Placement/cs: Difference between revisions
(Updating to match new version of source page) |
(Updating to match new version of source page) |
||
| Line 44: | Line 44: | ||
'''Yaw-Pitch-Roll = (y,p,r)''' is a tuple that specifies the attitude of the object. Values for y,p,r specify degrees of rotation about each of the z,y,x axis (see note). |
'''Yaw-Pitch-Roll = (y,p,r)''' is a tuple that specifies the attitude of the object. Values for y,p,r specify degrees of rotation about each of the z,y,x axis (see note). |
||
{{clear}} |
{{clear}} |
||
{{Code|code= |
|||
<syntaxhighlight> |
|||
>>> App.getDocument("Sans_nom").Cylinder.Placement=App.Placement(App.Vector(0,0,0), App.Rotation(10,20,30), App.Vector(0,0,0)) |
>>> App.getDocument("Sans_nom").Cylinder.Placement=App.Placement(App.Vector(0,0,0), App.Rotation(10,20,30), App.Vector(0,0,0)) |
||
}} |
|||
</syntaxhighlight> |
|||
App.Rotation(10,20,30) = Euler Angle |
App.Rotation(10,20,30) = Euler Angle |
||
Revision as of 20:47, 11 October 2016
Celkový pohled
Umístění je vlastnost FreeCADu, která specifikuje místo a orientaci objektu v prostoru. Umístění může být specifikováno ve více formulářích a může být měněno pomocí skriptů v poli vlastnosti nebo v dialogovém okně Umístění (menu Úpravy).
Přístup k atributům Umístění
K atributům objektu Umístění lze přistupovat a modifikovat je 3 způsoby:
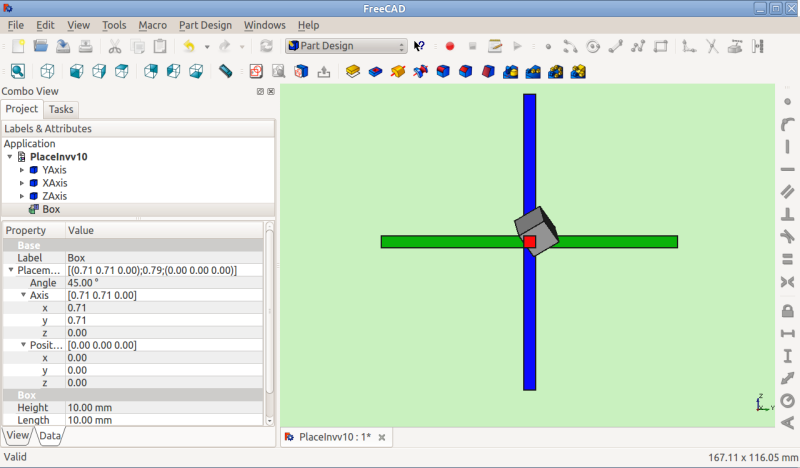
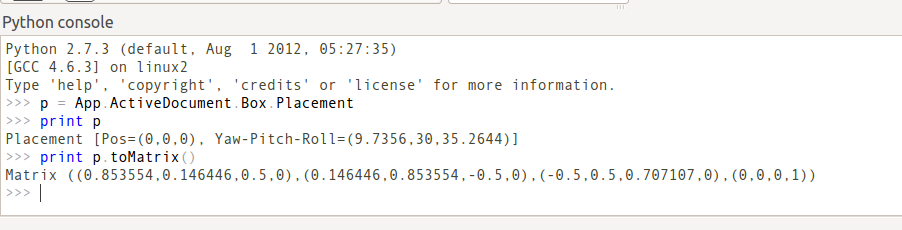
Forms of Placement
The placement is stored internally as a position, and a rotation (rotation axis and angle transformed into a quaternion [1]). While there are several forms to specify a rotation, for instance with a rotation center, this is only used to affect the rotation computation and is not stored for later operations. Similarly, if a rotation axis of (1,1,1) is specified, it may be normalized when stored in the quaternion and appear as (0.58, 0.58, 0.58) when browsing the object later.
Angle, Axis and Position
Placement = [Angle, Axis, Position]
První tvar zadání Umístění ustaví místo objektu v prostoru na Pozici a popíše jeho orientaci jako pootočení kolem osy.
Úhel = r je skalární hodnota udávající velikost pootočení objektu kolem osy. Zadává se ve stupních, ale interně je zaznamenán v radiánech.
Axis = (ax,ay,az) is a vector describing an axis of rotation (See Note about axis of rotation). Examples are:
(1,0,0) ==> about X axis
(0,1,0) ==> about Y axis
(0,0,1) ==> about Z axis
(0.71,0.71,0) ==> about the line y=x
Position = (x,y,z) is a Vector describing the point from which the object's geometry will be calculated (in effect, a "local origin" for the object). Note that in scripts, Placement.Base is used to denote the Position component of a placement. The Property Editor calls this value "Position" and the Placement dialog calls it "Translation".
Position and Yaw, Pitch and Roll
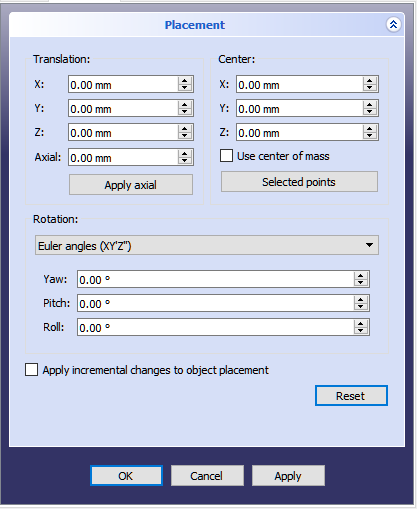
Placement = [Position, Yaw-Pitch-Roll]
Druhý tvar zadání Umístění ustaví místo objektu v prostoru pomocí Pozice (stejně jako předchozí tvar),ale popíše jeho orientaci použitím úhlů Yaw, Pitch a Roll (Yaw, Pitch, Roll). Tyto úhly jsou někdy také nazývány jako Eulerovy úhly nebo Tait-Bryanovy úhly (Eulerovy úhly). Yaw, Pitch a Roll jsou běžně užívány v letecké terminologii pro orientaci (nebo polohu) tělesa.
Position = (x,y,z) is a Vector describing the point from which the object's geometry will be calculated (in effect, a "local origin" for the object).
Yaw-Pitch-Roll = (y,p,r) is a tuple that specifies the attitude of the object. Values for y,p,r specify degrees of rotation about each of the z,y,x axis (see note).
>>> App.getDocument("Sans_nom").Cylinder.Placement=App.Placement(App.Vector(0,0,0), App.Rotation(10,20,30), App.Vector(0,0,0))
App.Rotation(10,20,30) = Euler Angle
Yaw = 10 degrees (Z)
Pitch = 20 degrees (Y)
Roll = 30 degrees (X)
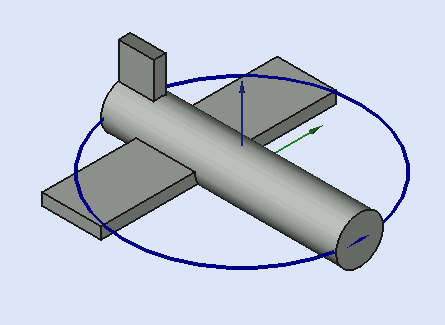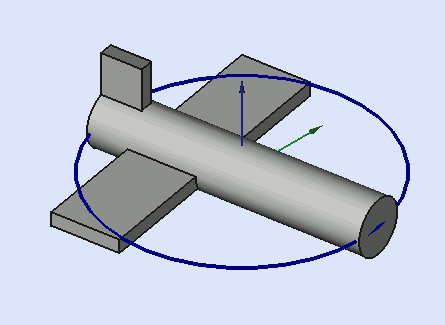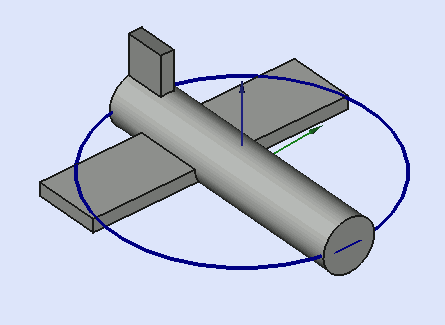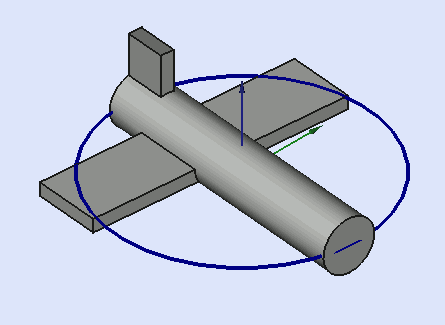
Yaw is the rotation about the Z axis, that is to say a rotation from left to right.
(The yaw angle is the Psi ψ).
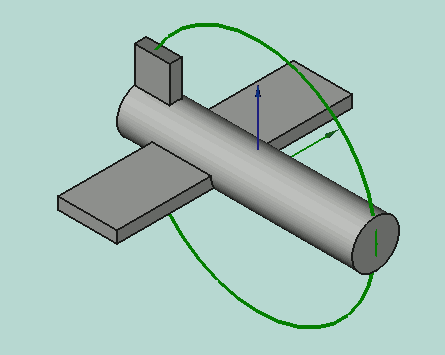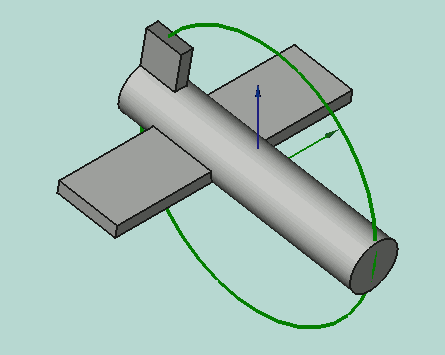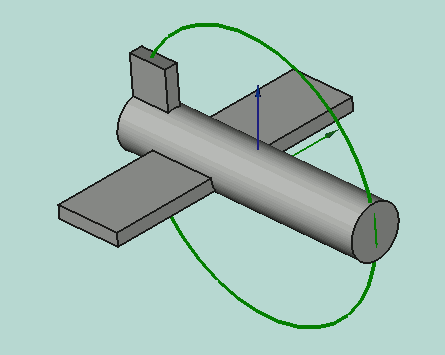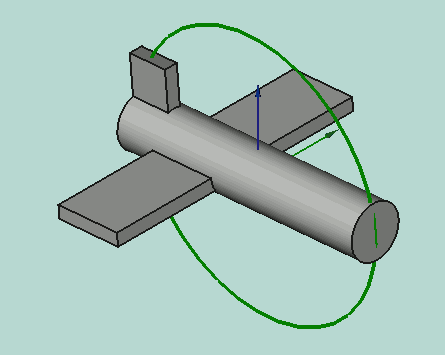
Pitch is rotation about the Y axis, that is to say nose-up and nose-down.
(The Pitch angle is the Phi φ).
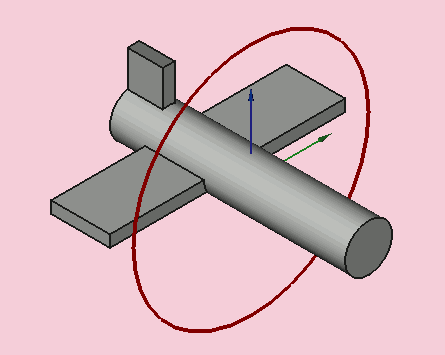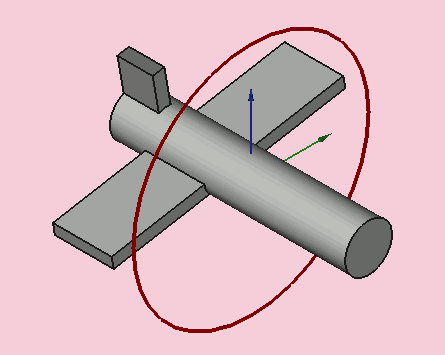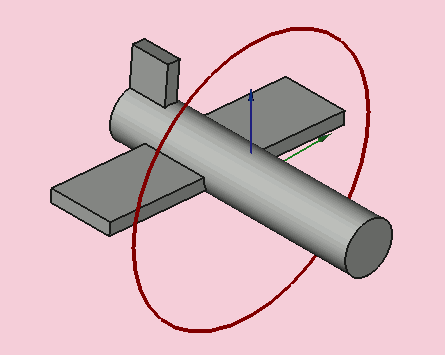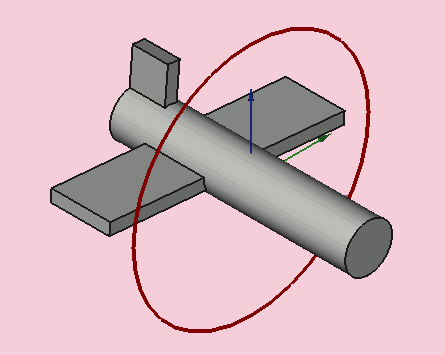
Roll is rotation about the X axis, that is to say wing up and down.
(The Roll angle is the Thêta θ).
Matrix (matice)
Umístění = Matrix
Třetí tvar zadání Umístění popisuje pozici a orientaci objektu pomocí 4x4 afinní transformační matice (Affine Transformation).
Matrix (matice) =
((r11,r12,r13,t1), (r21,r22,r23,t2), (r31,r32,r33,t3), (0,0,0,1)) , with rij specifying rotation and ti specifying translation.
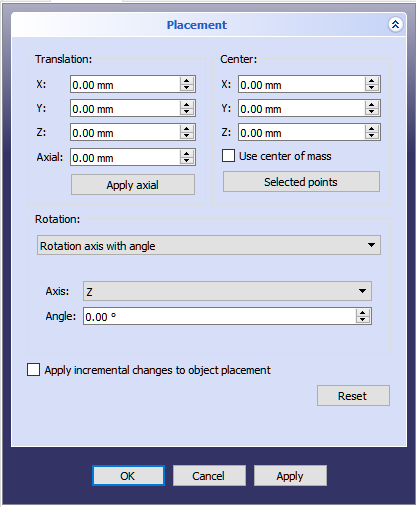
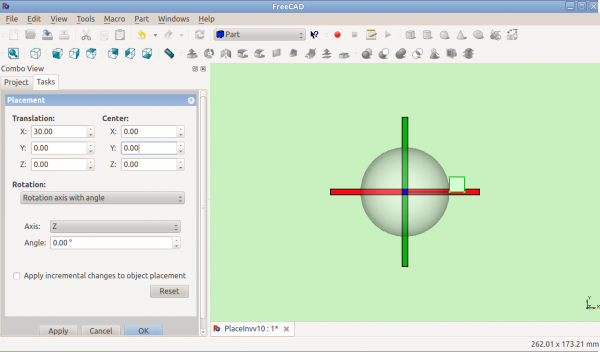
The Placement Dialog
The Placement Dialog is invoked from the Edit menu. It is used to precisely rotate/translate objects. It is also used when we need to create a sketch on a "non standard" plane or change a sketch's orientation to a new plane.
The Translation section adjusts the object's location in space. The Center section adjusts the rotational axis to one that does not pass through the object's reference point. The Rotation section adjusts the rotational angle(s) and the method of specifying those angles.
The Apply incremental changes to object placement tick box is useful when translations/rotations are to be made relative the object's current position/attitude, rather than to the original position/attitude. Ticking this box resets the dialog's input fields to zero, but does not change the object's orientation or location. Subsequent entries do change the orientation/location, but are applied from the object's current position.
Examples
Rotations about a single axis:
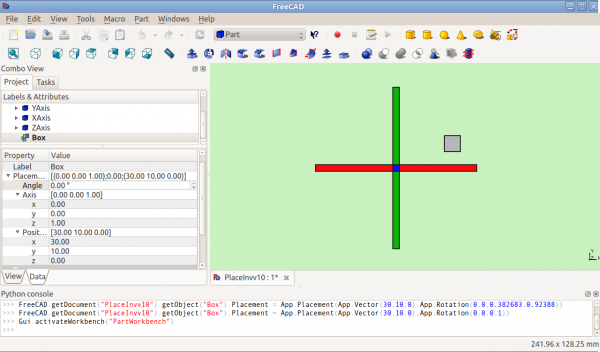
Před otočením (pohled shora)
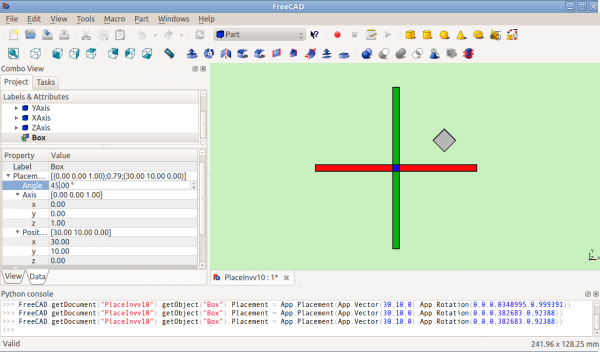
Po otočení kolem osy Z (pohled shora)
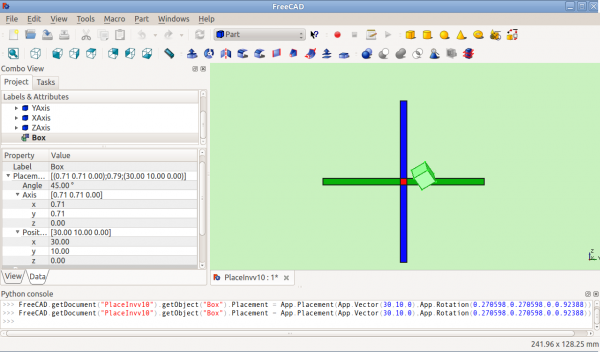
Po otočení když y=x (pohled zprava)
Otočení s posunutím středového bodu:
Před otočením (pohled shora)
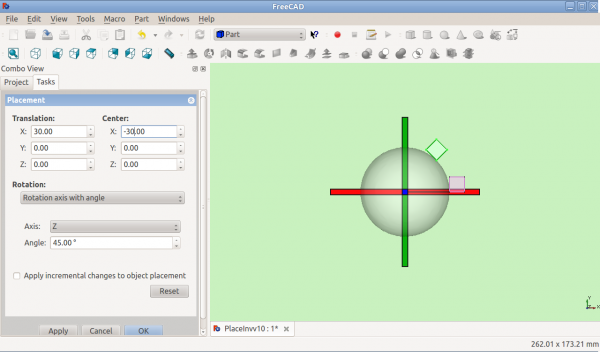
Po otočení kolem osy Z (pohled shora)
Otočení s použitím Eulerových úhlů:
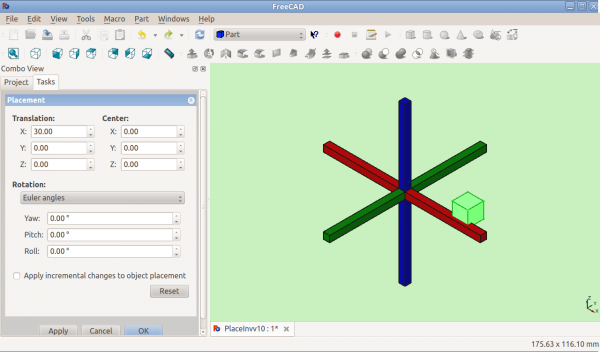
Před otočením
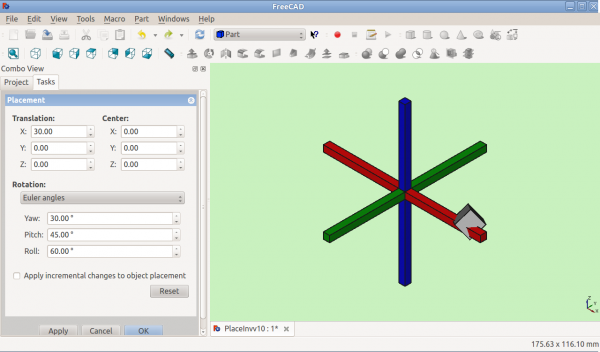
Po otočení
Placement.Base vs Shape Definition
Umístění není jediný způsob pozicování objektů v prostoru. Všimněte si Pythonovské konzoly na tomto obrázku:

Both cubes have the same value for Placement, but are in different locations! This is because the 2 shapes are defined by different vertices (curves in more complex shapes). For the 2 shapes in the above illustration:
>>> ev = App.ActiveDocument.Extrude.Shape.Vertexes >>> for v in ev: print v.X,",",v.Y,",",v.Z ... 30.0,30.0,0.0 30.0,30.0,10.0 40.0,30.0,0.0 40.0,30.0,10.0 40.0,40.0,0.0 40.0,40.0,10.0 30.0,40.0,0.0 30.0,40.0,10.0 >>> e1v = App.ActiveDocument.Extrude001.Shape.Vertexes >>> for v in e1v: print v.X,",",v.Y,",",v.Z ... 0.0,10.0,0.0 0.0,10.0,10.0 10.0,10.0,0.0 10.0,10.0,10.0 10.0,0.0,0.0 10.0,0.0,10.0 0.0,0.0,0.0 0.0,0.0,10.0 >>>
The Vertices (or Vectors) that define the shape use the Placement.Base attribute as their origin. So if you want to move a shape 10 units along the X axis, you could add 10 to the X coordinates of all the Vertices or you could set Placement.Base to (10,0,0).
Using "Center" to Control Axis of Rotation
By default, the axis of rotation isn't really the x/y/z axis. It is a line parallel to the selected axis, but passing through the reference point (Placement.Base) of the object to be rotated. This can be changed by using the Center fields in the Placement dialog or, in scripts, by using the Center parameter of the FreeCAD.Placement constructor.
Například, představme si, že máme kostku (dále) pozicovanou na (20,20,10).
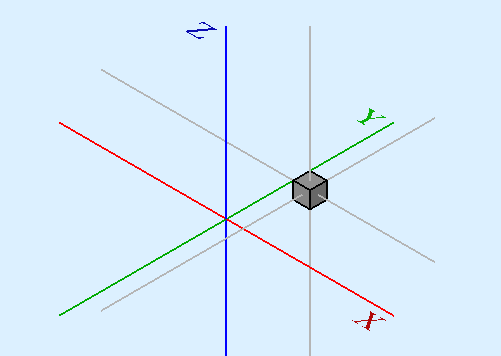
Chceme otočit kostku kolem její svislé středové přímky (tj. místní osy Z) s udržením stejné pozice. Můžeme toho snadno dosáhnout zadáním hodnoty Středu rovné souřadnicím středu kostky (25,25,15).

Ve skriptu by to vypadalo následovně:
import FreeCAD
obj = App.ActiveDocument.Box # our box
rot = FreeCAD.Rotation(FreeCAD.Vector(0,0,1),45) # 45° about Z
#rot = FreeCAD.Rotation(FreeCAD.Vector(1,0,1),45) # 45° about X and 45° about Z
#rot = FreeCAD.Rotation(10,20,30) # here example with Euler angle Yaw = 10 degrees (Z), Pitch = 20 degrees (Y), Roll = 30 degrees (X)
centre = FreeCAD.Vector(25,25,15) # central point of box
pos = obj.Placement.Base # position point of box
newplace = FreeCAD.Placement(pos,rot,centre) # make a new Placement object
obj.Placement = newplace # spin the box
Same script with the file example RotateCoG2.fcstd (discussion on the forum)
import FreeCAD
obj = App.ActiveDocument.Extrude # our box
rot = FreeCAD.Rotation(FreeCAD.Vector(0,0,1),45) # 45 about Z
#rot = FreeCAD.Rotation(FreeCAD.Vector(1,0,1),45) # 45° about X and 45° about Z
#rot = FreeCAD.Rotation(10,20,30) # here example with Euler angle Yaw = 10 degrees (Z), Pitch = 20 degrees (Y), Roll = 30 degrees (X)
centre = FreeCAD.Vector(25,25,0) # "centre" of rotation (where local Z cuts XY)
pos = obj.Placement.Base # original placement of obj
newplace = FreeCAD.Placement(pos,rot,centre) # make a new Placement object
obj.Placement = newplace # spin the box
Notes
- Axis and Angle can also be expressed as a quaternion.
- The reference point of an object varies depending on the object. Some examples for common objects:
| Object | Reference Point |
|---|---|
| Part.Box | left (minx), front (miny), bottom (minz) vertex |
| Part.Sphere | center of the sphere (ie centre of bounding box) |
| Part.Cylinder | center of the bottom face |
| Part.Cone | center of bottom face (or apex if bottom radius is 0) |
| Part.Torus | center of the torus |
| Features derived from Sketches | the Feature inherits the Position of the underlying Sketch. Sketches always start with Position = (0,0,0). This position corresponds to the origin in the sketch. |
Issues
- As of version 0.13, update of Placement properties in the Data tab has been disabled for objects created with PartDesign, except for the initial sketch from which the solid will be created. Therefore the Placement of a solid created in PartDesign from a sketch can only be altered by adjusting Placement parameters of the initial construction sketch (the first sketch) from which the solid was created.
- Placement functionality will eventually be handled in the Assembly workbench.
More
- This tutorial: Aeroplane covers the mechanics of changing an object's Placement extensively.
- A step-by-step explanation of the Placement Dialog can be found here Tasks_Placement.

