EM Plan FH
|
|
| Emplacement du menu |
|---|
| EM → FHPlane |
| Ateliers |
| EM (Aaddon) |
| Raccourci par défaut |
| E P |
| Introduit dans la version |
| 0.17 |
| Voir aussi |
| EM FHNode, EM FHPlaneHole, EM FHPlaneAddRemoveNodeHole |
Description
L'outil FHPlane insère un objet plan conducteur uniforme FastHenry.
FastHenry FHPlane
Utilisation
L'objet FHPlane doit être basé sur un autre objet, qui peut être un objet Draft Rectangle ou un objet Part Cube. Si vous avez basé votre FHPlane sur un objet Part Cube, le paramètre Thickness sera hérité de la valeur Box Height.
- Créez et sélectionnez un objet
Draft Rectangle ou un objet
Part Cube.
- Appuyez sur le bouton
EM FHPlane ou appuyez sur les touches E puis P.
De plus, vous pouvez également sélectionner conjointement avec l'objet de base (Draft Rectangle ou Part Cube) également un ou plusieurs EM FHNode et/ou un ou plus EM FHPlaneHole qui seront adoptés par le FHPlane:
- Créez un objet Draft Rectangle ou Part Box
- Créez un ou plusieurs objets
EM FHNode
- Créez un ou plusieurs objets
EM FHPlaneHole
- Sélectionnez l'objet de base, les objets FHNode et les objets FHPlaneHole (pour cette sélection multiple, vous pouvez pointer et cliquer sur les objets dans la vue en arborescence ou dans la vue 3D et pour effectuer une sélection multiple maintenez simplement la touche CTRL enfoncée lors de la sélection).
- Appuyez sur le bouton
EM FHPlane ou appuyez sur les touches E puis P.
Remarques
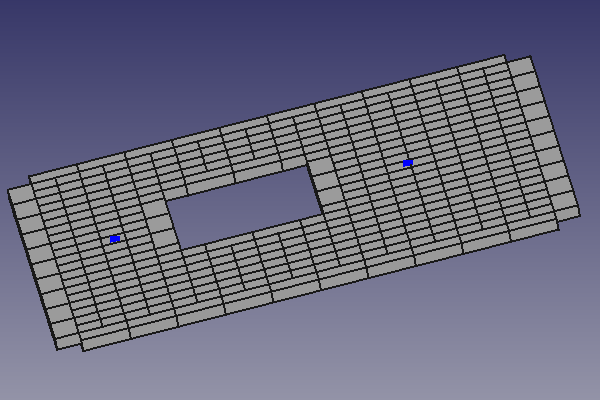
Un objet plan conducteur uniforme FastHenry est formé en posant une ceinture de nœuds (ci-après appelés "nœuds internes") et en connectant les nœuds avec un maillage 2D de segments dans les directions (relatives) X et Y. Des trous sont formés dans le plan en supprimant certains nœuds internes, et donc également les segments qui se connectent à ces nœuds. Pour plus de détails sur les plans conducteurs uniformes FastHenry, consultez le guide de l'utilisateur FastHenry.
- As the FHPlane object is based on a Draft Rectangle or Part Box object, you can NOT freely move the FHPlane. The FHPlane will always be constrained to the base object. To change the position of the FHPlane, apply the change to the underlying base object (the base object is hidden by default, you can show it again by selecting the object in the tree and pressing Space. The origin of the FHPlane is the origin of the base object.
- When the FHNode objects are adopted by the FHPlane, their (X, Y, Z) coordinates will be made relative to the FHPlane origin (so while the FHNode will retain the same position in space, the relative coordinates (X, Y, Z) of the FHNode will be modified to be relative to the FHPlane origin). Also, once adopted, the Z coordinate of the FHNode will be reset to zero (as the coordinates are relative to the FHPlane, the Z coordinate is the height of the object from the plane). For this reason, the node will be visible only from the bottom of the FHPlane, or changing the transparency of the FHPlane to see the FHNodes through, or hiding the FHPlane altogether. Moreover, to show that the FHNode now belongs to the FHPlane, the color of the FHNode is changed.
- When the FHPlaneHole objects are adopted by the FHPlane, their (X, Y, Z) coordinates will be made relative to the FHPlane origin (so while the FHPlaneHole will retain the same position in space, the relative coordinates (X, Y, Z) of the FHPlaneHole will be modified to be relative to the FHPlane origin). Also, once adopted, the Z coordinate of the FHPlaneHole will be reset to zero (as the coordinates are relative to the FHPlane, the Z coordinate is the height of the object from the plane). For this reason, the node will be visible only from the bottom of the FHPlane, or changing the transparency of the FHPlane to see the FHNodes through, or hiding the FHPlane altogether. Moreover, to show that the FHNode now belongs to the FHPlane, the color of the FHNode is changed.
- If you want to remove the FHNodes or the FHPlaneHoles from the FHPlane later on, you can use the EM FHPlaneAddRemoveNodeHole command.
Properties
- DonnéesBase: The base object this component is built upon (a Draft Rectangle or a Part Box)
- DonnéesThickness: the FHPlane thickness ('thick' plane parameter in FastHenry). If the FHPlane is based on a Part Box, this value is inherited from the Part Box Height parameter
- Donnéesseg1: the Number of segments along the length direction ('seg1' plane parameter in FastHenry)
- Donnéesseg2: the Number of segments along the width direction ('seg2' plane parameter in FastHenry)
- Donnéesnhinc: the Number of filaments the plane thickness ('nhinc' plane parameter in FastHenry)
- Donnéesrh: the ratio of adjacent filaments along the thickness ('rh' plane parameter in FastHenry)
- DonnéesSigma: the FHPlane conductivity ('sigma' plane parameter in FastHenry)
- Donnéessegwid1: the Width of segments along the plane length direction ('segwid1' plane parameter in FastHenry)
- Donnéessegwid2: the Width of segments along the plane width direction ('segwid2' plane parameter in FastHenry)
- DonnéesNodes: the list of FHNode objects for connections to the plane
- DonnéesHoles: the list of FHPlaneHoles in the plane
- DonnéesFineMesh: specifies if this the plane fine mesh is shown (i.e. composing segments)
- DonnéesShowNodes: show the internal node grid supporting the plane (i.e. internal nodes)
Scripting
See also: FreeCAD Scripting Basics.
The FHPlane object can be used in macros and from the Python console by using the following function:
plane = makeFHPlane(baseobj=None, thickness=None, seg1=None, seg2=None, nodes=[], holes=[], name='FHPlane')
- Creates a
FHPlaneobject. baseobjis the Draft Rectangle object or Part Box object that can be used as base for the FHPlane. If nobaseobjis given, the user must assign a base object later on, to be able to use this object.thicknessis the plane thickness. If thebaseobjis a Part Box, this parameter is ignored, and the Part Box height is used instead. Defaults toEMFHPLANE_DEF_THICKNESS.seg1is an integer defining the number of segments along the x dimension of the plane ('seg1' parameter in FastHenry)seg2is an integer defining the number of segments along the y dimension of the plane ('seg2' parameter in FastHenry)nodesis an array of FHNode objects, specifying the nodes that will be adopted by the plane.holesis an array of FHPlaneHole objects, specifying the holes that will be adopted by the plane.nameis the name of the object
Example:
import FreeCAD, Draft, EM
pl = FreeCAD.Placement()
pl.Rotation.Q = (0.0,0.0,0.0,1.0)
pl.Base = FreeCAD.Vector(1.0,1.0,0.0)
rec = Draft.makeRectangle(length=10.0,height=5.0,placement=pl,face=True,support=None)
fhnode1 = EM.makeFHNode(X=1.0,Y=3.5,Z=0)
fhnode2 = EM.makeFHNode(X=8.0,Y=3.5,Z=0)
hole = EM.makeFHPlaneHole(X=6.0,Y=3.5,Z=0.0)
fhplane = EM.makeFHPlane(rect, thickness=1.0, seg1=15, seg2=15, nodes=[fhnode1, fhnode2], holes=[hole])
- Outils FastHenry : Noeud FH, Segment FH, Chemin FH, Plan FH, Trou FH, Bascule noeud trou FH, Équivalence FH, Port FH, Solveur FH, Fichier entrée FH
- Outils FasterCap : voir le code source sur GitHub
- Démarrer avec FreeCAD
- Installation : Téléchargements, Windows, Linux, Mac, Logiciels supplémentaires, Docker, AppImage, Ubuntu Snap
- Bases : À propos de FreeCAD, Interface, Navigation par la souris, Méthodes de sélection, Objet name, Préférences, Ateliers, Structure du document, Propriétés, Contribuer à FreeCAD, Faire un don
- Aide : Tutoriels, Tutoriels vidéo
- Ateliers : Std Base, Arch, Assembly, CAM, Draft, FEM, Inspection, Mesh, OpenSCAD, Part, PartDesign, Points, Reverse Engineering, Robot, Sketcher, Spreadsheet, Surface, TechDraw, Test