Std Workbench/ro: Difference between revisions
(Updating to match new version of source page) |
(Updating to match new version of source page) |
||
| Line 11: | Line 11: | ||
This command is used to activate the graphical user interface (GUI) and the tools of a specific workbench. |
This command is used to activate the graphical user interface (GUI) and the tools of a specific workbench. |
||
| ⚫ | |||
It is possible to execute it in three different ways: |
|||
* the '''View''' menu, |
|||
* the drop-down menu, or, |
|||
* a Python command. |
|||
| ⚫ | |||
<div class="mw-translate-fuzzy"> |
<div class="mw-translate-fuzzy"> |
||
| Line 33: | Line 28: | ||
=== Via Python console === |
=== Via Python console === |
||
* Type the command in the console, for example: |
* Type the command in the Python console, for example: to invoke the Draft workbench type: |
||
{{incode|Gui.activateWorkbench ("DraftWorkbench")}} |
|||
== Examples == |
== Examples == |
||
| ⚫ | |||
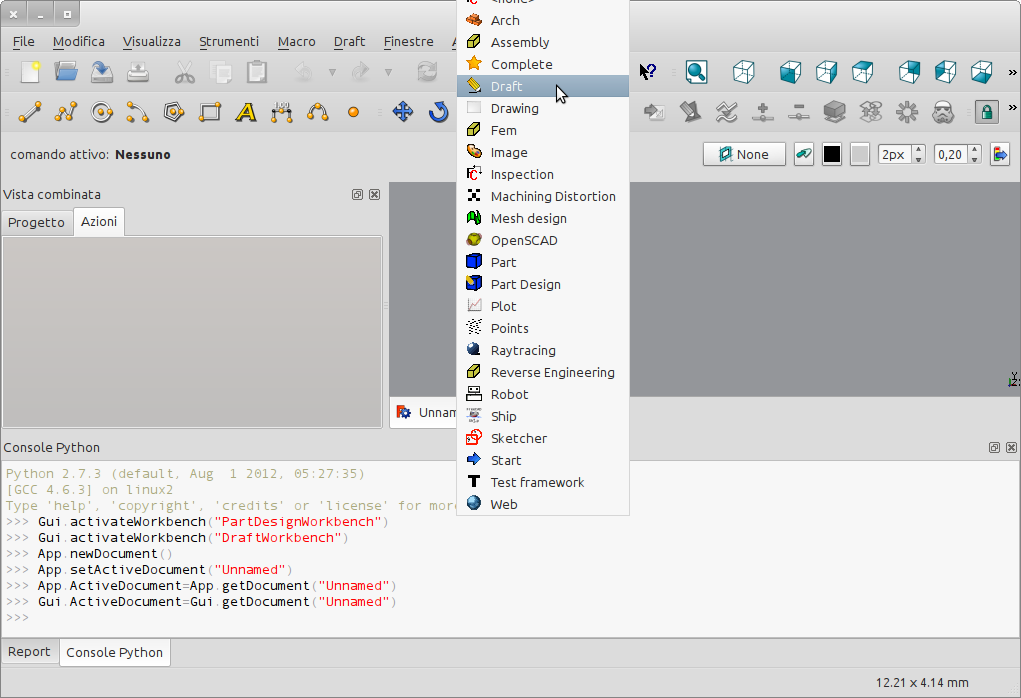
Start from the drop-down menu: |
|||
{{Caption|Using the the Workbench drop-down menu}} |
|||
| ⚫ | |||
{{Clear}} |
{{Clear}} |
||
| ⚫ | |||
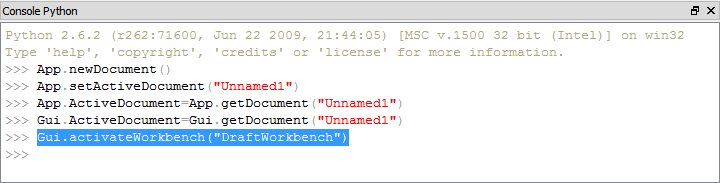
Starting from the Python console: |
|||
{{Caption|Invoking a different workbench using the Python console}} |
|||
| ⚫ | |||
{{Clear}} |
{{Clear}} |
||
| ⚫ | |||
Through the console the command can also be copied: |
|||
{{Caption|'''Tip:''' If the Python console is open you will see that FreeCAD records the actions it executes in python code. Theoretically, the user can change something in the interface and see the comparable python code generated. This is a very useful way to learn python, FreeCAD, and how to automate redundant tasks (see [[Macros]] for more details).}} |
|||
| ⚫ | |||
{{Clear}} |
{{Clear}} |
||
| Line 56: | Line 53: | ||
{{Std Base}} |
{{Std Base}} |
||
{{Userdocnavi}} |
{{Userdocnavi}} |
||
{{clear}} |
{{clear}} |
||
Revision as of 20:01, 6 February 2020
This documentation is not finished. Please help and contribute documentation.
GuiCommand model explains how commands should be documented. Browse Category:UnfinishedDocu to see more incomplete pages like this one. See Category:Command Reference for all commands.
See WikiPages to learn about editing the wiki pages, and go to Help FreeCAD to learn about other ways in which you can contribute.
|
Std Workbench |
| Menu location |
|---|
| View → Workbench |
| Workbenches |
| All |
| Default shortcut |
| ... |
| Introduced in version |
| - |
| See also |
| ... |
Description
This command is used to activate the graphical user interface (GUI) and the tools of a specific workbench.
There are also two special options available: None (no workbench) and Complete obsolete in version 0.17
ToDo.
Often the project starts in a workbench, for example with Sketch, then continues in a different workbench, for example with Part, to create objects. You can switch from the current workbench to a new one with one of the following ways:
- In the top menu, open the View → Workbench menu and select a workbench. This menu is always available, even when you have previously selected the Complete or None workbench.
- In the top menu, open the drop-down menu and select a workbench. This menu is not available when you have previously selected the Complete or None workbench.
Via Python console
- Type the command in the Python console, for example: to invoke the Draft workbench type:
Gui.activateWorkbench ("DraftWorkbench")
Examples
Using the the Workbench drop-down menu
Invoking a different workbench using the Python console
Tip: If the Python console is open you will see that FreeCAD records the actions it executes in python code. Theoretically, the user can change something in the interface and see the comparable python code generated. This is a very useful way to learn python, FreeCAD, and how to automate redundant tasks (see Macros for more details).
Other references
For a general description of the workbenches, see the page Workbenches.
- File: New, Open, Close, Close All, Save, Save As, Save a Copy, Save All, Revert, Import, Export,Merge project, Project information, Print, Print preview, Export PDF, Recent files, Exit
- Edit: Undo, Redo, Cut, Copy, Paste, Duplicate selection, Refresh, Box selection, Box element selection, Select All, Delete, Send to Python Console, Placement, Transform, Alignment, Toggle Edit mode, Edit mode, Preferences
- View:
- Miscellaneous: Create new view, Orthographic view, Perspective view, Fullscreen, Bounding box, Toggle axis cross, Clipping plane, Texture mapping, Toggle navigation/Edit mode, Appearance, Random color, Workbench, Status bar
- Standard views: Fit all, Fit selection, Isometric, Dimetric, Trimetric, Home, Front, Top, Right, Rear, Bottom, Left, Rotate Left, Rotate Right
- Freeze display: Save views, Load views, Freeze view, Clear views
- Draw style: As is, Points, Wireframe, Hidden line, No shading, Shaded, Flat lines
- Stereo: Stereo red/cyan, Stereo quad buffer, Stereo Interleaved Rows, Stereo Interleaved Columns, Stereo Off, Issue camera position
- Zoom: Zoom In, Zoom Out, Box zoom
- Document window: Docked, Undocked, Fullscreen
- Visibility: Toggle visibility, Show selection, Hide selection, Select visible objects, Toggle all objects, Show all objects, Hide all objects, Toggle selectability, Toggle measurement, Clear measurement
- Toolbars: File, Edit, Clipboard, Workbench, Macro, View, Structure, Help
- Panels: Tree view, Property view, Selection view, Tasks, Python console, DAG view, Model, Report view
- Link navigation: Go to linked object, Go to the deepest linked object, Select all links
- Tree view actions: Sync view, Sync selection, Sync placement, Pre-selection, Record selection, Single document, Multi document, Collapse/Expand, Initiate dragging, Go to selection, Selection Back, Selection Forward
- Tools: Edit parameters, Save image, Load image, Scene inspector, Dependency graph, Project utility, Measure distance, Add text document, View turntable, Units calculator, Customize, Addon manager
- Macro: Macro recording, Macros, Recent macros, Execute macro, Attach to remote debugger, Debug macro, Stop debugging, Step over, Step into, Toggle breakpoint
- Help: Help, FreeCAD Website, Donate, Users documentation, Python scripting documentation, Automatic Python modules documentation, FreeCAD Forum, FreeCAD FAQ, Report a bug, About FreeCAD, What's This
- Getting started
- Installation: Download, Windows, Linux, Mac, Additional components, Docker, AppImage, Ubuntu Snap
- Basics: About FreeCAD, Interface, Mouse navigation, Selection methods, Object name, Preferences, Workbenches, Document structure, Properties, Help FreeCAD, Donate
- Help: Tutorials, Video tutorials
- Workbenches: Std Base, Arch, Assembly, CAM, Draft, FEM, Inspection, Mesh, OpenSCAD, Part, PartDesign, Points, Reverse Engineering, Robot, Sketcher, Spreadsheet, Surface, TechDraw, Test Framework
- Hubs: User hub, Power users hub, Developer hub