Draft CircularArray/it: Difference between revisions
Renatorivo (talk | contribs) (Created page with "Draft: Serie circolare") |
No edit summary |
||
| (46 intermediate revisions by 4 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
<languages/> |
<languages/> |
||
{{Docnav |
{{Docnav |
||
|[[Draft_PolarArray/it|Serie polare]] |
|||
|[[Draft_Draft2Sketch|Draft to Sketch]] |
|||
|[[Draft_PathArray/it|Serie su tracciato]] |
|||
|[[Draft_LinkArray|Link Array]] |
|||
|[[ |
|[[Draft_Workbench/it|Draft]] |
||
|IconL= |
|IconL=Draft_PolarArray.svg |
||
|IconR=Draft_PathArray.svg |
|||
|IconC=Workbench_Draft.svg |
|IconC=Workbench_Draft.svg |
||
|IconR=Draft_LinkArray.svg |
|||
}} |
}} |
||
{{GuiCommand |
{{GuiCommand/it |
||
|Name=Draft CircularArray |
|Name=Draft CircularArray |
||
|Name/it=Serie circolare |
|||
|MenuLocation=Draft → Circular array |
|||
|MenuLocation=Modifiche → Strumenti serie → Serie circolare |
|||
|Workbenches=[[Draft Module|Draft]] |
|||
|Workbenches=[[Draft_Workbench/it|Draft]], [[Arch_Workbench/it|Arch]] |
|||
|Version=0.19 |
|Version=0.19 |
||
|SeeAlso=[[ |
|SeeAlso=[[Draft_OrthoArray/it|Serie ortogonale]], [[Draft_PolarArray/it|Serie polare]], [[Draft_PathArray/it|Serie su tracciato]], [[Draft_PathLinkArray/it|Serie di link su tracciato]], [[Draft_PointArray/it|Serie su punti]], [[Draft_PointLinkArray/it|Serie di link su punti]] |
||
}} |
}} |
||
= |
<span id="Description"></span> |
||
==Descrizione== |
|||
Il comando [[Image:Draft_CircularArray.svg|24px]] '''Serie circolare''' crea una serie (array) da un oggetto selezionato posizionando copie lungo circonferenze concentriche. Il comando può facoltativamente creare una Serie di [[App_Link/it|Link]], che è più efficiente di una Serie normale. |
|||
The {{Button|[[File:Draft_CircularArray.svg|16px]] [[Draft_CircularArray|Draft CircularArray]]}} tool creates an array from a selected object placing the copies along concentric circumferences. This is like using [[Image:Draft_PolarArray.svg|16px]] [[Draft PolarArray|Draft PolarArray]] with a polar angle of 360 degrees, and creating several such concentric arrays. |
|||
Il comando può essere utilizzato su oggetti 2D creati con [[Draft_Workbench/it|Draft]] o [[Sketcher_Workbench/it|Sketcher]], ma anche su molti oggetti 3D come quelli creati con gli ambienti [[Part_Workbench/it|Part]], [[PartDesign_Workbench/it|PartDesign]] o [[Arch_Workbench/it|Arch]]. |
|||
This tool can be used on 2D shapes created with the [[Image:Workbench_Draft.svg|16px]] [[Draft_Workbench|Draft Workbench]] but can also be used on many types of 3D objects such as those created with the [[Image:Workbench_Part.svg|16px]] [[Part_Workbench|Part Workbench]] or [[Image:Workbench_PartDesign.svg|16px]] [[PartDesign_Workbench|PartDesign Workbench]]. |
|||
To position copies in a rectangular grid use [[Image:Draft_Array.svg|16px]] [[Draft_Array|Array]]; to position in a polar pattern use [[Image:Draft_PolarArray.svg|16px]] [[Draft_PolarArray|PolarArray]]; to position copies along a path use [[Image:Draft_PathArray.svg|16px]] [[Draft_PathArray|PathArray]]; to position copies at specified points use [[Image:Draft_PointArray.svg|16px]] [[Draft_PointArray|PointArray]]; to create copies or clones, and manually place them use [[Image:Draft_Move.svg|16px]] [[Draft_Move|Move]], [[Image:Draft_Rotate.svg|16px]] [[Draft_Rotate|Rotate]], and [[Image:Draft_Clone.svg|16px]] [[Draft_Clone|Clone]]. |
|||
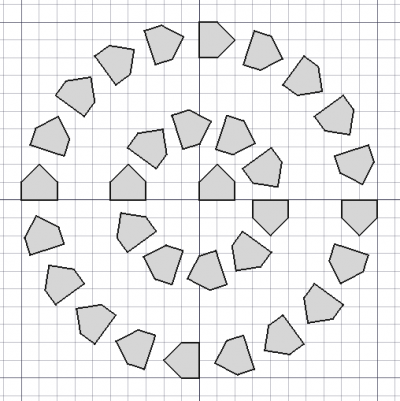
[[Image:Draft_CircularArray_example.png|400px]] |
[[Image:Draft_CircularArray_example.png|400px]] |
||
{{Caption|Serie circolare.}} |
|||
<span id="Usage"></span> |
|||
{{Caption|A circular array of an object.}} |
|||
==Utilizzo== |
|||
Vedere anche: [[Draft_Snap/it|Aggancio]]. |
|||
== Usage == |
|||
# Facoltativamente selezionare un oggetto. |
|||
# Select an object from which you wish to make the circular array. |
|||
# Esistono diversi modi per invocare il comando: |
|||
# Press the {{Button|[[File:Draft_CircularArray.svg|16px]] [[Draft_CircularArray|Circular array]]}} button. If no object is selected, the [[task_panel|task panel]] will open, but you still need to select an object to proceed. |
|||
#* Premere il pulsante {{Button|[[Image:Draft_CircularArray.svg|16px]] [[Draft_CircularArray/it|Serie circolare]]}}. |
|||
# Choose the radial distance, which determines the distance from the center of the array to the next circular layer, and between subsequent circular layers. |
|||
#* Selezionare l'opzione {{MenuCommand|Modifiche → Strumenti array → [[Image:Draft_CircularArray.svg|16px]] Serie circolare}} dal menu. |
|||
# Choose the tangential distance, which determines the distance from one element in the array to the next element in the same circular layer. This distance determines how many elements will be in the array; if the number is small, there will be many tightly packed copies; if the number is large, there will only be a few copies. This distance cannot be zero. |
|||
# Si apre il pannello attività {{MenuCommand|Serie circolare}}. Vedere [[#Opzioni|Opzioni]] per maggiori informazioni. |
|||
# Choose the number of circular layers. The original object is considered one layer by itself. Minimum of 2, maximum of 99. |
|||
# Se non si ha ancora selezionato un oggetto: selezionare un oggetto. |
|||
# Choose the symmetry, which determines how symmetric the objects will be distributed in the array.<br />With symmetry = 1 you might have to rotate the array a full circle to match ''positions'' on itself, with symmetry = 2 a rotation of half a circle (180°) is always sufficient, with symmetry = 3 a rotation of ⅓ of a circle (120°), …, with symmetry = n a rotation of 360°/n. If symmetry gets higher the number of objects in some circles decreases, it even might not be possible to place objects in the inner circle(s) at all.<br />In most cases you want a number between 1 and 6. |
|||
# Immettere i parametri richiesti nel pannello delle attività. |
|||
# Choose the center of the axis of rotation. You can click on the [[3D_view|3D view]], to simultaneously set the position of the center of rotation, and complete the command. |
|||
# Per completare il comando, eseguire una delle seguenti operazioni: |
|||
# Optionally, check the fuse or link options. |
|||
#* Scegliere un punto nella [[3D_view/it|Vista 3D]] per il {{MenuCommand|Centro di rotazione}}. |
|||
# Press {{Button|OK}} to complete the command. |
|||
#* Premere {{KEY|Enter}}. |
|||
#* Premere il pulsante {{Button|OK}}. |
|||
<span id="Options"></span> |
|||
==Notes== |
|||
== Opzioni == |
|||
* By default, the axis of rotation is the positive Z axis {{Value|(0, 0, 1)}}. This can be changed in the [[property_editor|property editor]] after the object is created. |
|||
* Each element in the array is an exact clone of the original object, but the entire array is considered a single unit in terms of properties and appearance. |
|||
* This command creates the same object as the one created with the [[Image:Draft_Array.svg|16px]] [[Draft_Array|Array]] and [[Image:Draft_PolarArray.svg|16px]] [[Draft_PolarArray|PolarArray]] tools. Therefore, the array can be converted to orthogonal, polar, or circular just by changing its properties. |
|||
* Immettere {{MenuCommand|Distanza radiale}} per specificare la distanza tra gli strati circolari e tra il centro e il primo strato circolare. |
|||
== Options == |
|||
* Immettere {{MenuCommand|Distanza tangenziale}} per specificare la distanza tra gli elementi sullo stesso strato circolare. Deve essere maggiore di zero. |
|||
* Inserire il {{MenuCommand|Numero di strati circolari}}. L'elemento al centro conta come uno strato. Deve essere almeno {{Value|2}}. Il massimo che può essere inserito nel pannello delle attività è {{Value|99}}, ma sono possibili valori più alti modificando la proprietà {{PropertyData|Number Circles}} della serie. |
|||
* Inserire il valore {{MenuCommand|Simmetria}}. Questo numero determina come sono distribuiti gli elementi. Un valore di {{Value|3}}, ad esempio, genera un modello con tre segmenti di torta uguali a 120°. Valori più grandi per {{MenuCommand|Simmetria}} e {{MenuCommand|Distanza tangenziale}} comportano meno o addirittura nessun elemento sugli strati interni. |
|||
* Scegliere un punto nella [[3D_view/it|Vista 3D]], nota che anche questo terminerà il comando, oppure digitare le coordinate per {{MenuCommand|Centro di rotazione}}. L'asse di rotazione della serie passerà per questo punto. Si consiglia di spostare il puntatore fuori dalla [[3D_view/it|ista 3D]] prima di inserire le coordinate. |
|||
* Premere il pulsante {{MenuCommand|Resetta il punto}} per reimpostare il {{MenuCommand|Centro di rotazione}} all'origine. |
|||
* Se la casella di controllo {{MenuCommand|Fusione}} è selezionata, gli elementi sovrapposti nella serie vengono fusi. Questo non funziona per le Serie di link. |
|||
* Se la casella {{MenuCommand|Serie di Link}} è spuntata, viene creato una Serie di Link invece di una Serie normale. Una Serie di Link è più efficiente perché i suoi elementi sono oggetti [[App_Link/it|App Link]]. |
|||
* Premere {{KEY|Esc}} o il pulsante {{Button|Annulla}} per annullare il comando. |
|||
<span id="Notes"></span> |
|||
* Press {{Button|Reset point}} to set the center of the circular patterns to the origin {{Value|(0, 0, 0)}}. |
|||
==Note== |
|||
* If the {{MenuCommand|Fuse}} checkbox is ticked, the resulting objects in the array will be fused into a single shape, if they touch or intersect each other. |
|||
* If the {{MenuCommand|Use Links}} checkbox is ticked, the resulting objects in the array will be [[App_Link|App Links]] instead of simple copies. This improves the memory usage of the array, as the App Link re-uses the [[Shape|shape]] of the original object, and does not create new shapes. If this option is used, the {{MenuCommand|Fuse}} checkbox has no effect. |
|||
* Press {{KEY|Esc}} or the {{Button|Cancel}} button to abort the current command. |
|||
* L'asse di rotazione predefinito per la serie è l'asse Z positivo. Questo può essere cambiato modificando la sua proprietà {{PropertyData|Axis}}. |
|||
== Properties == |
|||
* Una Serie circolare può essere trasformata in una [[Draft_OrthoArray/it|Serie ortogonale]] o in una [[Draft_PolarArray/it|Serie polare]] modificandone la proprietà {{PropertyData|Array Type}}. |
|||
* Una Serie di link non può essere trasformata in una serie normale o viceversa. Il tipo di serie deve essere deciso al momento della creazione. |
|||
<span id="Properties"></span> |
|||
An [[Draft_PolarArray|Array]] object is based on [[Part_Feature|Part Feature]] ({{incode|Part::Feature}} class), and thus shares all properties of the latter. In addition to the properties listed in [[Part_Feature|Part Feature]], the Array object has additional properties. |
|||
== Proprietà == |
|||
Vedere [[Draft_OrthoArray/it#Propertà|Serie ortogonale]]. |
|||
See the {{Button|[[Image:Draft_Array.svg|16px]] [[Draft_OrthoArray|OrthoArray]]}} tool for the complete information. |
|||
= |
<span id="Scripting"></span> |
||
== Script == |
|||
Vedere anche: [https://freecad.github.io/SourceDoc/ Autogenerated API documentation] e [[FreeCAD Scripting Basics/it|Script di base per FreeCAD]]. |
|||
Per creare una serie circolare usare il metodo {{incode|make_array}} ({{Version/it|0.19}}) del modulo Draft. Questo metodo sostituisce il metodo deprecato {{incode|makeArray}}. Il metodo {{incode|make_array}} può creare [[Draft_OrthoArray/it|Serie ortognali]], [[Draft_PolarArray/it|Serie polari]] e Serie circolari. Per ogni tipo di serie sono disponibili uno o più wrapper. |
|||
The Array tool can be used in [[macros|macros]] and from the [[Python_console|Python console]] by using the following function. |
|||
Il metodo principale: |
|||
{{Code|code= |
{{Code|code= |
||
array = make_array(base_object, arg1, arg2, arg3, arg4=None, arg5=None, arg6=None, use_link=True) |
|||
array_list = make_circular_array(obj, r_distance, tan_distance, |
|||
axis, center, number, symmetry, |
|||
use_link) |
|||
}} |
}} |
||
Il wrapper per le Serie circolari è: |
|||
* Creates an array from the objects contained in {{incode|obj}}, which can be a single object or a list of objects. |
|||
* The values of {{incode|r_distance}} and {{incode|tan_distance}} correspond to the radial and tangential distances of the elements in the array. |
|||
{{Code|code= |
|||
* The values of {{incode|axis}} and {{incode|center}} are vectors that describe the direction of the axis of rotation, and a point through which that axis goes. |
|||
array = make_circular_array(base_object, |
|||
* The value of {{incode|number}} is the number of circular layers in the circular pattern; the original object counts as the first layer. |
|||
r_distance=100, tan_distance=50, |
|||
* The value of {{incode|symmetry}} is an integer that participates in some calculations that affect the way the copies are distributed around the circumferences. Try different values, from 1 to 10, to get different placements of the copies. |
|||
number=3, symmetry=1, |
|||
* If {{incode|use_link}} is {{TRUE}} the created copies will be [[App_Link|App Links]] and not regular copies. |
|||
axis=App.Vector(0, 0, 1), center=App.Vector(0, 0, 0), |
|||
* {{incode|array_list}} is returned with the new copies. |
|||
use_link=True) |
|||
** {{incode|array_list}} is either a single object or a list of objects, depending on the input {{incode|obj}}. |
|||
}} |
|||
* {{incode|base_object}} è l'oggetto da disporre in serie. Può anche essere la {{incode|Label}} (string) di un oggetto nel documento corrente. |
|||
* {{incode|r_distance}} e {{incode|tan_distance}} sono le distanze radiali e tangenziali tra gli elementi. |
|||
* {{incode|number}} è il numero di strati circolari nel modello, l'oggetto originale conta come primo strato. |
|||
* {{incode|symmetry}} è un numero intero utilizzato in alcuni calcoli che influenzano il modo in cui gli elementi sono distribuiti attorno alle circonferenze. I valori usuali vanno da 1 a 6. Valori più alti non sono consigliati e faranno scomparire gli elementi negli strati interni. |
|||
* {{incode|axis}} e {{incode|center}} sono vettori che descrivono la direzione dell'asse di rotazione e un punto attraverso il quale passa tale asse. |
|||
* Se {{incode|use_link}} è {{incode|True}} gli elementi creati sono [[App_Link/it|App Links]] invece di normali copie. |
|||
* {{incode|array}} viene restituito con l'oggetto serie creato. |
|||
Esempio: |
|||
Example: |
|||
{{Code|code= |
{{Code|code= |
||
import FreeCAD as App |
import FreeCAD as App |
||
import Draft |
import Draft |
||
import draftobjects.circulararray as ca |
|||
doc = App.newDocument() |
doc = App.newDocument() |
||
tri = Draft. |
tri = Draft.make_polygon(3, 600) |
||
axis = App.Vector(0, 0, 1) |
|||
array = Draft.make_circular_array(tri, 1800, 1200, 4, 1) |
|||
center = App.Vector(0, 0, 0) |
|||
doc.recompute() |
|||
arr = ca.make_circular_array(tri, 1800, 1200, axis, center, 4, 1) |
|||
App.ActiveDocument.recompute() |
|||
}} |
}} |
||
{{Docnav |
{{Docnav |
||
|[[Draft_PolarArray/it|Serie polare]] |
|||
|[[Draft_Draft2Sketch|Draft to Sketch]] |
|||
|[[Draft_PathArray/it|Serie su tracciato]] |
|||
|[[Draft_LinkArray|Link Array]] |
|||
|[[ |
|[[Draft_Workbench/it|Draft]] |
||
|IconL= |
|IconL=Draft_PolarArray.svg |
||
|IconR=Draft_PathArray.svg |
|||
|IconC=Workbench_Draft.svg |
|IconC=Workbench_Draft.svg |
||
|IconR=Draft_LinkArray.svg |
|||
}} |
}} |
||
{{Draft Tools navi{{#translation:}}}} |
{{Draft Tools navi{{#translation:}}}} |
||
{{Userdocnavi{{#translation:}}}} |
{{Userdocnavi{{#translation:}}}} |
||
{{clear}} |
|||
Latest revision as of 16:42, 8 December 2023
|
|
| Posizione nel menu |
|---|
| Modifiche → Strumenti serie → Serie circolare |
| Ambiente |
| Draft, Arch |
| Avvio veloce |
| Nessuno |
| Introdotto nella versione |
| 0.19 |
| Vedere anche |
| Serie ortogonale, Serie polare, Serie su tracciato, Serie di link su tracciato, Serie su punti, Serie di link su punti |
Descrizione
Il comando Serie circolare crea una serie (array) da un oggetto selezionato posizionando copie lungo circonferenze concentriche. Il comando può facoltativamente creare una Serie di Link, che è più efficiente di una Serie normale.
Il comando può essere utilizzato su oggetti 2D creati con Draft o Sketcher, ma anche su molti oggetti 3D come quelli creati con gli ambienti Part, PartDesign o Arch.
Serie circolare.
Utilizzo
Vedere anche: Aggancio.
- Facoltativamente selezionare un oggetto.
- Esistono diversi modi per invocare il comando:
- Premere il pulsante
Serie circolare.
- Selezionare l'opzione Modifiche → Strumenti array →
Serie circolare dal menu.
- Premere il pulsante
- Si apre il pannello attività Serie circolare. Vedere Opzioni per maggiori informazioni.
- Se non si ha ancora selezionato un oggetto: selezionare un oggetto.
- Immettere i parametri richiesti nel pannello delle attività.
- Per completare il comando, eseguire una delle seguenti operazioni:
- Scegliere un punto nella Vista 3D per il Centro di rotazione.
- Premere Enter.
- Premere il pulsante OK.
Opzioni
- Immettere Distanza radiale per specificare la distanza tra gli strati circolari e tra il centro e il primo strato circolare.
- Immettere Distanza tangenziale per specificare la distanza tra gli elementi sullo stesso strato circolare. Deve essere maggiore di zero.
- Inserire il Numero di strati circolari. L'elemento al centro conta come uno strato. Deve essere almeno
2. Il massimo che può essere inserito nel pannello delle attività è99, ma sono possibili valori più alti modificando la proprietà DatiNumber Circles della serie. - Inserire il valore Simmetria. Questo numero determina come sono distribuiti gli elementi. Un valore di
3, ad esempio, genera un modello con tre segmenti di torta uguali a 120°. Valori più grandi per Simmetria e Distanza tangenziale comportano meno o addirittura nessun elemento sugli strati interni. - Scegliere un punto nella Vista 3D, nota che anche questo terminerà il comando, oppure digitare le coordinate per Centro di rotazione. L'asse di rotazione della serie passerà per questo punto. Si consiglia di spostare il puntatore fuori dalla ista 3D prima di inserire le coordinate.
- Premere il pulsante Resetta il punto per reimpostare il Centro di rotazione all'origine.
- Se la casella di controllo Fusione è selezionata, gli elementi sovrapposti nella serie vengono fusi. Questo non funziona per le Serie di link.
- Se la casella Serie di Link è spuntata, viene creato una Serie di Link invece di una Serie normale. Una Serie di Link è più efficiente perché i suoi elementi sono oggetti App Link.
- Premere Esc o il pulsante Annulla per annullare il comando.
Note
- L'asse di rotazione predefinito per la serie è l'asse Z positivo. Questo può essere cambiato modificando la sua proprietà DatiAxis.
- Una Serie circolare può essere trasformata in una Serie ortogonale o in una Serie polare modificandone la proprietà DatiArray Type.
- Una Serie di link non può essere trasformata in una serie normale o viceversa. Il tipo di serie deve essere deciso al momento della creazione.
Proprietà
Vedere Serie ortogonale.
Script
Vedere anche: Autogenerated API documentation e Script di base per FreeCAD.
Per creare una serie circolare usare il metodo make_array (disponibile dalla versione 0.19) del modulo Draft. Questo metodo sostituisce il metodo deprecato makeArray. Il metodo make_array può creare Serie ortognali, Serie polari e Serie circolari. Per ogni tipo di serie sono disponibili uno o più wrapper.
Il metodo principale:
array = make_array(base_object, arg1, arg2, arg3, arg4=None, arg5=None, arg6=None, use_link=True)
Il wrapper per le Serie circolari è:
array = make_circular_array(base_object,
r_distance=100, tan_distance=50,
number=3, symmetry=1,
axis=App.Vector(0, 0, 1), center=App.Vector(0, 0, 0),
use_link=True)
base_objectè l'oggetto da disporre in serie. Può anche essere laLabel(string) di un oggetto nel documento corrente.r_distanceetan_distancesono le distanze radiali e tangenziali tra gli elementi.numberè il numero di strati circolari nel modello, l'oggetto originale conta come primo strato.symmetryè un numero intero utilizzato in alcuni calcoli che influenzano il modo in cui gli elementi sono distribuiti attorno alle circonferenze. I valori usuali vanno da 1 a 6. Valori più alti non sono consigliati e faranno scomparire gli elementi negli strati interni.axisecentersono vettori che descrivono la direzione dell'asse di rotazione e un punto attraverso il quale passa tale asse.- Se
use_linkèTruegli elementi creati sono App Links invece di normali copie. arrayviene restituito con l'oggetto serie creato.
Esempio:
import FreeCAD as App
import Draft
doc = App.newDocument()
tri = Draft.make_polygon(3, 600)
array = Draft.make_circular_array(tri, 1800, 1200, 4, 1)
doc.recompute()
- Drafting: Line, Polyline, Fillet, Arc, Arc by 3 points, Circle, Ellipse, Rectangle, Polygon, B-spline, Cubic Bézier curve, Bézier curve, Point, Facebinder, ShapeString, Hatch
- Annotation: Text, Dimension, Label, Annotation styles, Annotation scale
- Modification: Move, Rotate, Scale, Mirror, Offset, Trimex, Stretch, Clone, Array, Polar array, Circular array, Path array, Path link array, Point array, Point link array, Edit, Subelement highlight, Join, Split, Upgrade, Downgrade, Wire to B-spline, Draft to sketch, Set slope, Flip dimension, Shape 2D view
- Draft Tray: Select plane, Set style, Toggle construction mode, AutoGroup
- Snapping: Snap lock, Snap endpoint, Snap midpoint, Snap center, Snap angle, Snap intersection, Snap perpendicular, Snap extension, Snap parallel, Snap special, Snap near, Snap ortho, Snap grid, Snap working plane, Snap dimensions, Toggle grid
- Miscellaneous: Apply current style, Layer, Manage layers, Add a new named group, Move to group, Select group, Add to construction group, Toggle normal/wireframe display, Create working plane proxy, Heal, Show snap toolbar
- Additional: Constraining, Pattern, Preferences, Import Export Preferences, DXF/DWG, SVG, OCA, DAT
- Context menu:
- Layer container: Merge layer duplicates, Add new layer
- Layer: Activate this layer, Select layer contents
- Text: Open hyperlinks
- Wire: Flatten
- Working plane proxy: Write camera position, Write objects state
- Getting started
- Installation: Download, Windows, Linux, Mac, Additional components, Docker, AppImage, Ubuntu Snap
- Basics: About FreeCAD, Interface, Mouse navigation, Selection methods, Object name, Preferences, Workbenches, Document structure, Properties, Help FreeCAD, Donate
- Help: Tutorials, Video tutorials
- Workbenches: Std Base, Assembly, BIM, CAM, Draft, FEM, Inspection, Mesh, OpenSCAD, Part, PartDesign, Points, Reverse Engineering, Robot, Sketcher, Spreadsheet, Surface, TechDraw, Test Framework
- Hubs: User hub, Power users hub, Developer hub