core, e numerosi moduli che vengono avviati solo quando è necessario. Praticamente tutti gli strumenti vengono forniti come moduli. Questo permette di aggiungere e/o rimuovere moduli anche da una installazione preesistente di FreeCAD.
- Strumento di sviluppo di script integrato: FreeCAD fornisce un interpreter Python integrato nel programma e delle API che coprono la quasi totalità del programma, l'interfaccia, la geometria e la visualizzazione 3D. L'interpreter è in grado di gertire singoli comandi così come interi script comunque complessi. Tutti i moduli possono essere gestiti tramite Python.
- Un installer MSI modulare che garantisce una installazione flessibile in ambiente Windows. Sono disponibili anche pacchetti specifici per Ubuntu.
Struttura dei documenti
- Strumento annulla/ripristina: tutto si può annullare/ripristinare, tramite accesso diretto allo storico delle azioni. In questo modo è possibile annullare più modifiche allo stesso tempo.
- Gestione delle modifiche: Lo storico annulla/ripristina conserva informazioni sulle modifiche globali e non sulla singola azione, in questo modo ogni singolo strumento può gestire esattamente ciò che deve essere annullato o ripristinato.
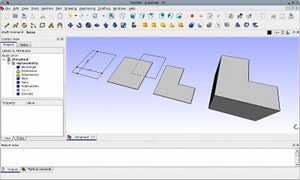
- Gestione parametrica degli ogetti: Tutti gli oggetti in un documento FreeCAD vengono definiti tramite parametri. Questi sono modificabili a piacere e gli effetti delle modifiche sono visibili in tempo reale. Vengono memorizzate anche le relazioni che intercorrono tra i vari oggetti, quindi modificando un determinato oggetto vengono modificati automaticamente tutti gli altri oggetti che hanno relazioni con esso.
- Formato di salvataggio parametrico: I documenti FreeCAD vengono salvati con estensione .fcstd e contengono numerose informazioni come ad esempio la geometria, gli script e le anteprime.
Interfaccia Utente
- G.U.I. completamente personalizzabile. L'interfaccia di FreeCAD, basata su Qt è completamente configurabile tramite il Python interpreter. is entirely accessible via the python interpreter. Aside from the simple functions that FreeCAD itself provides to workbenches, the whole Qt framework is accessible too, allowing any operation on the GUI, such as creating, adding, docking, modifying or removing widgets and toolbars.
- Workbench concept: In the FreeCAD interface, tools are grouped by workbenches. This allows to display only the tools used to accomplish a certain task, keeping the workspace uncluttered and responsive, and the application fast to load.
- Built-in Python console with syntax highlighting, autocomplete and class browser: Python commands can be issued directly in FreeCAD and immediately return results, permitting scriptwriters to test functionality on the fly, explore the contents of the modules and easily learn about FreeCAD internals.
- User interaction mirroring on the console: Everything the user does in the FreeCAD interface executes python code, which can be printed on the console and recorded in macros.
- Full macro recording & editing: The python commands issued when the user manipulates the interface can then be recorded, edited if needed, and saved to be reproduced later.
- Thumbnailer (Linux systems only at the moment): The FreeCAD document icons show the contents of the file in most file manager applications such as gnome's nautilus.
Application specific features
The functionality of FreeCAD is separated in modules, each one dealing with special data types and applications:
File:Workbench Mesh.png Meshes

- The Mesh Module deals with 3D meshes. It is intented primarily for import, healing and conversion of third-party generated mesh geometry into FreeCAD, and export of FreeCAD geometry into mesh formats. But FreeCAD itself also features much more advanced geometry types than meshes.
- Primitive creation (box, sphere, cylinder, etc), offset (trivial or after Jung/Shin/Choi) or boolean operations (add, cut, intersect)
- Import of the following formats: ASCII or binary STL (Stereo lithography format) (*.stl, *.ast), the OBJ format (*.obj), limited NASTRAN support (*.nas), Open Inventor meshes (*.iv), and FreeCAD native mesh kernel (*.bms)
- Export of the following formats: ASCII or binary STL (Stereo lithography format) (*.stl, *.ast), the OBJ format (*.obj), limited NASTRAN support (*.nas, *.brl), VRML meshes (*.wrl), FreeCAD native mesh kernel (*.bms), mesh as Python module (*.py)
- Testing and repairing tools for meshes: solid test, non-two-manifolds test, self-intersection test, hole filling and uniform orientation.
- Extensive Python scripting API.
 2D Drafting
2D Drafting
- Graphical creation of simple planar geometry like lines, wires, rectangles, arcs or circles in any plane of the 3D space
- Annotations like texts or dimensions
- Graphical modification operations like translation, rotation, scaling, mirroring, offset or shape conversion, in any plane of the 3D space
- Import and Export of the following formats: Autodesk's Drawing Exchange Format (*.dxf), Open Cad Format (*.oca, *.gcad) e SVG (*.svg)
 CAD
CAD

- The Part Module deals with everything around CAD modeling and the CAD data structures. The CAD functionality is under heavy development (see the PartDesign_project and Assembly_project in the Development_roadmap). The Part Module works with high-level Open CASCADE geometry.
- Parametric primitive shapes like box, sphere, cylinder, cone or torus.
- Topological components like vertices, edges, wires and planes (via python scripting).
- Modeling with straight or revolution extrusions, sections and fillets.
- Boolean operations like union, difference and intersection.
- Extensive Python scripting API.
- Import and Export of the following formats: STEP parts and assemblies (*.stp,*.step), IGES models (*.igs, *.iges) and BRep (*.brp), the native format of our Open CASCADE CAD kernel.
Raytracing
- The Raytracing Module permits the export of FreeCAD geometry to external renderers for generation of high-quality images. Currently, the only supported render engine is POV-Ray. The module currently permits the creation of a render sheet, and adding geometry to that render sheet for export to a POV-Ray file.
Drawing
- The Drawing Module allows to export projected views of your 3D geometry to a 2D SVG document. It allows the creation of a 2D sheet with an existing svg template, and the insertion of projected views of your geometry in that sheet. Then the sheet can be saved as a SVG file.
CAM
- The Cam Module is dedicated to mechanical machining like milling. This module is at the very beginning and at the moment mostly dedicated to Incremental Sheet Forming. Although there are some algorithms for toolpath planing they are not usable for the end-user at the moment.