User:DeepSOIC: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
|||
| (37 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
Mapping modes of the new Attacher |
|||
<translate> |
|||
<!--T:1--> |
|||
{{GuiCommand|Name=Constraint InternalAngle|Workbenches=[[Sketcher Workbench|Sketcher]], [[PartDesign Workbench|PartDesign]]|Shortcut=A|MenuLocation=Sketch → Sketcher constraints → Constrain angle|SeeAlso=[[Constraint Length|Constraint Length]], [[Constraint Perpendicular|Constraint Perpendicular]]}} |
|||
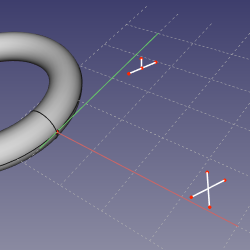
==Mode Deactivated== |
|||
==Description== |
|||
'''References:''' any |
|||
Angle constraint is a [[Sketcher Datum Constraint|datum constraint]] intended to fix angles in sketch. It is capable of setting slopes of individual lines, angles between lines, angles of intersections of curves, and angle spans of circular arcs. |
|||
'''Action:''' sketch remains where it was. Attachment is disabled. |
|||
==How to use== |
|||
There are four different ways the constraint can be applied: |
|||
# to individual lines |
|||
# between lines |
|||
# to intersections of curves |
|||
# to arcs of circles |
|||
==Mode Translate== |
|||
To apply angle constraint, one should the follow the steps: |
|||
'''References:''' vertex |
|||
* Select one, two or three entities in the sketch. |
|||
* Invoke the constraint by clicking its icon on the toolbar, or selecting the menu item, or using keyboard shortcut. A datum edit dialog box pops up. |
|||
* Modify the angle if necessary. The angle can be entered as an expression that will be evaluated and the result will be stored. Click OK. |
|||
'''Action:''' sketch origin is translated to coincide with the vertex. Sketch orientation doesn't change, and can be modified by changing Placement property. |
|||
As with any datum constraint, it is possible to change the angle value later by double-clicking the constraint in constraint list or 3d view. A negative value will cause the angle direction to flip. |
|||
[[image:Attacher_mode_Translate.png|250px]] |
|||
==Constraint modes== |
|||
===line slope angle=== |
|||
'''Accepted selection:''' line |
|||
[[Image:Sketcher ConsraintAngle mode1.png|600px]] |
|||
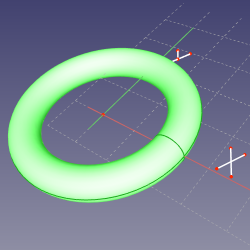
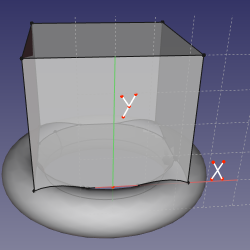
==Mode ObjectXY== |
|||
The constraint sets the polar angle of line's direction. It is the angle between the line and X axis of the sketch. This mode is applied if one line was selected. |
|||
'''References:''' object |
|||
'''Action:''' sketching plane is XY plane of object's local coordinate system (according to its Placement property). |
|||
===arc span (v0.15)=== |
|||
'''Accepted selection:''' arc of circle |
|||
[[ |
[[image:Attacher_mode_ObjectXY.png|250px]] |
||
In this mode, the constraint fixes angular span of a circular arc. This mode is applied when a circular arc was selected. |
|||
== |
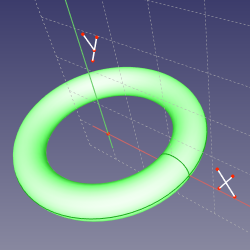
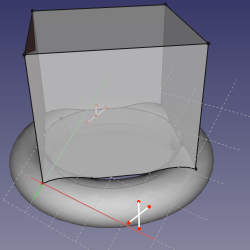
==Mode ObjectXZ== |
||
''' |
'''References:''' object |
||
'''Action:''' like ObjectXY. |
|||
[[Image:Sketcher ConsraintAngle mode3.png|600px]] |
|||
[[image:Attacher_mode_ObjectXZ.png|250px]] |
|||
In this mode, the constraint sets the angle between two lines. It is not required that the lines intersect. This mode is applied when two lines were selected. |
|||
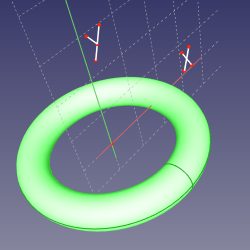
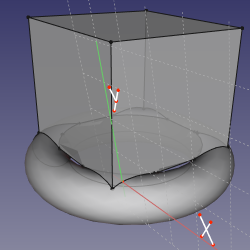
==Mode ObjectYZ== |
|||
===between curves at intersection (angle-via-point) (v0.15)=== |
|||
'''References:''' object |
|||
'''Accepted selection:''' any line/curve + any line/curve + any point |
|||
'''Action:''' like ObjectXY. |
|||
[[Image:Sketcher ConsraintAngle mode4.png|600px]] |
|||
[[image:Attacher_mode_ObjectYZ.png|250px]] |
|||
In this mode, angle between two curves is constrained at the point of their intersection. The intersection point can be on curves' extensions. The point should be specified explicitly, since curves typically intersect in more than one point. This mode is applied when two curves and a point were selected. |
|||
==Mode FlatFace== |
|||
For the constraint to work correctly, the point must be on both curves. So, as the constraint is invoked, the point will be automatically constrained onto both curves ([[Sketcher helper constraint|helper constraints]] will be added, if necessary), and the angle between curves will be constrained at the point. These [[Sketcher helper constraint|helper constraints]] are plain regular constraints. They can be added manually, or deleted. There are no helper constraints on the example picture above, because the point selected is already the intersection of curves. |
|||
'''References:''' face or plane |
|||
'''Action:''' legacy. Sketching on a flat face. |
|||
==Scripting== |
|||
[[image:Attacher_mode_FlatFace.png|250px]] |
|||
Angle Constraint can be created from [[macros]] and from the python console by using the following: |
|||
</translate> |
|||
{{Code|code= |
|||
# line slope angle |
|||
Sketch.addConstraint(Sketcher.Constraint('Angle',iline,angle)) |
|||
# angular span of arc |
|||
Sketch.addConstraint(Sketcher.Constraint('Angle',iarc,angle)) |
|||
==Mode TangentPlane== |
|||
# angle between lines |
|||
'''References:''' face+vertex or vertex+face |
|||
Sketch.addConstraint(Sketcher.Constraint('Angle',iline1,pointpos1,iline2,pointpos2,angle)) |
|||
'''Action:''' sketching plane is tangent to surface of face at the point on the surface that is closest to the vertex. If vertex is linked in first, the plane is translated to go through the vertex. If face is first, the plane touches the surface. X axis of sketch is chosen to go along internal face's parametrization. |
|||
# angle-via-point (no helper constraints are added automatically when from python) |
|||
Sketch.addConstraint(Sketcher.Constraint('AngleViaPoint',icurve1,icurve2,geoidpoint,pointpos,angle)) |
|||
}} |
|||
<translate> |
|||
where: |
|||
:* <tt>Sketch</tt> is a sketch object |
|||
:* <tt>iline, iline1, iline2</tt> are integers specifying the lines by their ordinal numbers in <tt>Sketch</tt>. |
|||
:* <tt>pointpos1, pointpos2</tt> should be 1 for start point and 2 for end point. The choice of endpoints allows to set internal angle (or external), and it affects how the constraint is drawn on the screen. |
|||
:* <tt>geoidpoint</tt> and <tt>pointpos</tt> in AngleViaPoint are the indexes specifying the point of intersection. |
|||
:* <tt>angle</tt> is the angle value in radians. The angle is counted between tangent vectors in counterclockwise direction. Tangent vectors are pointing from start to end for the lines (or vice versa if ending point is supplied in angle between lines mode), and along counterclockwise direction for circles, arcs and ellipses. Quantity is also accepted as an angle (e.g. <tt>App.Units.Quantity('45 deg')</tt>) |
|||
[[image:Attacher_mode_TangentPlane.png|250px]] |
|||
</translate> |
|||
{{clear}} |
|||
<languages/> |
|||
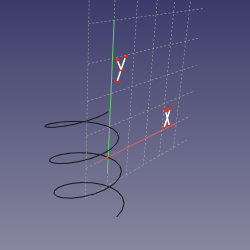
==Mode NormalToEdge== |
|||
'''References:''' edge or edge+vertex or vertex+edge |
|||
'''Action:''' sketching plane is normal to the edge at the point of the edge's curve that is closest to the vertex (or defined by MapPathParameter property, if vertex is not linked). The origin of sketch is translated to the vertex if the virtex is first, or kept at where the curve pierces the sketch plane if edge is first. X axis of sketch is chosen automatically. |
|||
[[image:Attacher_mode_NormalToEdge.png|250px]] |
|||
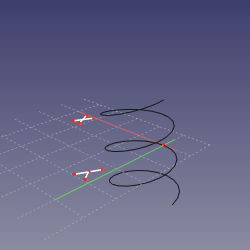
==Mode FrenetNB== |
|||
'''References:''' curved edge OR curved edge+vertex OR vertex+curved edge |
|||
'''Action:''' sketching plane is normal-binormal (NB) axes of Frenet-Serret coordinates at the point of the edge's curve that is closest to the vertex (or defined by MapPathParameter property, if vertex is not linked). The origin of sketch is translated to the vertex if the vertex is first, or kept at the curve if edge is first. This mode is similar to NormalToEdge, except that X axis is well-defined. |
|||
[[image:Attacher_mode_FrenetNB.png|250px]] |
|||
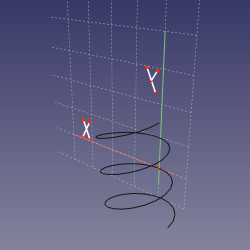
==Mode TrenetTN== |
|||
'''References:''' curved edge OR curved edge+vertex OR vertex+curved edge |
|||
'''Action:''' sketching plane is tangent-normal (TN) axes of Frenet-Serret coordinates at the point of the edge's curve that is closest to the vertex (or defined by MapPathParameter property, if vertex is not linked). The origin of sketch is translated to the vertex if the vertex is first, or kept at the curve if edge is first. Effectively, if the curve is planar, the sketching plane is the plane of the curve. |
|||
[[image:Attacher_mode_FrenetTN.png|250px]] |
|||
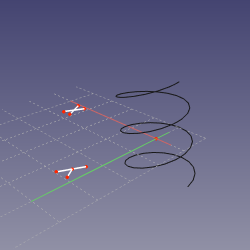
==Mode FrenetTB== |
|||
'''References:''' curved edge OR curved edge+vertex OR vertex+curved edge |
|||
'''Action:''' sketching plane is tangent-binormal (TB) axes of Frenet-Serret coordinates at the point of the edge's curve that is closest to the vertex (or defined by MapPathParameter property, if vertex is not linked). The origin of sketch is translated to the vertex if the vertex is first, or kept at the curve if edge is first. |
|||
[[image:Attacher_mode_FrenetTB.png|250px]] |
|||
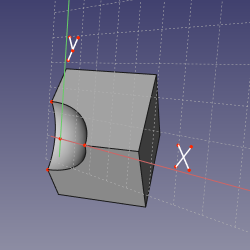
==Mode Concentric== |
|||
'''References:''' curved edge OR curved edge+vertex OR vertex+curved edge |
|||
'''Action:''' same as FrenetTN, but sketch origin is placed at the center of curvature of the edge. |
|||
[[image:Attacher_mode_Concentric.png|250px]] |
|||
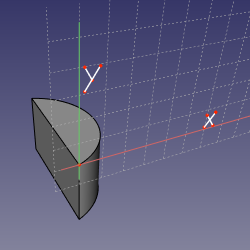
==Mode SectionOfRevolution== |
|||
'''References:''' curved edge OR curved edge+vertex OR vertex+curved edge |
|||
'''Action:''' same as FrenetNB, but sketch origin is placed at the center of curvature of the edge, and Y axis is the axis of osculating circle. Useful to make grooves on bodies of revolution. |
|||
[[image:Attacher_mode_SectionOfRevolution.png|250px]] |
|||
==Mode ThreePointsPlane== |
|||
'''References:''' vertex+vertex+vertex or line+vertex or vertex+line or line+line |
|||
'''Action:''' sketching plane goes through three vertices defined by references. Line is treated as if it is two vertices. |
|||
[[image:Attacher_mode_ThreePointsPlane.png|250px]] |
|||
==Mode ThreePointsNormal== |
|||
'''References:''' vertex+vertex+vertex or line+vertex or vertex+line or line+line |
|||
'''Action:''' sketching plane contains first two vertices, and is normal to the plane defined by three vertices. |
|||
[[image:Attacher_mode_ThreePointsNormal.png|250px]] |
|||
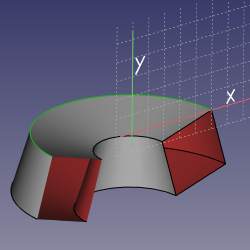
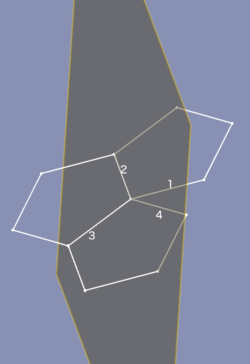
==Mode Folding== |
|||
'''References:''' line+line+line+line |
|||
'''Action:''' specialty mode to fold polyhedra. See picture. It is required that all four lines share an endpoint. It is not required that both leafs to fold together are the same, like on the picture. |
|||
[[image:Attacher_mode_Folding.png|250px]] |
|||
Latest revision as of 17:21, 1 July 2015
Mapping modes of the new Attacher
Mode Deactivated
References: any
Action: sketch remains where it was. Attachment is disabled.
Mode Translate
References: vertex
Action: sketch origin is translated to coincide with the vertex. Sketch orientation doesn't change, and can be modified by changing Placement property.
Mode ObjectXY
References: object
Action: sketching plane is XY plane of object's local coordinate system (according to its Placement property).
Mode ObjectXZ
References: object
Action: like ObjectXY.
Mode ObjectYZ
References: object
Action: like ObjectXY.
Mode FlatFace
References: face or plane
Action: legacy. Sketching on a flat face.
Mode TangentPlane
References: face+vertex or vertex+face
Action: sketching plane is tangent to surface of face at the point on the surface that is closest to the vertex. If vertex is linked in first, the plane is translated to go through the vertex. If face is first, the plane touches the surface. X axis of sketch is chosen to go along internal face's parametrization.
Mode NormalToEdge
References: edge or edge+vertex or vertex+edge
Action: sketching plane is normal to the edge at the point of the edge's curve that is closest to the vertex (or defined by MapPathParameter property, if vertex is not linked). The origin of sketch is translated to the vertex if the virtex is first, or kept at where the curve pierces the sketch plane if edge is first. X axis of sketch is chosen automatically.
Mode FrenetNB
References: curved edge OR curved edge+vertex OR vertex+curved edge
Action: sketching plane is normal-binormal (NB) axes of Frenet-Serret coordinates at the point of the edge's curve that is closest to the vertex (or defined by MapPathParameter property, if vertex is not linked). The origin of sketch is translated to the vertex if the vertex is first, or kept at the curve if edge is first. This mode is similar to NormalToEdge, except that X axis is well-defined.
Mode TrenetTN
References: curved edge OR curved edge+vertex OR vertex+curved edge
Action: sketching plane is tangent-normal (TN) axes of Frenet-Serret coordinates at the point of the edge's curve that is closest to the vertex (or defined by MapPathParameter property, if vertex is not linked). The origin of sketch is translated to the vertex if the vertex is first, or kept at the curve if edge is first. Effectively, if the curve is planar, the sketching plane is the plane of the curve.
Mode FrenetTB
References: curved edge OR curved edge+vertex OR vertex+curved edge
Action: sketching plane is tangent-binormal (TB) axes of Frenet-Serret coordinates at the point of the edge's curve that is closest to the vertex (or defined by MapPathParameter property, if vertex is not linked). The origin of sketch is translated to the vertex if the vertex is first, or kept at the curve if edge is first.
Mode Concentric
References: curved edge OR curved edge+vertex OR vertex+curved edge
Action: same as FrenetTN, but sketch origin is placed at the center of curvature of the edge.
Mode SectionOfRevolution
References: curved edge OR curved edge+vertex OR vertex+curved edge
Action: same as FrenetNB, but sketch origin is placed at the center of curvature of the edge, and Y axis is the axis of osculating circle. Useful to make grooves on bodies of revolution.
Mode ThreePointsPlane
References: vertex+vertex+vertex or line+vertex or vertex+line or line+line
Action: sketching plane goes through three vertices defined by references. Line is treated as if it is two vertices.
Mode ThreePointsNormal
References: vertex+vertex+vertex or line+vertex or vertex+line or line+line
Action: sketching plane contains first two vertices, and is normal to the plane defined by three vertices.
Mode Folding
References: line+line+line+line
Action: specialty mode to fold polyhedra. See picture. It is required that all four lines share an endpoint. It is not required that both leafs to fold together are the same, like on the picture.