Draft CircularArray/it: Difference between revisions
(Updating to match new version of source page) |
(Updating to match new version of source page) |
||
| Line 13: | Line 13: | ||
</div> |
</div> |
||
<div class="mw-translate-fuzzy"> |
|||
{{GuiCommand/it |
{{GuiCommand/it |
||
|Name=Draft CircularArray |
|Name=Draft CircularArray |
||
| Line 21: | Line 22: | ||
|SeeAlso=[[Draft_OrthoArray/it|Serie ortogonale]], [[Draft_PolarArray/it|Serie polare]], [[Draft_PathArray/it|Serie su tracciato]], [[Draft_PathLinkArray/it|Serie di link su tracciato]], [[Draft_PointArray/it|Serie su punti]], [[Draft_Clone/it|Clona]] |
|SeeAlso=[[Draft_OrthoArray/it|Serie ortogonale]], [[Draft_PolarArray/it|Serie polare]], [[Draft_PathArray/it|Serie su tracciato]], [[Draft_PathLinkArray/it|Serie di link su tracciato]], [[Draft_PointArray/it|Serie su punti]], [[Draft_Clone/it|Clona]] |
||
}} |
}} |
||
</div> |
|||
==Descrizione== |
==Descrizione== |
||
<div class="mw-translate-fuzzy"> |
|||
Lo strumento [[File:Draft_CircularArray.svg|16px]] [[Draft_CircularArray/it|Serie circolare]] crea una serie da un oggetto selezionato posizionando le copie lungo circonferenze concentriche. È come usare la [[Image:Draft_PolarArray.svg|16px]] [[Draft PolarArray/it|Serie polare]] con un angolo polare di 360 gradi e creando diverse serie concentriche. |
Lo strumento [[File:Draft_CircularArray.svg|16px]] [[Draft_CircularArray/it|Serie circolare]] crea una serie da un oggetto selezionato posizionando le copie lungo circonferenze concentriche. È come usare la [[Image:Draft_PolarArray.svg|16px]] [[Draft PolarArray/it|Serie polare]] con un angolo polare di 360 gradi e creando diverse serie concentriche. |
||
</div> |
|||
<div class="mw-translate-fuzzy"> |
|||
Questo strumento può essere utilizzato su qualsiasi oggetto che abbia una [[Part_TopoShape/it|Part TopoShape]], che significa forme 2D create con [[Draft_Workbench/it|Draft]], ma anche solidi 3D creati con altri ambienti, ad esempio [[Part_Workbench/it|Part]], [[PartDesign_Workbench/it|PartDesign]] o [[Arch_Workbench/it|Arch]]. Può anche creare [[App_Link/it|App Link]] anziché semplici copie. |
Questo strumento può essere utilizzato su qualsiasi oggetto che abbia una [[Part_TopoShape/it|Part TopoShape]], che significa forme 2D create con [[Draft_Workbench/it|Draft]], ma anche solidi 3D creati con altri ambienti, ad esempio [[Part_Workbench/it|Part]], [[PartDesign_Workbench/it|PartDesign]] o [[Arch_Workbench/it|Arch]]. Può anche creare [[App_Link/it|App Link]] anziché semplici copie. |
||
</div> |
|||
* To create orthogonal or polar arrays, use the corresponding {{Button|[[File:Draft_OrthoArray.svg|16px]] [[Draft_OrthoArray|OrthoArray]]}} and {{Button|[[File:Draft_PolarArray.svg|16px]] [[Draft_PolarArray|PolarArray]]}} tools. |
|||
* To position copies along a path use {{Button|[[File:Draft_PathArray.svg|16px]] [[Draft_PathArray|PathArray]]}} or {{Button|[[File:Draft_PathLinkArray.svg|16px]] [[Draft_PathLinkArray|PathLinkArray]]}}. |
|||
* To position copies at specified points use {{Button|[[File:Draft_PointArray.svg|16px]] [[Draft_PointArray|PointArray]]}} or {{Button|[[File:Draft_PointLinkArray.svg|16px]] [[Draft_PointLinkArray|PointLinkArray]]}}. |
|||
* To create copies and manually place them use {{Button|[[File:Draft_Move.svg|16px]] [[Draft_Move|Move]]}} or {{Button|[[File:Draft_Rotate.svg|16px]] [[Draft_Rotate|Rotate]]}}. |
|||
* To create exact copies and manually place or scale them, use {{Button|[[File:Draft_Clone.svg|16px]] [[Draft_Clone|Clone]]}} or {{Button|[[File:Std_LinkMake.svg|16px]] [[Std_LinkMake|Std LinkMake]]}}. |
|||
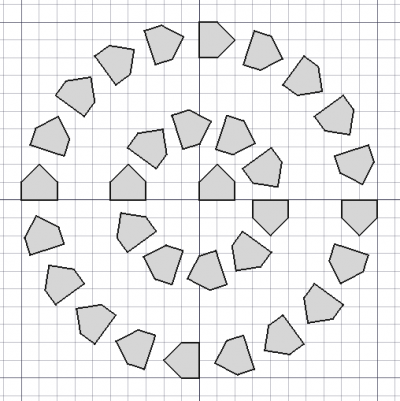
[[Image:Draft_CircularArray_example.png|400px]] |
[[Image:Draft_CircularArray_example.png|400px]] |
||
<div class="mw-translate-fuzzy"> |
|||
{{Caption|Una serie circolare di un oggetto.}} |
{{Caption|Una serie circolare di un oggetto.}} |
||
</div> |
|||
==Utilizzo== |
==Utilizzo== |
||
See also: [[Draft_Snap|Draft Snap]]. |
|||
# Select the object from which you wish to array. |
|||
| ⚫ | |||
# The [[task_panel|task panel]] is launched where you can select the radial distance, the tangential distance, the number of circular layers, the symmetry parameter, and the center of the axis of rotation. |
|||
# You can click on the [[3D_view|3D view]] to simultaneously set the position of the center of rotation, and complete the command. Otherwise, just press {{KEY|Enter}} or the {{Button|OK}} button to complete the operation. |
|||
# Optionally select one object. |
|||
| ⚫ | |||
# There are several ways to invoke the command: |
|||
| ⚫ | |||
* By default, the axis of rotation is the positive Z axis {{Value|(0, 0, 1)}}. This can be changed in the [[property_editor|property editor]] after the object is created. |
|||
#* Select the {{MenuCommand|Modification → Array tools → [[Image:Draft_CircularArray.svg|16px]] Circular array}} option from the menu. |
|||
* Each element in the array is an exact clone of the original object, but the entire array is considered a single unit in terms of properties and appearance. |
|||
# The {{MenuCommand|Circular array}} task panel opens. See [[#Options|Options]] for more information. |
|||
* This command creates the same parametric "Array" object as the one created with the {{Button|[[File:Draft_OrthoArray.svg|16px]] [[Draft_OrthoArray|OrthoArray]]}} and {{Button|[[File:Draft_PolarArray.svg|16px]] [[Draft_PolarArray|PolarArray]]}} tools. Therefore, the array can be converted to orthogonal, polar, or circular by changing its {{PropertyData|Array Type}} property. |
|||
# If you have not yet selected an object: select one object. |
|||
# Enter the required parameters in the task panel. |
|||
# To finish the command do one of the following: |
|||
#* Pick a point in the [[3D_view|3D view]] for the {{MenuCommand|Center of rotation}}. |
|||
#* Press {{KEY|Enter}}. |
|||
#* Press the {{Button|OK}} button. |
|||
== Opzioni == |
== Opzioni == |
||
| ⚫ | |||
These are the options displayed in the [[task_panel|task panel]]. |
|||
* Enter the {{MenuCommand|Tangential distance}} to specify the distance between the elements on the same circular layer. Must be larger than zero. |
|||
* Enter the {{MenuCommand|Number of circular layers}}. The element at the center counts as one layer. Must be at least {{Value|2}}. The maximum that can be entered in the task panel is {{Value|99}}, but higher values are possible by changing the {{PropertyData|Number Circles}} property of the array. |
|||
* Enter the {{MenuCommand|Symmetry}} value. This number determines how the elements are distributed. A value of {{Value|3}}, for example, results in a pattern with three equal 120° pie segments. Larger values for the {{MenuCommand|Symmetry}} and the {{MenuCommand|Tangential distance}} result in fewer or even no elements on the inner layers. |
|||
* Pick a point in the [[3D_view|3D view]], note that this will also finish the command, or type [[Draft_Coordinates|coordinates]] for the {{MenuCommand|Center of rotation}}. The rotation axis of the array will pass through this point. It is advisable to move the pointer out of the [[3D_view|3D view]] before entering coordinates. |
|||
| ⚫ | |||
* If the {{MenuCommand|Fuse}} checkbox is checked overlapping elements in the array are fused. This does not work for Link arrays. |
|||
* If the {{MenuCommand|Link array}} checkbox is checked a Link array instead of a regular array is created. A Link array is more efficient because its elements are [[App_Link|App Link]] objects. |
|||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
* {{MenuCommand|Tangential distance}}: the distance from one element in the array to the next element in the same circular layer. This distance determines how many elements will be in the array; if the number is small, there will be many tightly packed copies; if the number is large, there will only be a few copies. This distance cannot be zero. |
|||
* {{MenuCommand|Number of circular layers}}: the original object is considered one layer by itself. There must be minimum 2, maximum 99. |
|||
* {{MenuCommand|Symmetry}}: determines how the objects will be distributed in the array. |
|||
:With symmetry 1 the first element needs to be rotated a full circle to reach the same position, with 2 a rotation of half a circle (180°) is sufficient, with 3 a one third rotation of a circle (120°) is enough. This means that the symmetry parameter determines a rotation of 360°/n. For large values of symmetry the number of objects in the circular layers decreases, that eventually no object will be placed in the inner circle at all. In most cases you want a number between 1 and 6. |
|||
* {{MenuCommand|Center of rotation}}: the coordinates through which the axis of rotation goes through. |
|||
| ⚫ | |||
* {{MenuCommand|Fuse}}: if it is checked, the resulting objects in the array will fuse together if they touch each other. This only works if {{MenuCommand|Link array}} is unchecked. |
|||
* {{MenuCommand|Link array}}: if it is checked, the resulting array will be a "Link array". This array internally uses [[App_Link|App Link]] objects, so it is more efficient when handling many copies of complex shapes. However, in this case, the objects cannot be fused together. |
|||
| ⚫ | |||
* The default rotation axis for the array is the positive Z axis. This can be changed by editing its {{PropertyData|Axis}} property. |
|||
{{Emphasis|Note:}} if a Link array is created, this object cannot be converted to a regular array. And similarly, a regular array cannot be converted to a Link array. Therefore, you must choose the type of array that you want at creation time. |
|||
* A Draft CircularArray can be turned into a [[Draft_OrthoArray|Draft OrthoArray]] or a [[Draft_PolarArray|Draft PolarArray]] by changing its {{PropertyData|Array Type}} property. |
|||
* A Link array cannot be turned into a regular array or vice versa. The type of array must be decided at creation time. |
|||
== |
==Preferences== |
||
See also: [[Preferences_Editor|Preferences Editor]] and [[Draft_Preferences|Draft Preferences]]. |
|||
A [[Draft_CircularArray|CircularArray]] object internally is the same object produced with the {{Button|[[Image:Draft_OrthoArray.svg|16px]] [[Draft_OrthoArray|OrthoArray]]}} tool. It is based on [[Part_Feature|Part Feature]] ({{incode|Part::Feature}} class), and thus shares all properties of the latter. |
|||
* To change the number of decimals used for the input of coordinates and distances: {{MenuCommand|Edit → Preferences... → General → Units → Units settings → Number of decimals}}. |
|||
See the {{Button|[[Image:Draft_OrthoArray.svg|16px]] [[Draft_OrthoArray|OrthoArray]]}} tool for the complete description of the properties. All properties apply, except for those under the {{TitleProperty|Orthogonal array}} and {{TitleProperty|Polar array}} groups. |
|||
== Proprietà == |
|||
* For circular arrays, the {{PropertyData|Center|VectorDistance}} specifies an offset from the {{PropertyData|Placement}} of the {{PropertyData|Base}} object. That is, to keep the circular array centered on the {{PropertyData|Base}} object, keep {{PropertyData|Center}} to the default value {{Value|(0, 0, 0)}}. |
|||
See [[Draft_OrthoArray#Properties|Draft OrthoArray]]. |
|||
== Script == |
== Script == |
||
See also: [https:// |
See also: [https://freecad.github.io/SourceDoc/ Autogenerated API documentation] and [[FreeCAD Scripting Basics|FreeCAD Scripting Basics]]. |
||
To create a circular array use the {{incode|make_array}} method ({{Version|0.19}}) of the Draft module. This method replaces the deprecated {{incode|makeArray}} method. The {{incode|make_array}} method can create [[Draft_OrthoArray|Draft OrthoArrays]], [[Draft_PolarArray|Draft PolarArrays]] and Draft CircularArrays. For each array type one or more wrappers are available. |
|||
The main method: |
|||
{{Code|code= |
|||
array = make_array(base_object, arg1, arg2, arg3, arg4=None, arg5=None, arg6=None, use_link=True) |
|||
}} |
|||
The wrapper for circular arrays is: |
|||
The Array tool can be used in [[macros|macros]] and from the [[Python_console|Python console]] by using the following function. |
|||
{{Code|code= |
{{Code|code= |
||
| Line 86: | Line 102: | ||
number=3, symmetry=1, |
number=3, symmetry=1, |
||
axis=App.Vector(0, 0, 1), center=App.Vector(0, 0, 0), |
axis=App.Vector(0, 0, 1), center=App.Vector(0, 0, 0), |
||
use_link=True) |
use_link=True) |
||
}} |
}} |
||
* |
* {{incode|base_object}} is the object to be arrayed. It can also be the {{incode|Label}} (string) of an object in the current document. |
||
* {{incode|r_distance}} and {{incode|tan_distance}} are the radial and tangential distances between the elements. |
|||
* {{incode|number}} is the number of circular layers in the pattern, the original object counts as the first layer. |
|||
* {{incode|symmetry}} is an integer used in some calculations that affect the way the elements are distributed around the circumferences. Usual values are from 1 to 6. Higher values are not recommended and will make the elements in the inner layers disappear. |
|||
* {{incode|axis}} and {{incode|center}} are vectors that describe the direction of the axis of rotation, and a point through which that axis passes. |
|||
* If {{incode|use_link}} is {{incode|True}} the created elements are [[App_Link|App Links]] instead of regular copies. |
|||
* {{incode|array}} is returned with the created array object. |
|||
Esempio: |
Esempio: |
||
Revision as of 08:26, 16 June 2021
|
|
| Posizione nel menu |
|---|
| Modifiche → Strumenti serie → Serie circolare |
| Ambiente |
| Draft |
| Avvio veloce |
| Nessuno |
| Introdotto nella versione |
| 0.19 |
| Vedere anche |
| Serie ortogonale, Serie polare, Serie su tracciato, Serie di link su tracciato, Serie su punti, Clona |
Descrizione
Lo strumento Serie circolare crea una serie da un oggetto selezionato posizionando le copie lungo circonferenze concentriche. È come usare la
Serie polare con un angolo polare di 360 gradi e creando diverse serie concentriche.
Questo strumento può essere utilizzato su qualsiasi oggetto che abbia una Part TopoShape, che significa forme 2D create con Draft, ma anche solidi 3D creati con altri ambienti, ad esempio Part, PartDesign o Arch. Può anche creare App Link anziché semplici copie.
Una serie circolare di un oggetto.
Utilizzo
See also: Draft Snap.
- Optionally select one object.
- There are several ways to invoke the command:
- Press the
Draft CircularArray button.
- Select the Modification → Array tools →
Circular array option from the menu.
- Press the
- The Circular array task panel opens. See Options for more information.
- If you have not yet selected an object: select one object.
- Enter the required parameters in the task panel.
- To finish the command do one of the following:
- Pick a point in the 3D view for the Center of rotation.
- Press Enter.
- Press the OK button.
Opzioni
- Enter the Radial distance to specify the distance between the circular layers, and between the center and the first circular layer.
- Enter the Tangential distance to specify the distance between the elements on the same circular layer. Must be larger than zero.
- Enter the Number of circular layers. The element at the center counts as one layer. Must be at least
2. The maximum that can be entered in the task panel is99, but higher values are possible by changing the DatiNumber Circles property of the array. - Enter the Symmetry value. This number determines how the elements are distributed. A value of
3, for example, results in a pattern with three equal 120° pie segments. Larger values for the Symmetry and the Tangential distance result in fewer or even no elements on the inner layers. - Pick a point in the 3D view, note that this will also finish the command, or type coordinates for the Center of rotation. The rotation axis of the array will pass through this point. It is advisable to move the pointer out of the 3D view before entering coordinates.
- Press the Reset point button to reset the Center of rotation to the origin.
- If the Fuse checkbox is checked overlapping elements in the array are fused. This does not work for Link arrays.
- If the Link array checkbox is checked a Link array instead of a regular array is created. A Link array is more efficient because its elements are App Link objects.
- Press Esc or the Cancel button to abort the command.
Notes
- The default rotation axis for the array is the positive Z axis. This can be changed by editing its DatiAxis property.
- A Draft CircularArray can be turned into a Draft OrthoArray or a Draft PolarArray by changing its DatiArray Type property.
- A Link array cannot be turned into a regular array or vice versa. The type of array must be decided at creation time.
Preferences
See also: Preferences Editor and Draft Preferences.
- To change the number of decimals used for the input of coordinates and distances: Edit → Preferences... → General → Units → Units settings → Number of decimals.
Proprietà
See Draft OrthoArray.
Script
See also: Autogenerated API documentation and FreeCAD Scripting Basics.
To create a circular array use the make_array method (introduced in version 0.19) of the Draft module. This method replaces the deprecated makeArray method. The make_array method can create Draft OrthoArrays, Draft PolarArrays and Draft CircularArrays. For each array type one or more wrappers are available.
The main method:
array = make_array(base_object, arg1, arg2, arg3, arg4=None, arg5=None, arg6=None, use_link=True)
The wrapper for circular arrays is:
array = make_circular_array(base_object,
r_distance=100, tan_distance=50,
number=3, symmetry=1,
axis=App.Vector(0, 0, 1), center=App.Vector(0, 0, 0),
use_link=True)
base_objectis the object to be arrayed. It can also be theLabel(string) of an object in the current document.r_distanceandtan_distanceare the radial and tangential distances between the elements.numberis the number of circular layers in the pattern, the original object counts as the first layer.symmetryis an integer used in some calculations that affect the way the elements are distributed around the circumferences. Usual values are from 1 to 6. Higher values are not recommended and will make the elements in the inner layers disappear.axisandcenterare vectors that describe the direction of the axis of rotation, and a point through which that axis passes.- If
use_linkisTruethe created elements are App Links instead of regular copies. arrayis returned with the created array object.
Esempio:
import FreeCAD as App
import Draft
doc = App.newDocument()
tri = Draft.make_polygon(3, 600)
array = Draft.make_circular_array(tri, 1800, 1200, 4, 1)
doc.recompute()
- Drafting: Line, Polyline, Fillet, Arc, Arc by 3 points, Circle, Ellipse, Rectangle, Polygon, B-spline, Cubic Bézier curve, Bézier curve, Point, Facebinder, ShapeString, Hatch
- Annotation: Text, Dimension, Label, Annotation styles, Annotation scale
- Modification: Move, Rotate, Scale, Mirror, Offset, Trimex, Stretch, Clone, Array, Polar array, Circular array, Path array, Path link array, Point array, Point link array, Edit, Subelement highlight, Join, Split, Upgrade, Downgrade, Wire to B-spline, Draft to sketch, Set slope, Flip dimension, Shape 2D view
- Draft Tray: Select plane, Set style, Toggle construction mode, AutoGroup
- Snapping: Snap lock, Snap endpoint, Snap midpoint, Snap center, Snap angle, Snap intersection, Snap perpendicular, Snap extension, Snap parallel, Snap special, Snap near, Snap ortho, Snap grid, Snap working plane, Snap dimensions, Toggle grid
- Miscellaneous: Apply current style, Layer, Manage layers, Add a new named group, Move to group, Select group, Add to construction group, Toggle normal/wireframe display, Create working plane proxy, Heal, Show snap toolbar
- Additional: Constraining, Pattern, Preferences, Import Export Preferences, DXF/DWG, SVG, OCA, DAT
- Context menu:
- Layer container: Merge layer duplicates, Add new layer
- Layer: Activate this layer, Select layer contents
- Text: Open hyperlinks
- Wire: Flatten
- Working plane proxy: Write camera position, Write objects state
- Getting started
- Installation: Download, Windows, Linux, Mac, Additional components, Docker, AppImage, Ubuntu Snap
- Basics: About FreeCAD, Interface, Mouse navigation, Selection methods, Object name, Preferences, Workbenches, Document structure, Properties, Help FreeCAD, Donate
- Help: Tutorials, Video tutorials
- Workbenches: Std Base, Assembly, BIM, CAM, Draft, FEM, Inspection, Mesh, OpenSCAD, Part, PartDesign, Points, Reverse Engineering, Robot, Sketcher, Spreadsheet, Surface, TechDraw, Test Framework
- Hubs: User hub, Power users hub, Developer hub